Sel language – IAI America DS-S-C1 User Manual
Page 37
35
12. SEL Language
n
o
i
s
n
a
p
x
E
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
c
)
R
O
·
D
N
A
(
t
u
p
n
I
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
c
)
g
a
l
F
·
O
/
I
(
d
n
a
m
m
o
C
t
s
o
P
)
g
a
l
F
·
t
r
o
p
t
u
p
t
u
O
(
d
n
a
m
m
o
C
1
d
n
a
r
e
p
O
2
d
n
a
r
e
p
O
l
a
n
o
i
t
p
O
l
a
n
o
i
t
p
O
T
L
U
M
.
o
N
e
l
b
a
i
r
a
V
a
t
a
D
R
Z
●
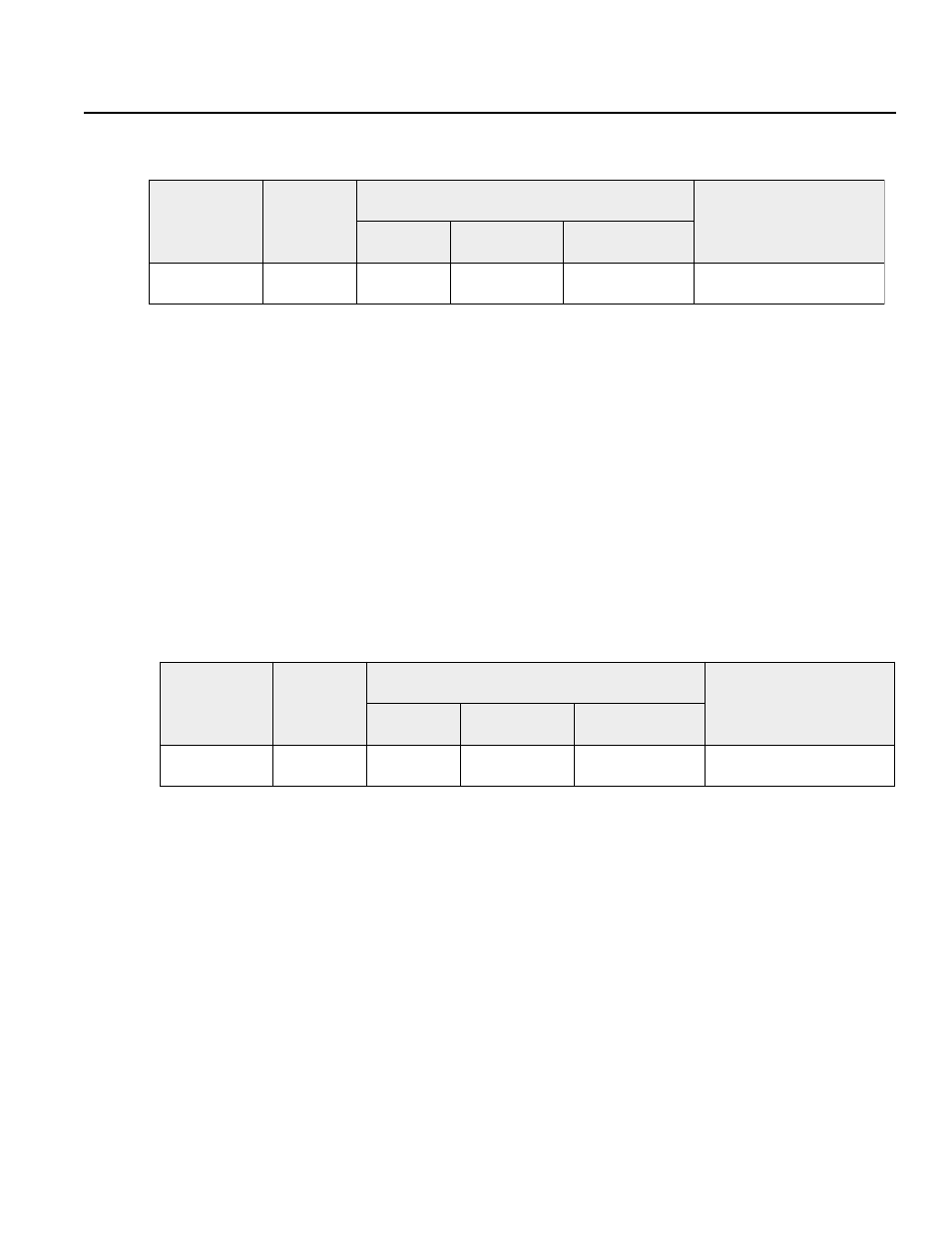
MULT (Multiply)
[Function]
Multiplies the contents of the variable in operand 1 by the value in operand 2, then stores this
in the varible in operand 1. The output turns ON when the result of the operation is 0.
[Example 1]
LET
1
3
Assign 3 to variable 1.
MULT
1
2
Multiply 3 (content of variable 1) by 2.
[Example 2]
LET
1
2
Assign 2 to variable 1.
LET
2
3
Assign 3 to variable 2.
LET
3
2
Assign 2 to variable 3.
MULT
*1 *2
Multiply variable 2 (content of variable 1) by 2
(content of variable 1).
3x2 is 6 which is entered in variable 2.
n
o
i
s
n
a
p
x
E
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
c
)
R
O
·
D
N
A
(
t
u
p
n
I
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
c
)
g
a
l
F
·
O
/
I
(
d
n
a
m
m
o
C
t
s
o
P
)
g
a
l
F
·
t
r
o
p
t
u
p
t
u
O
(
d
n
a
m
m
o
C
1
d
n
a
r
e
p
O
2
d
n
a
r
e
p
O
l
a
n
o
i
t
p
O
l
a
n
o
i
t
p
O
V
I
D
.
o
N
e
l
b
a
i
r
a
V
a
t
a
D
R
Z
[Function]
Divides the contents of the variable in operand 1 by the value in operand 2, then stores this
in the varible in operand 1. The output turns ON when the result of the operation is 0.
Note:
When operand 1 is an integer type variable, anything beyond the decimal point is disregarded.
[Example 1]
LET
1
3
Assign6 to variable 1.
DIV
1
2
Divide 6 (content of variable 1) by 2.
[Example 2]
LET
1
2
Assign 2 to variable 1.
LET
2
6
Assign 3 to variable 2.
LET
3
2
Assign 2 to variable 3.
MULT
*1 *3
Divide variable 2 (content of variable 1) by 2
(content of variable 1).
6
÷
2
is 3 which is entered in variable 2.
●
DIV (Divide)
