Switching waveforms – Rainbow Electronics AT75C220 User Manual
Page 22
AT75C220
22
Switching Waveforms
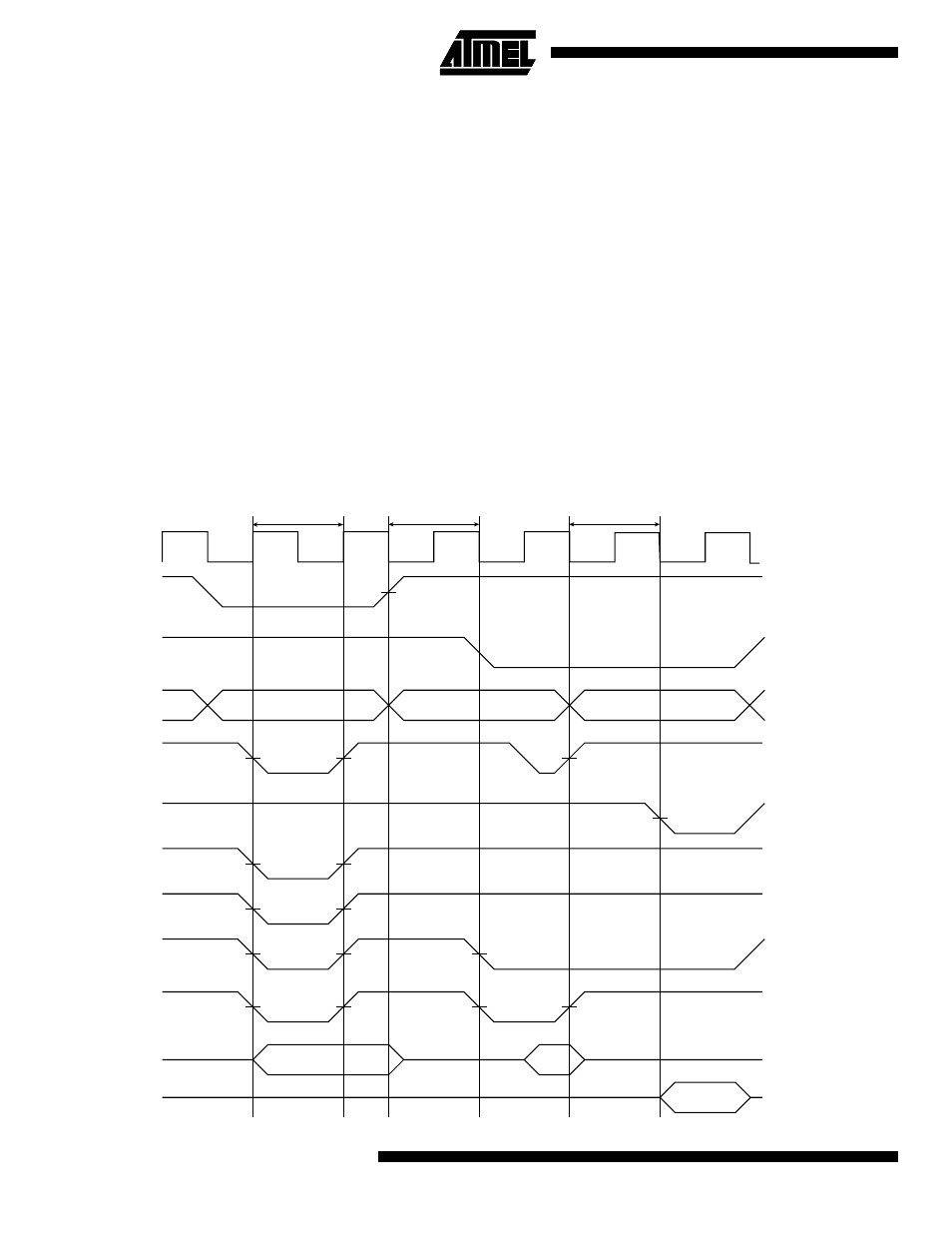
Figure 6 shows a write to memory 0 followed by a write and
a read to memory 1. SMC_CSR0 is programmed for one
wait state with BAT = 0 and DFT = 0. SMC_CSR1 is pro-
grammed for zero wait states with BAT = 1 and DFT = 0.
SMC_ MCR is programmed for early re ads from all
memories.
The write to memory 0 is a word access and therefore all
four NWE strobes are active. As BAT = 0, they are config-
ured as write strobes and have the same timing as NWR.
As the access employs a single wait state, the write strobe
pulse is one clock cycle long.
There is a chip select change wait state between the mem-
ory 0 write and the memory 1 write. The new address is
output at the end of the memory 0 access, but the strobes
are delayed for one clock cycle.
The write to memory 1 is a half-word access to an odd half-
word address and, therefore, NWE2 and NWE3 are active.
As BAT = 1, they are configured as byte select signals and
have the same timing as NCE. As the access has no inter-
nal wait states, the write strobe pulse is one- half clock
cycle long. Data and address are driven until the write
strobe rising edge is sensed at the SIAP pin to guarantee
positive hold times.
There is an early read wait state between memory 1 write
and memory 1 read to provide time for the AT75C220 to
disable the output data before the memory is read. If the
read was normal mode, i.e., not early, the NSOE strobe
would not fall until the rising edge of BCLK and no wait
state would be inserted. If the write and early read were to
different memories, then the early read wait state is not
required as a chip select wait state will be implemented.
The read from memory 1 is a byte access to an address
with a byte offset of 2 and therefore only NWE2 is active.
Figure 6. Write to Memory 0, Write and Read to Memory 1
BCLK
NCE0
NCE1
A
NWR
NSOE
NWE0
NWE1
NWE2
NWE3
D (SIAP)
D (MEM)
Internal Wait State
Chip Select Wait State
Early Read Wait State
