HP Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager Software Licenses User Manual
Page 188
set path= ( $path /opt/DynamicLinkManager/bin )
If the PATH environment variable is not set, specify an absolute path to
execute commands and utilities.
If you have performed steps 10, go to step 13.
12
.
Restart the host.
Execute the following command to restart the host:
# shutdown -r now
A path will be established in the HDLM device and the HDLM manager will
start.
13
.
If you have edited the /etc/fstab file as described in
Required for Devices to Be Managed by HDLM on page 3-102
in
Preparations for a New Installation of HDLM on page 3-102
show below to change the setting from a SCSI device specification to an
HDLM device specification.
The Linux functionality that adds LABEL= to a SCSI device is not
supported in HDLM. Do not use this functionality.
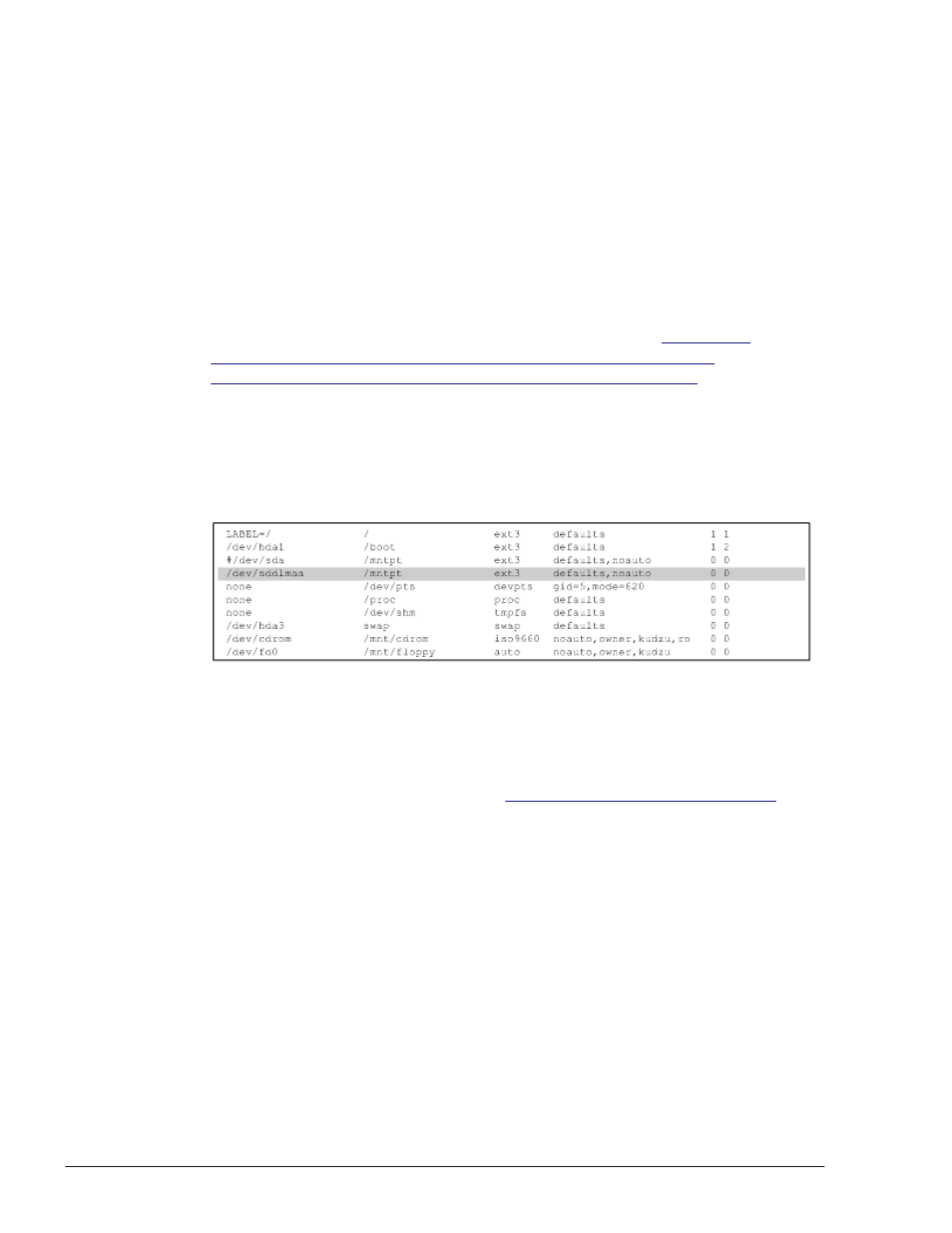
An example of how to edit the /etc/fstab file is shown in the following
figure:
Add the shaded line shown in the above figure.
14
.
Specify the settings required for using LUKS.
Perform this step if your host OS uses LUKS. If HDLM manages a SCSI
device that has been configured to use LUKS, the LUKS settings must be
migrated from the SCSI device to an HDLM device.
For details on setting up LUKS, see
Settings for LUKS on page 3-157
.
15
.
If md devices are used, execute the following command to activate them:
# mdadm -A -scan
mdadm: /dev/md0 has been started with 2 drives.
16
.
If md devices are used, execute the following command to make sure that
they have been activated.
In the following example, RAID1 (mirroring) is used:
# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1]
md0 : active raid1 sddlmaa1[0] sddlmab1[1]
5238528 blocks [2/2] [UU]
3-116
Creating an HDLM Environment
Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager (for Linux®) User Guide
