Care and use manual – Waters Spherisorb Columns User Manual
Page 2
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
Waters Spherisorb Columns
2
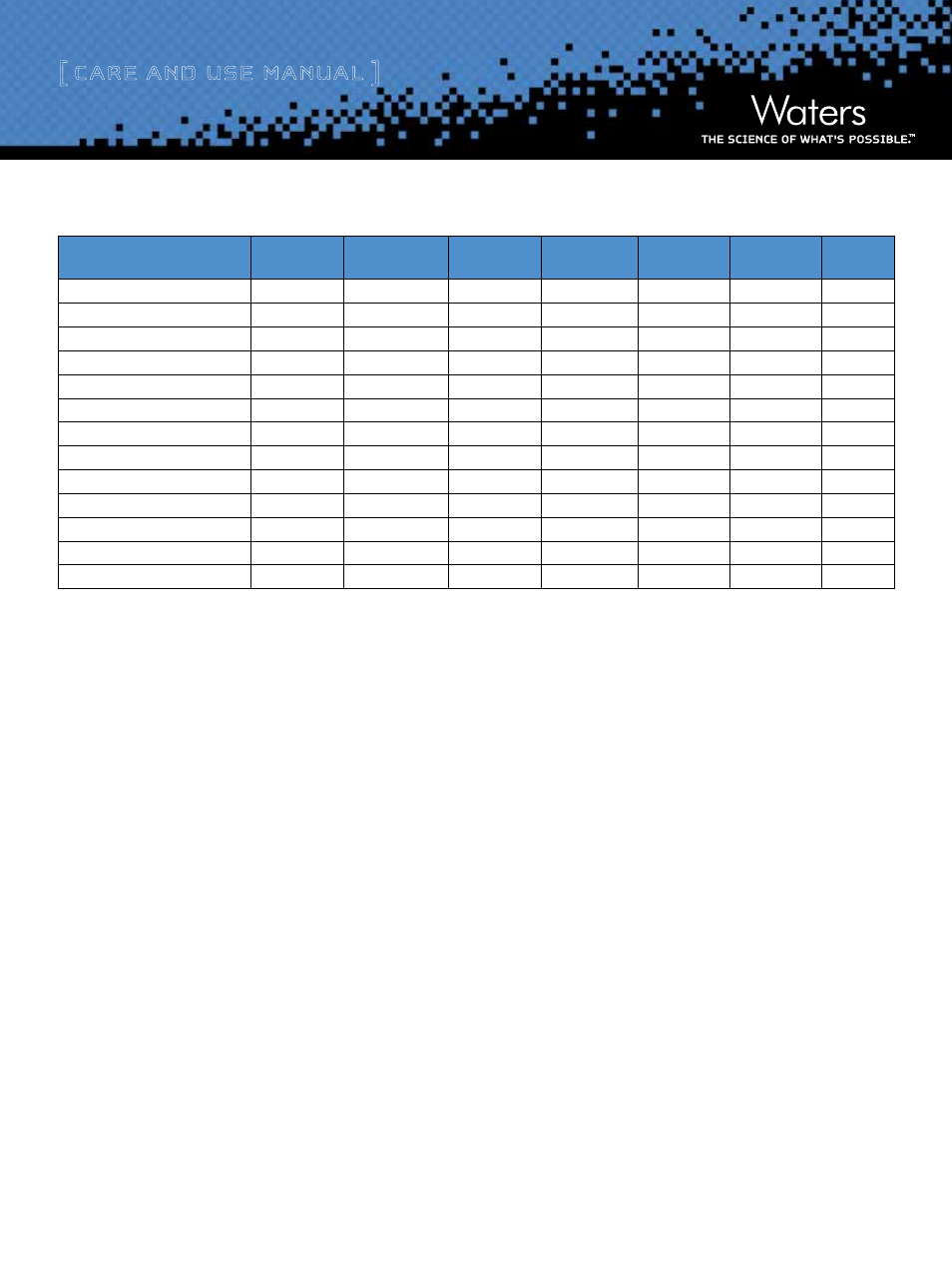
Chemistry
Particle
Shape
Particle Size
(µm)
Pore Size
(Å)
Surface Area
(m
2
/g)
Pore Volume
(cc/g)
% Carbon
Load
Endcapped
Silica
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
n/a
n/a
ODS2 (C
18
) - Fully End Capped
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
11.5
yes
ODS1 (C
18
) - Partially End Capped
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
6.2
no
ODSB (C
18
) - Base De-activated
Spherical
5
80
220
0.50
11.5
yes*
C
8
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
5.8
yes
C
6
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
4.7
yes
C
1
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
2.2
no
Nitrile (CN)
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
3.1
no
Amino (NH
2
)
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
1.9
no
Phenyl
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
2.5
no
OD/CN (Mixed Mode)
Spherical
5
80
220
0.50
5.0
yes
SAX
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
4.0
no
SCX
Spherical
3, 5 and 10
80
220
0.50
4.0
no
i. Get tinG started
Each Spherisorb column comes with a Performance Test
Chromatogram. This Performance Test Chromatogram is specific
to each individual column and contains the following information:
gel batch number, column serial number, USP plate count, USP
tailing factor, capacity factor, and chromatographic conditions.
The performance test chromatogram should be stored for future
reference.
a. Column Installation
Note: The flow rates given in the procedure below are for a typical
4.6 mm i.d. column. Scale the flow rate up or down accordingly based
upon the column i.d., length, particle size, and backpressure of the
Spherisorb column being installed. See “Scaling Up/Down Isocratic
Separations” for calculating flow rates when changing column i.d.
and/or length. See “Connecting the Column to the HPLC” for a more
detailed discussion on HPLC connections.
1. Reversed-Phase Columns
1. Purge the pumping system of any buffer-containing mobile phases and
connect the inlet end of the column to the injector outlet.
2. Flush column with 100% organic mobile phase (methanol or
acetonitrile) by setting the pump flow rate to 0.1 mL/min and increase
the flow rate to 1 mL/min over 5 minutes.
3. When the mobile phase is flowing freely from the column outlet, stop
the flow and attach the column outlet to the detector. This prevents
entry of air into the detection system and gives more rapid baseline
equilibration.
4. Gradually increase the flow rate as described in step 2.
5. Once a steady backpressure and baseline have been achieved, proceed
to the next section.
2. Normal-Phase Columns
Note: It is assumed that your system has been used for reversed-phase
chromatography. If this is not the case, you can start with step 3.
1. Purge the pumping system of any buffer containing mobile phases.
2. Flush the system thoroughly with acetonitrile.
3. Switch the system over to the mobile phase that you are planning to use
in normal-phase chromatography.
4. Connect the column and equilibrate it with the mobile phase.
Note: Equilibration with the mobile phase may require a larger amount of
solvent than in reversed-phase chromatography.
Table 1. Spherisorb Column Physical Characteristics
* polar endcapping
