Data table, Questions, Data table questions – PASCO ME-9502 Statics System User Manual
Page 80
S t a t i c s S y s t e m
E x p . 1 2 : S i m p l e M a c h i n e s – T h e L e v e r
®
76
012-12876B
A wheelbarrow is an example of a Class II Lever, and the human forearm is an example of a Class III Lever.
When a lever is in equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise torques about the pivot point (fulcrum) is equal to the
sum of the counterclockwise torques about the pivot point.
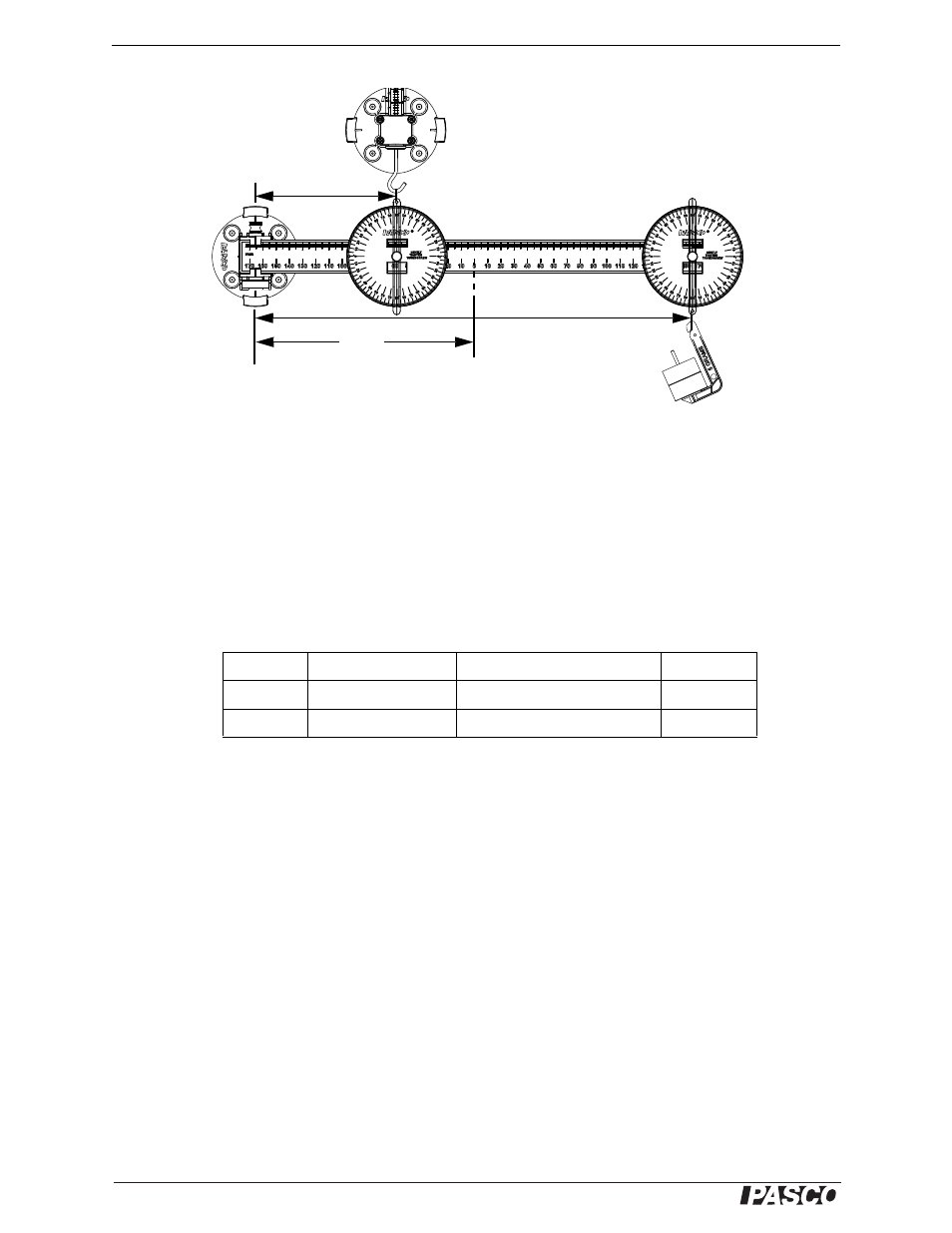
Make and record the measurements that are necessary to determine if the sum of the clockwise torques equals the
sum of the counterclockwise torques for the Class II and Class III levers. Will you need to take the mass of the pro-
tractors and the mass of the Balance Arm beam into account?
Diagram your results and show your measurements and calculations on a separate sheet of paper.
Data Table
Questions
1.
For the Class II Lever, is the net torque equal to zero when the lever is in equilibrium?
2.
For the Class III Lever, is the net torque equal to zero when the lever is in equilibrium?
Table 16.1:
Lever
clockwise torque
counterclockwise torque
Net torque
Class II
Class III
Figure 12.6: Class III Lever
Load
Applied
force
L
cm
Fulcrum
