Fitting a curve to 2var data, Regression coefficients – HP 38g Graphing Calculator User Manual
Page 127
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
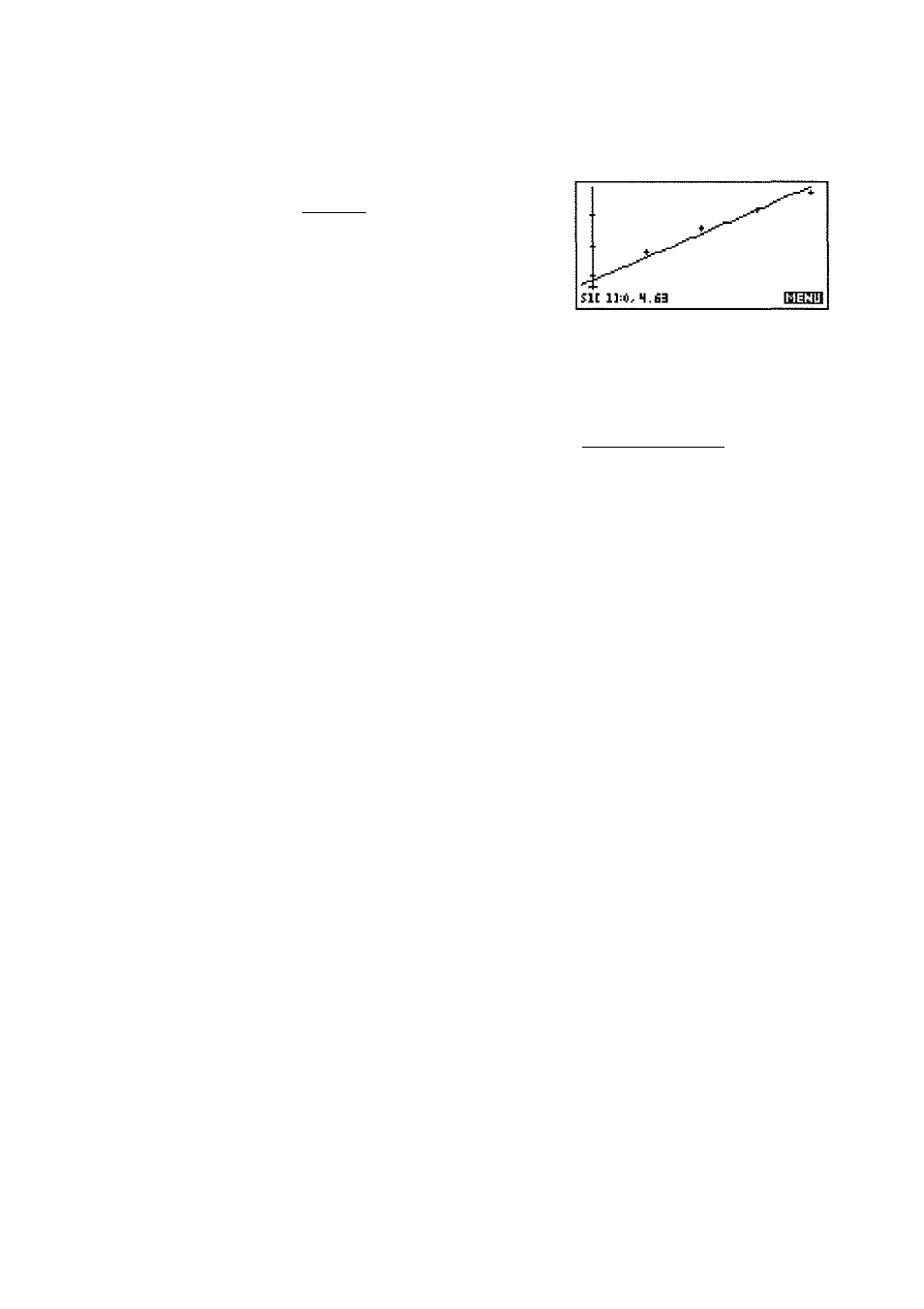
Fitting a Curve to 2VAR Data
In the Plot view, press
{{FIT}}
to turn on
{{FIT«}}.
This
calculates a curve to fit the checked two-variable data set(s).
I PLOT I {{MENU}} {{FIT}}
(assuming 2VAR is set and
two data sets are defined and
checked in Numeric and
Symbolic views)
SYMB
The expression in
Fit
1
shows that the slope=0.03865
and they-intercept=4.856.
i^^STATISTICf fVMEDLIC VIEH^W
.'Sl:C3
C4
S2!
Fit2!m*X+b
f
EHTER U;Eli DEFINED FIT__________________
Regression Coefficients
As shown above, the
{{FIT«}}
mode (in Plot view) calculates
and draws a curve to fit the data points using the given
regression model. It also substitutes calculated values for the
regression coefficient variables in the Fit expression.
CORK
CORK, the
correlation coefficient,
is a measure of fit to a
linear
curve only. Regardless of the Fit model you have chosen,
CORR relates to the linear model.
Relative Error The
relative error
is stored in a variable named RelErr. The
relative error provides a measure of fit accuracy for all fits,
and it
does
depend on the Fit model you have chosen.
The relative error is a measure of the error between predicted
values and actual values based on the specified Fit. A smaller
number means a smaller error, which means a better fit.
Statistics S21
