ETC Unison Mosaic Show Control User Manual
Page 46
46
LED
TEST & ADDRESS WHEEL
Wheel settings '1' to '43’ directly set the LED's DMX start address to the corresponding
channel number. Alternatively, use the managed ('M') setting to set the DMX start address via
the RDM protocol (see Designer Help for details) in which case the LED can be addressed to
any DMX channel number.
Wheel settings 'T1' to 'T6’ and ‘TA’ provide test facilities for the installer by bringing the
corresponding channel or all channels to 25%. The DMX control data is ignored when testing
channels in this way. Note that there is a small delay (0.5sec) in the response of the wheel to
avoid intermediate settings taking effect.
LED FIXTURE TYPES (LOW VOLTAGE ARCHITECTURAL ONLY)
LED fixtures are totally unlike conventional lighting fixtures due to the behaviour of the semi-
conducting Light Emitting Diode (LED) itself:
• Correct polarity must be observed to avoid “breakdown”
• Specified forward voltage (Vf) must at least be applied (the LED will “drop” Vf)
• Specified drive current (If) must be carefully maintained
• Dimming is achieved by “chopping” the drive current, typically by PWM
• Thermal management is critical for long life and reliability, choose your fixtures well
LED fixtures typically comprise either one or more LEDs in a module (“light engine”) or as an
array on a substrate, commonly a flexible “tape” that can be cut to the desired length. This is
the first important distinction to make since the former require a constant current driver (the
fixture is just LEDs) and the latter a constant voltage driver (the fixture includes current control
electronics):
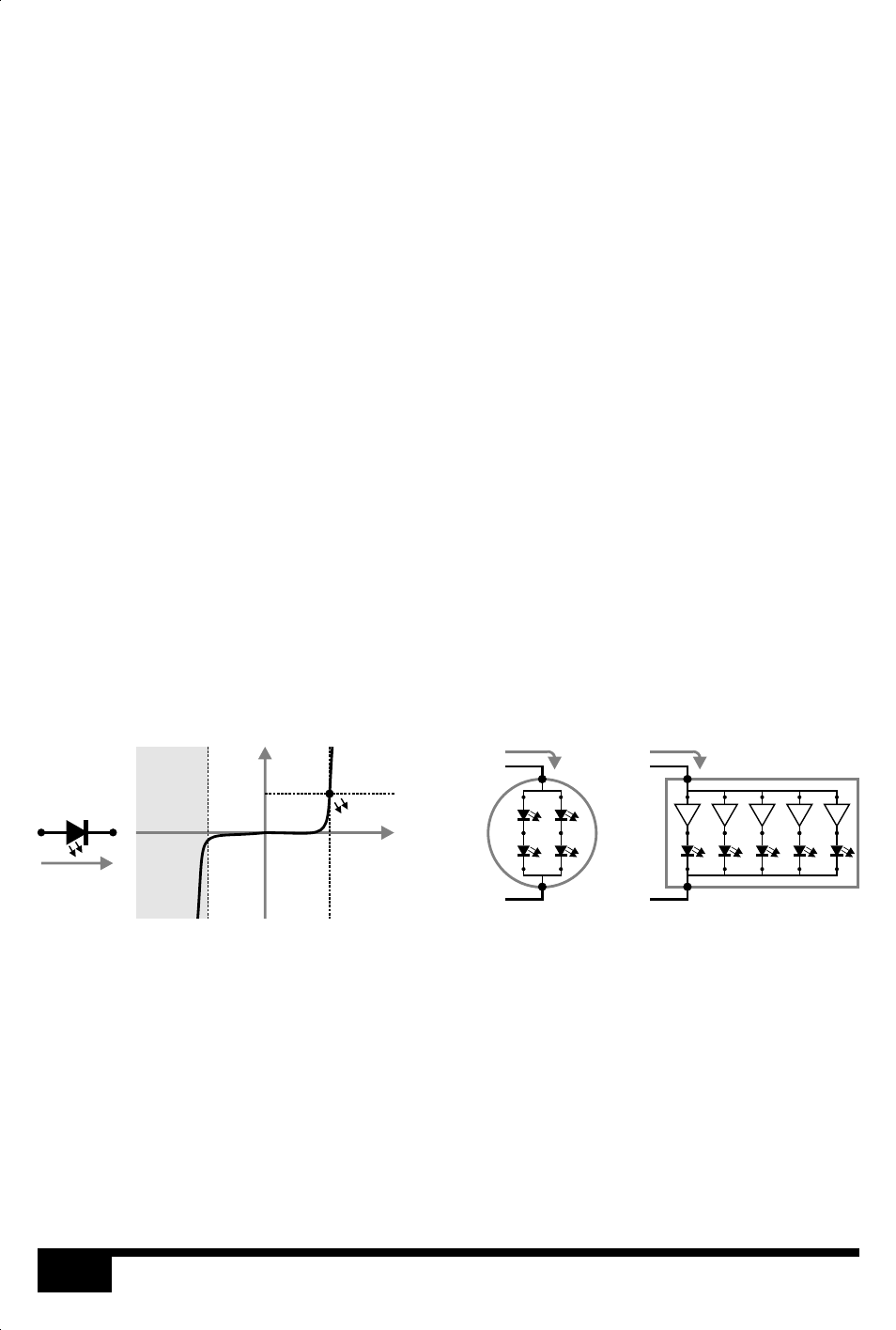
LED SYMBOL & VOLTAGE vs CURRENT GRAPH
LED MODULE
LED ARRAY
I
V
BREAKDOWN
Vf
If
Vf
-
+
If
Vf(module) +
If(module)
-
Is(array)
Vs(array) +
-
So before you can select the correct LED driver you must determine the fixture type and then
gather the drive characteristics from the manufacturer:
LED MODULE - CONSTANT CURRENT DRIVE
• Module forward current If(module) which is typically 350, 500 or 700mA
• Module forward voltage Vf(module) which is module power divided by If(module)
LED ARRAY - CONSTANT VOLTAGE DRIVE
• Array supply voltage Vs(array) which is typically 12 or 24V
• Array power dissipation Ps(array) which is determined by its size/length (eg. Watt/metre)
