Managing public keys, Overview, Fips compliance – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 130
118
6B
Managing public keys
85B
Overview
This chapter describes public key management for the asymmetric key algorithms including the
Revest-Shamir-Adleman Algorithm (RSA), the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA), and the Elliptic Curve
Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA).
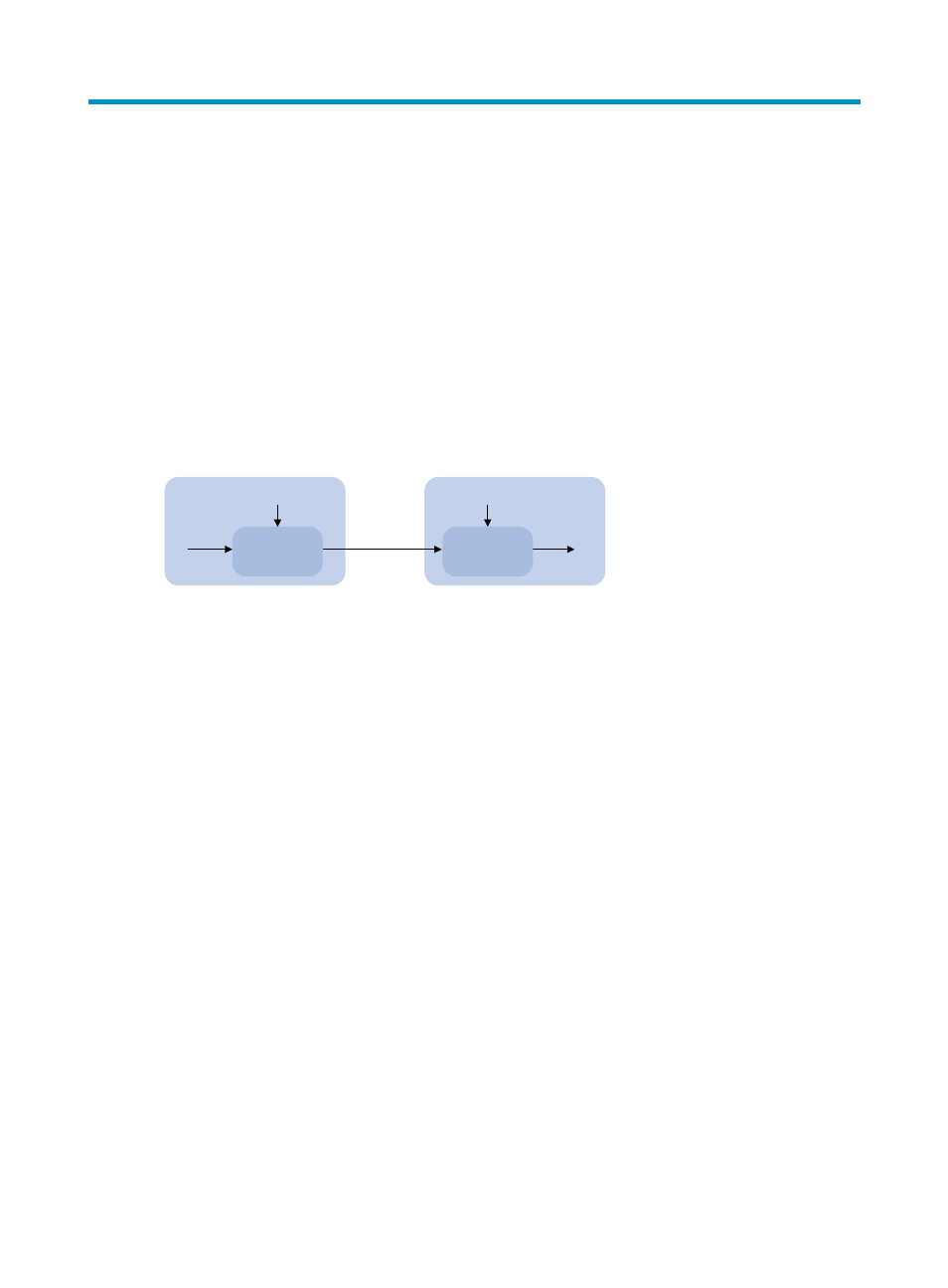
Many security applications, for example, SSH, use asymmetric key algorithms to secure communications
between two parties, as shown in
824H
Figure 37
. Asymmetric key algorithms use two separate keys (one
public and one private) for encryption and decryption, in contrast to the symmetric key algorithms, which
use only one key.
Figure 37 Encryption and decryption
A key owner can distribute the public key in plain text on the network but must keep the private key in
privacy. It is mathematically infeasible to calculate the private key even if an attacker knows the algorithm
and the public key.
The security applications use the asymmetric key algorithms for the following purposes:
•
Encryption and decryption—Any public key receiver can use the public key to encrypt information,
but only the private key owner can decrypt the information.
•
Digital signature—The key owner uses the private key to "sign" information to be sent, and the
receiver decrypts the information with the sender's public key to verify information authenticity.
RSA, DSA, and ECDSA can all perform digital signature, but only RSA can perform encryption and
decryption.
Asymmetric key algorithms enables secure key distribution on an insecure network, but the security
strength of an asymmetric key algorithm still depends on key size as with any symmetric key algorithm.
86B
FIPS compliance
The device supports the FIPS mode that complies with NIST FIPS 140-2 requirements. Support for features,
commands, and parameters might differ in FIPS mode (see "
825H
Configuring FIPS
") and non-FIPS mode.
Receiver
Key
Plain text
Cipher text
Plain text
Sender
Encryption
Decryption
Key
- H3C S5560 Series Switches H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C S9800 Series Switches H3C S5130 Series Switches H3C S5120 Series Switches
