On-off control, Proportional control, Proportional plus integral (pi) control – Watlow Series SD31 PID with Optional Countdown Timer User Manual
Page 55
To transfer to auto mode from manual mode, press
the Infinity Key
ˆ to get to the Operations Page. Press
the Down Key
¯ until [A-M] appears in the display.
Press and hold the
ß Key to display [Man] for man-
ual mode. Use the Up
¿ or Down ¯ keys to select
[Auto] . The automatic set point value will be recalled
from the last automatic operation.
Changes take effect after three seconds or immedi-
ately upon moving to the next parameter or by pressing
the Infinity Key
ˆ.
On-Off Control
On-off control switches the output either full on or
full off, depending on the input, set point and hysteresis
values. The hysteresis value indicates the amount the
process value must deviate from the set point to turn on
the output. Increasing the value decreases the number of
times the output will cycle. Decreasing hysteresis im-
proves controllability. With hysteresis set to 0, the
process value would stay closer to the set point, but the
output would switch on and off more frequently, and
may result in the output “chattering.” On-off control can
be selected with Heat Control Method
[ht;m] or Cool
Control Method
[Cl;m] (Operations parameters).
NOTE:
Input Error Failure Mode
[fail] does not function in on-off control
mode. The output goes off.
NOTE:
In on-off control set Power Limit 1 and 2 (
[PL`1], and [PL`2] )
and Output Power Scale High 1 and 2 ([
PSH1] and [PSH2] ) to
100%. Set Output Power Scale Low 1 and 2 (
[PSL1] and [PSL2] )
to 0%.
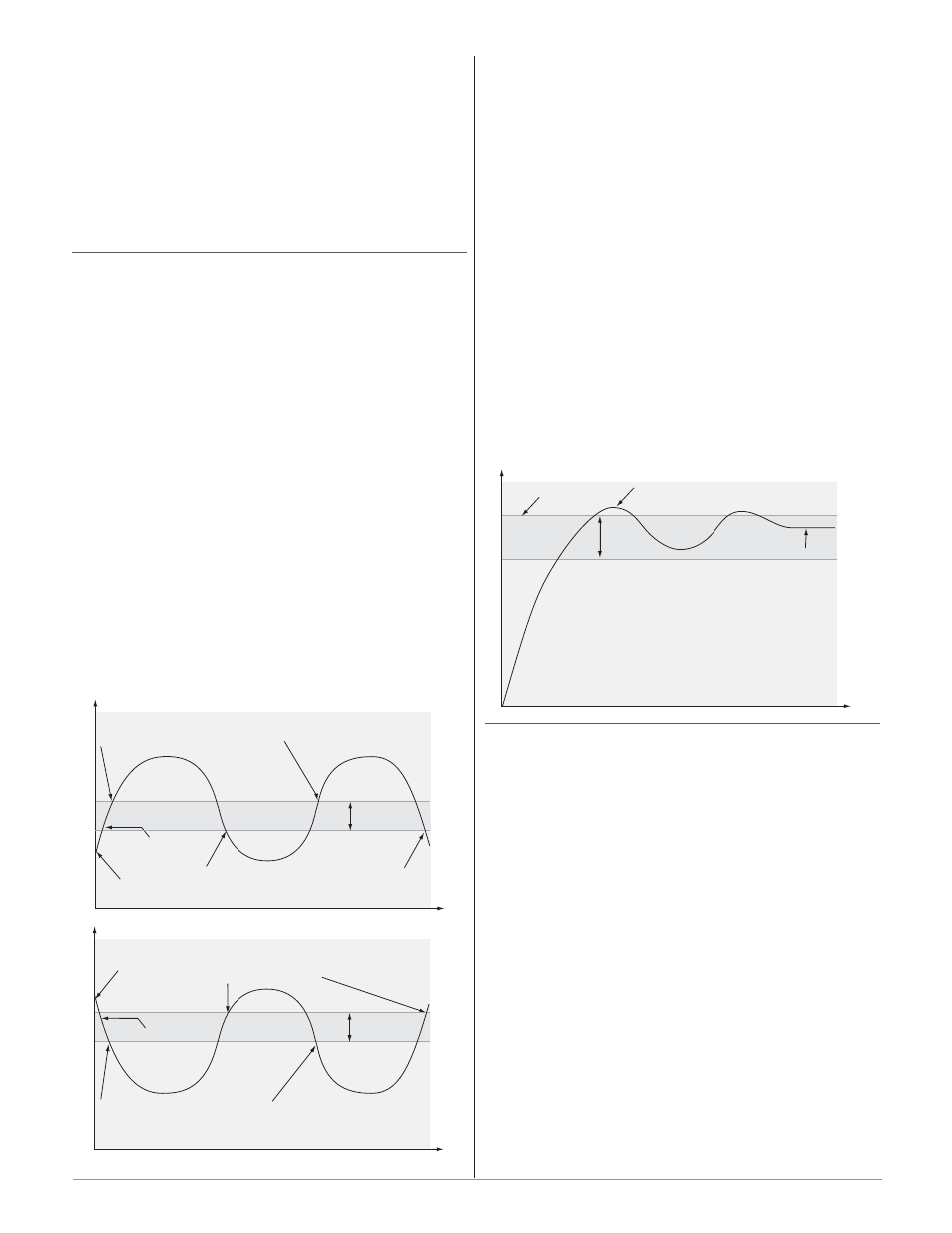
Proportional Control
Some processes need to maintain a temperature or
process value closer to the set point than on-off control
can provide. Proportional control provides closer control
by adjusting the output when the temperature or
process value is within a proportional band. When the
value is in the band, the controller adjusts the output
based on how close the process value is to the set point.
The closer the process value is to the set point, the low-
er the output power. This is similar to backing off on the
gas pedal of a car as you approach a stop sign. It keeps
