Appendix 2 output flow of fifo data, Appendix 2 – Yokogawa µR20000 User Manual
Page 94
App-2
IM 04P01B01-17E
Appendix 2 Output Flow of FIFO Data
The recorder has a dedicated internal memory for outputting measured/computed data.
This memory is structured as a FIFO (First-In-First-Out). Measured/computed data are
constantly acquired to the internal memory at the specified acquiring interval (FIFO
acquiring interval, set with the FR command). By using this function, it is possible to read
measured/computed data that have been saved at the specified intervals regardless of
the frequency at which the PC periodically reads the measured/computed data.
The following example shows the case when the acquiring interval is 1 s and the
buffer capacity is for 8 intervals.
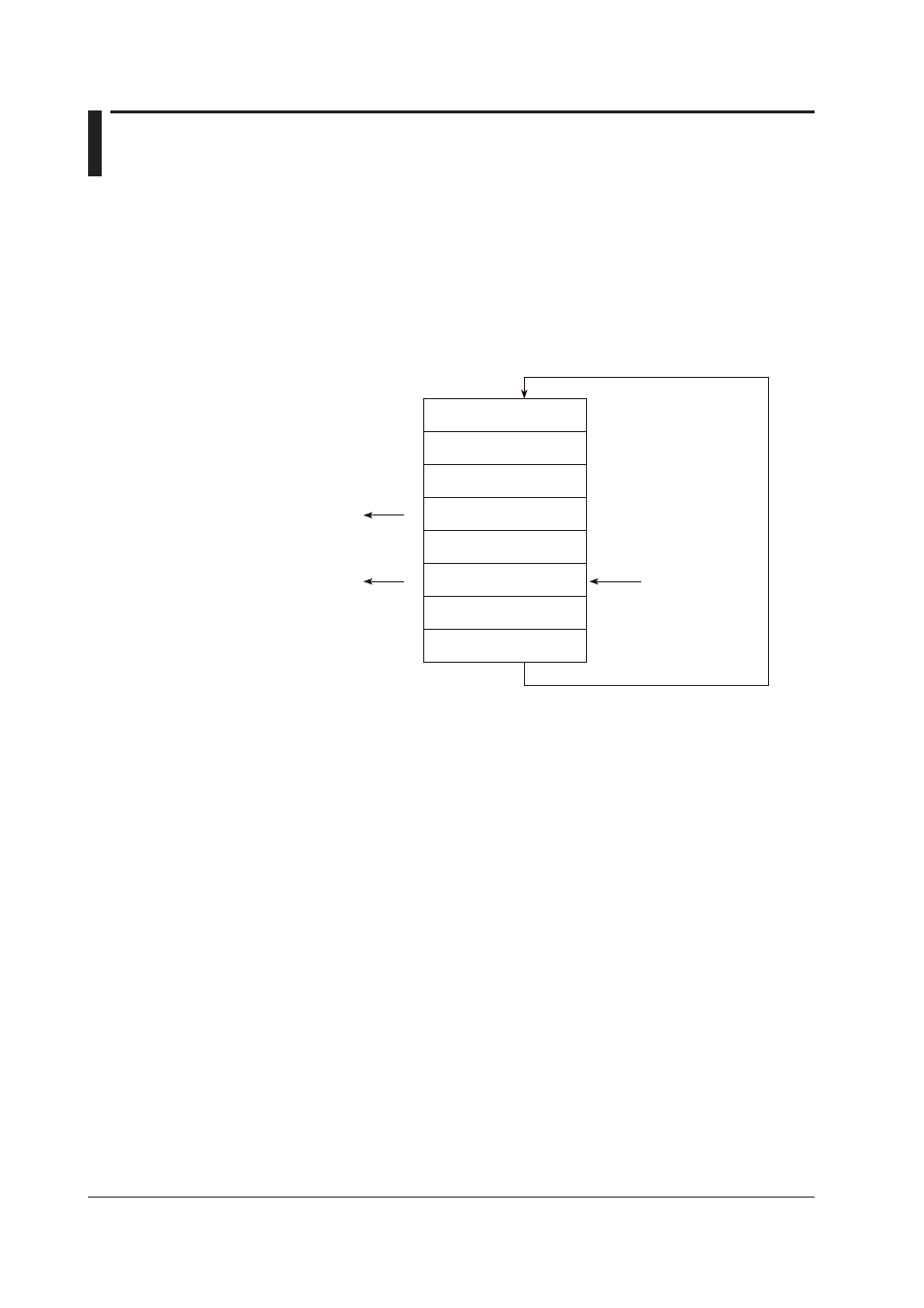
Most recent acquire
Position: WP
Previous read
Position: RP1
Current read
Position: RP2
Block 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Block 8
• Acquiring of the measured/computed data
• The measured/computed data are acquired to the internal memory at 1 s intervals.
• Measured/computed data are acquired to blocks 1 through 8 in order. After
acquiring to block 8, the next acquiring operation returns to block 1.
• Reading the measured/computed data (FF GET command is used,
logging output)
Outputs the data from the next to the previous read position (RP1) to the most recent
acquire position (WP).
In this example, more than 2 s has elapsed from the previous read operation.
Therefore, data in blocks 5 and 6 are output.
• Reading the measured/computed data (FF GETNEW command is used,
output of the most recent value)
Output the specified number of blocks of FIFO data back starting from the recent
acquire position (WP).
In this example, if you specify the number of blocks to “5,” data in blocks 2 to 6 are
output.
The buffer capacity varies depending on the model.
Pen model: 240 intervals (30 s at an acquiring interval of 125 ms)
Dot model: 60 intervals (60 s at an acquiring interval of 1 s)
