HP Storage Mirroring V5.1 Software User Manual
Page 88
12 - 5
e.
Select Bin and the hexadecimal number will change to the binary equivalent.
f.
Pad the beginning of the binary equivalent with zeroes (0) so that the number is 16 digits
long. For example, hexadecimal number 23 converts to 100011, so the 16-digit binary
equivalent would be 0000000000100011.
3.
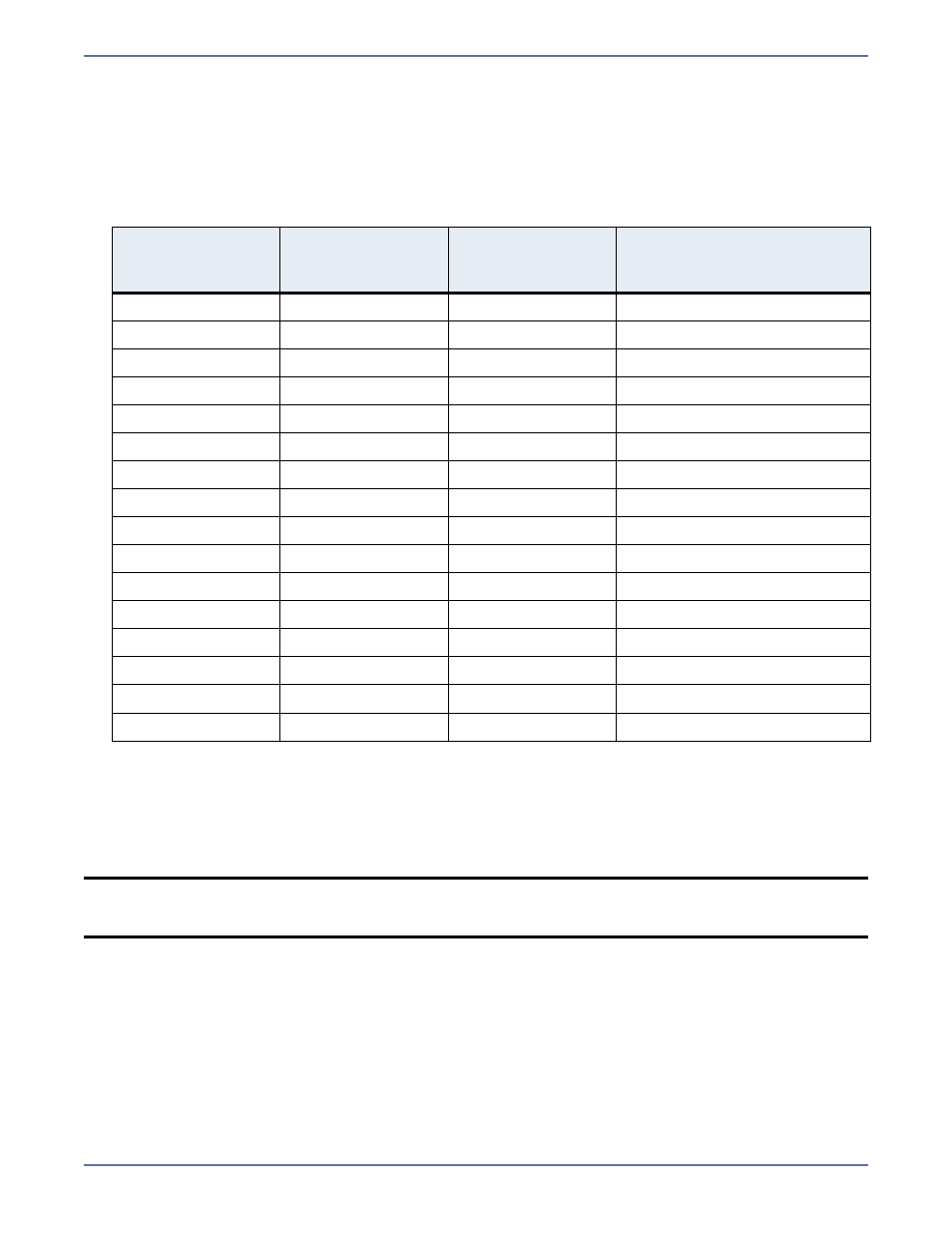
Determine what number appears in each position of the binary number. Because binary numbers
count from right to left, start with position 1 on the right. For example, hexadecimal number 23,
which converted to 0000000000100011, is broken out into the following positions.
4.
Using the same chart above, identify those attributes that are enabled by those positions equal
to one (1). The positions equal to zero (0) are disabled and that attribute does not apply. So
hexadecimal number 23, which converted to 0000000000100011, indicates read only, hidden,
and archive. Another example might be mask 0x827 which converted to binary is
0000100000100111. Positions 1-3, 6, and 12 are all enabled which indicates the file is read only,
hidden, archive, and compressed.
Position
(from right to
left)
Sample
Hexadecimal
Number 23
Enter Your
Hexadecimal
Number
Attribute
1
1
Read only
2
1
Hidden
3
0
None
4
0
System
5
0
Directory
6
1
Archive
7
0
Encrypted
8
0
Normal
9
0
Temporary
10
0
Sparse file
11
0
Reparse point
12
0
Compressed
13
0
Offline
14
0
Not content indexed
15
0
None
16
0
None
NOTE:
Files that were replicated with the Replicate NT Security by Name feature enabled, will
be identified as different in the log file because of the local name attribute. The files will
be the same.
