4 synchronisation with "distributed clocks" (dc), Synchronisation with "distributed clocks" (dc), 6commissioning – Lenze E84AYCET EtherCAT MCI module User Manual
Page 37
Lenze · E84AYCET communication module (EtherCAT) · Communication Manual · DMS 5.0 EN · 05/2013 · TD17
37
6
Commissioning
6.4
Synchronisation with "Distributed Clocks" (DC)
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
6.4
Synchronisation with "Distributed Clocks" (DC)
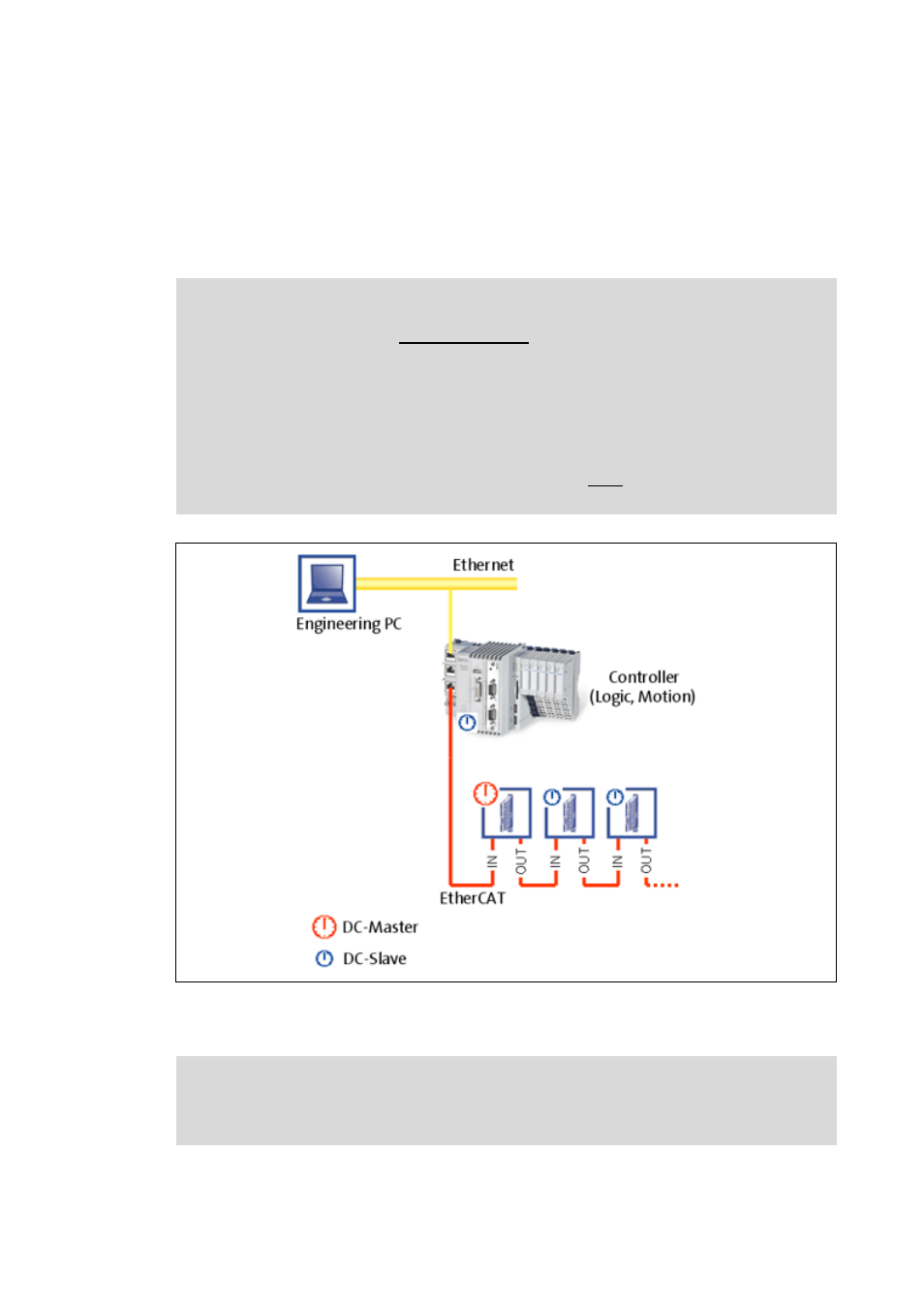
The "Distributed clocks" (DC) functionality enables exact time synchronisation for applications in
which several axes perform a coordinated movement simultaneously. Data are incorporated
synchronously with the PLC program. During DC synchronisation, all slaves are synchronised with a
reference clock, the so-called "DC master".
[6-1]
Example: "Distributed clocks" in the EtherCAT bus system with Lenze Controller 3231 C
The DC synchronisation is set with the EtherCAT configuration software.
Note!
• DC synchronisation is absolutely required for Motion applications.
• DC synchronisation can also be used for Logic applications.
• Not all slaves support the DC functionality.
• On order to be able to use the DC functionality, the first slave connected to the
EtherCAT master (e.g. Lenze Controller) must have DC master capability.
When further slaves are connected, DC-capable and non-DC-capable devices can be
mixed.
• The first EtherCAT slave after the Lenze Controller must be the DC master that
supplies the other EtherCAT nodes (incl. Controller) with the exact time.
"Control technology EtherCAT" communication manual
Here you can find some detailed information about the EtherCAT configuration and the
commissioning of Lenze devices in the EtherCAT network.
