Calculations – PASCO ME-9502 Statics System User Manual
Page 34
S t a t i c s S y s t e m
E x p . 5 B : E q u i l i b r i u m o f P h y s i c a l B o d i e s
®
30
012-12876B
Data Table.
Calculations
1.
Calculate and record the sum of the clockwise and counterclockwise torques.
cw
= _________________________
ccw
= _______________________
•
Are the torques balanced?
2.
Calculate and record the sum of the upward and downward forces.
F
up
= _________________________
F
down
= _______________________
•
Are the translational forces balanced?
3.
On the basis of your answers to the questions, what conditions must be met for a physical body to be in equi-
librium (no acceleration)?
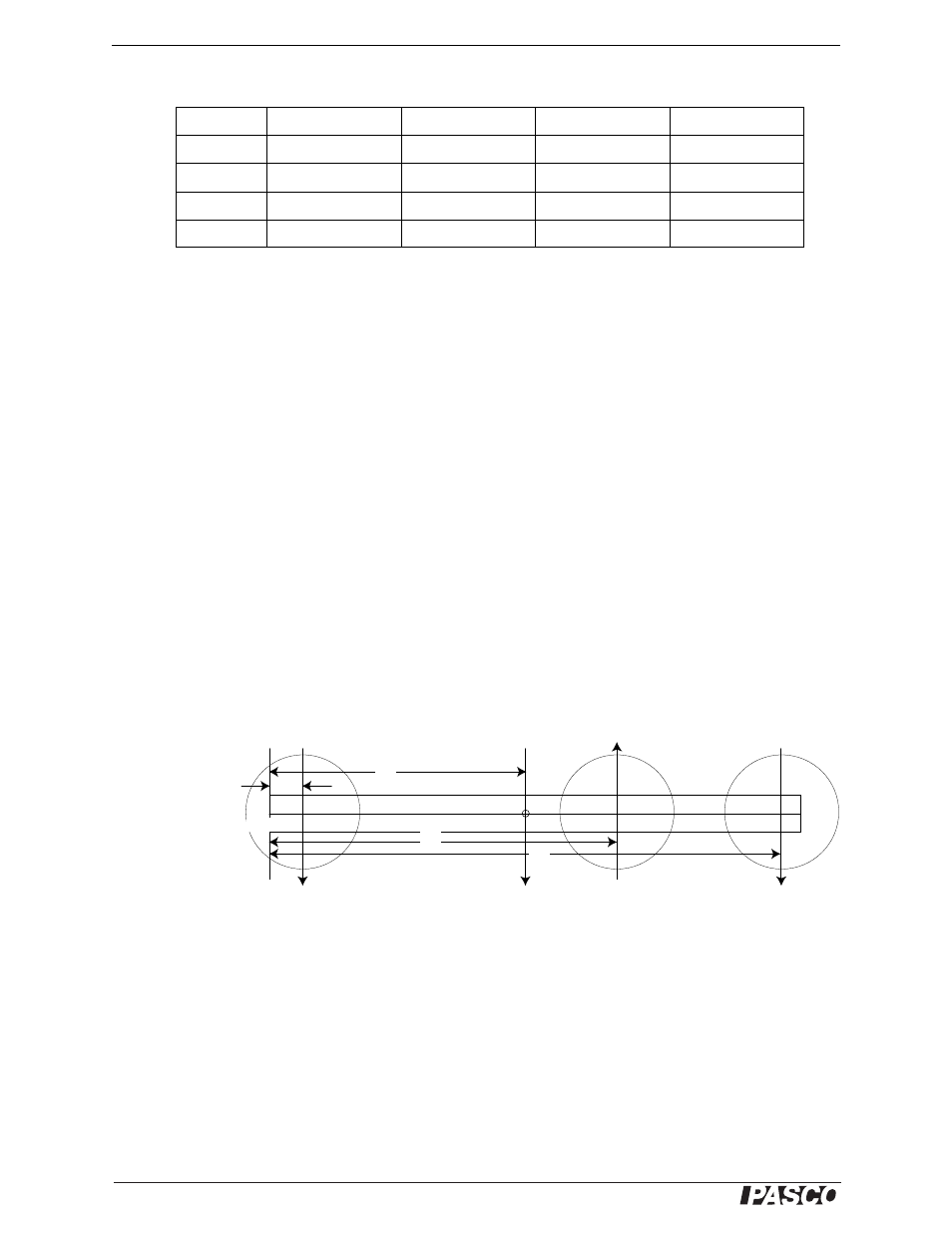
Change the Origin
In measuring the torques the first time, all the distances were measured from the point of suspension of the Bal-
ance Arm. This measures the tendency of the beam to rotate about this point of suspension. You can also measure
the torques about any other point, on or off the beam. Using the same forces as you used before, re-measure the
distances, measuring from the left end of the balance beam as shown in the diagram.
Recalculate the
torques to
determine the
tendency of the
beam to rotate
about the left
end of the
beam.
Record your
data in the sec-
ond table. As
before, indi-
cate whether each torque is clockwise (cw) or counterclockwise (ccw).
Position
mass (M)
force (F)
distance (d)
torque (
)
1
2
3
4
—
F
1
F
2
F
3
F
4
d
1
d
2
d
3
d
4
Figure 5.6: Change the Origin
Origin