the temperature or process value from swinging as
widely as it would with simple on-off control. However,
when the system settles down, the temperature or
process value tends to “droop” short of the set point.
With proportional control the output power level
equals (set point minus process value) divided by the
proportional band value.
Adjust the proportional band with Proportional Band
Heat
[Pb;ht] or Proportional Band Cool [Pb;Cl] (Opera-
tions parameters).
Proportional plus Integral (PI) Control
The droop caused by proportional control can be cor-
rected by adding integral (reset) control. When the sys-
tem settles down, the integral value is tuned to bring
the temperature or process value closer to the set point.
Integral determines the speed of the correction, but this
may increase the overshoot at startup or when the set
point is changed. Too much integral action will make
the system unstable. Integral is cleared when the
process value is outside of the proportional band.
Integral is in effect if PID Units are set to SI, and is
measured in minutes per repeat. A low integral value
causes a fast integrating action.
Reset is in effect if PID Units are set to U.S., and is
measured in repeats per minute. A high reset value
causes a fast integrating action.
Adjust the integral with Integral Heat
[It;ht] or In-
tegral Cool
[It;Cl] (Operations parameters).
Adjust the reset with Reset Heat
[rE;ht] or Reset
Cool
[rE;CL] (Operations parameters).
Time
Temperature
Set Point
Proportional Band
Droop
Overshoot
Set Point
Time
Temperature
The heating action switches off when the process
temperature rises above the set point.
The heating action
switches on at startup.
Hysteresis
Process Temperature
Hysteresis
Time
Temperature
The cooling action
switches
on at startup.
Process Temperature
The cooling action switches on when
the process temperature rises above
the set point plus the hysteresis.
Set Point
The heating action switches on when the process temperature
drops below the set point minus the hysteresis.
The cooling action switches off when the process
temperature drops below the set point.
Wa t l o w S e r i e s S D 3 1
■
5 3
■
C h a p t e r 1 0 F e a t u r e s
