Kk absolute value and argument, Kk conjugate complex numbers – Casio fx-9860G SD User Manual
Page 110
20050401
2-6-3
Complex Number Calculations
k
k
k
k
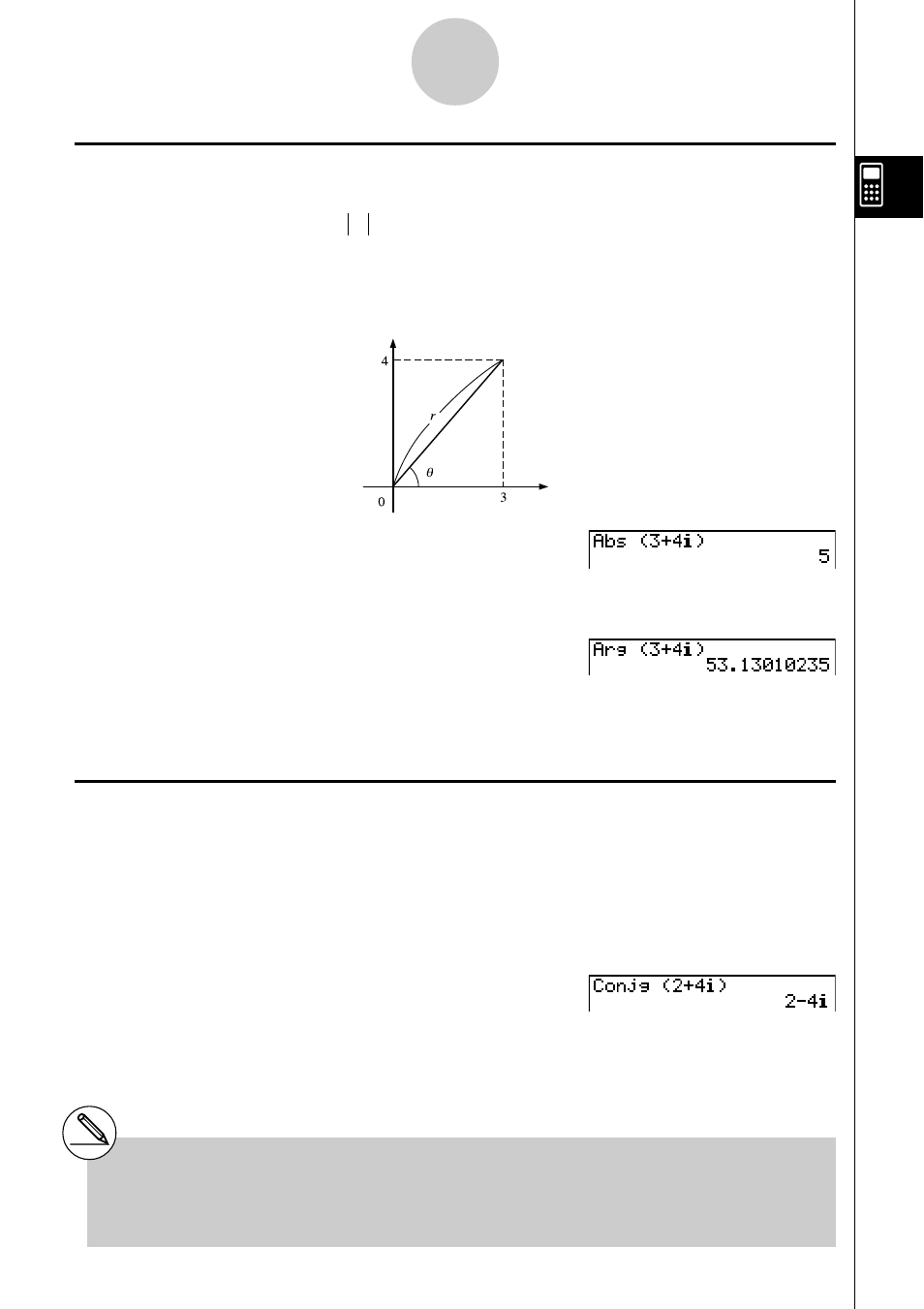
k Absolute Value and Argument
[OPTN]-[CPLX]-[Abs]/[Arg]
The unit regards a complex number in the form
a
+
bi
as a coordinate on a Gaussian plane,
and calculates absolute value Z and argument (arg).
○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Example
To calculate absolute value (
r
) and argument (
θ) for the complex
number 3 + 4
i
, with the angle unit set for degrees
AK3(CPLX)2(Abs)
(d+e
1(
i
))w
(Calculation of absolute value)
AK3(CPLX)3(Arg)
(d+e
1(
i
))w
(Calculation of argument)
k
k
k
k
k Conjugate Complex Numbers
[OPTN]-[CPLX]-[Conj]
A complex number of the form
a + bi
becomes a conjugate complex number of the form
a – bi
.
○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Example
To calculate the conjugate complex number for the complex number 2
+ 4
i
AK3(CPLX)4(Conj)
(c+e
1(
i
))w
# The result of the argument calculation differs
in accordance with the current angle unit
setting (degrees, radians, grads).
Imaginary axis
Real axis
