Exp. 11b: minimum period of a physical pendulum, Theory – PASCO ME-9502 Statics System User Manual
Page 67
®
M o d e l N o . M E - 9 5 0 2
E x p . 1 1 B : M i n i m u m P e r i o d o f a P h y s i c a l P e n d u l u m
0 1 2 - 1 2 8 7 6 B
63
Exp. 11B: Minimum Period of a Physical Pendulum
Equipment Needed
Theory
The period of oscillation for a physical pendulum can be written as
follows:
where I is the moment of inertia (rotational inertia) for the physical
pendulum, L
cm
is the perpendicular distance from the axis at the pivot
point to the parallel axis at the center of mass, cm, and m is the mass
of the pendulum.
The moment of inertia, I
cm
, for a rectangular-type rod about its center
of mass is:
where a is the length and b is the thickness of the rectangular-type
rod. However, if the length, a, is much greater than the thickness, b,
then the following can be used as a very good approximation of the
moment of inertia around the center of mass:
where m is the mass and L is the length of the rod.
If the rod pivots around any other axis that is parallel to the axis through the center of mass, the Parallel Axis The-
orem states that the moment of inertia about the parallel axis, I
parallel
, is the sum of the moment of inertia around
the center of mass, I
cm
, plus mL
cm
2
, where m is the mass of the rod and L
cm
is the perpendicular distance from the
center of mass to the pivot point, or
The formula for the period of oscillation becomes
At what distance, L
cm
, does the period of oscillation, T, become a minimum?
In this experiment you will determine the distance, L
cm
, from the pivot point to the center of mass that gives the
minimum period of oscillation for the physical pendulum.
Item
Item
Statics Board
Balance Arm
Stopwatch (ME-1234)
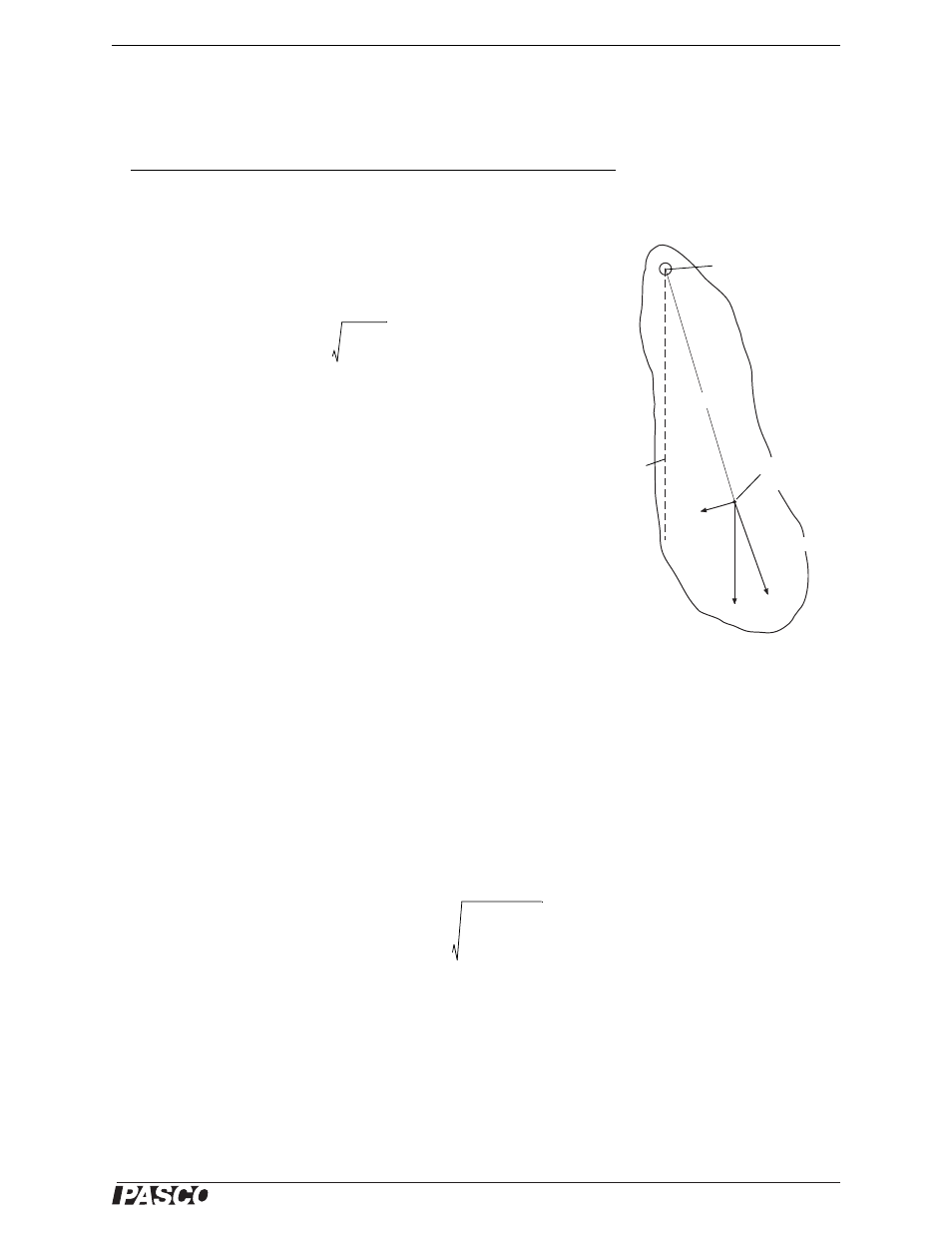
Figure 11.5: Physical Pendulum
mg
mg sin
mg cos
Equilibrium
position
Pivot
point
Center of
mass
L
cm
T
2
I
L
cm
mg
-----------------
=
I
cm
1
12
------m a
2
b
2
+
=
I
cm
1
12
------mL
2
=
I
parallel
I
cm
mL
cm
2
+
1
12
------mL
2
mL
cm
2
+
=
=
T
2
1
12
------L
2
L
cm
2
+
L
cm
g
-------------------------------
=
