Question, Normal force – PASCO ME-9502 Statics System User Manual
Page 42
S t a t i c s S y s t e m
E x p . 7 : T h e I n c l i n e d P l a n e
®
38
012-12876B
The force provided by the Spring Scale, F
measured
, equals the component of the force of gravity that is parallel to
the Inclined Plane, F
The calculated component of force that is parallel to the Inclined Plane, F
calculated
, is F sin
, where is the angle of the plane.
3.
Adjust the angle of inclination of the Inclined Plane to each of the values shown in the table. For accurate val-
ues, adjust the pulley and Spring Scale so that the thread remains parallel to the plane. At each value, record
the measured value, F
measured
, of the force parallel to the plane.
4.
At each value, calculate the magnitude of the force parallel to the plane, F
calculated
= F sin
and record the
calculated value.
5.
Calculate the percent difference between the measured and calculated values of the force parallel to the plane.
*The Percent Difference is the absolulte value of the ratio of the difference of the measured and calculated values, divided by the
average of the measured plus calculated values, converted to a percentage.
Question
How well does the calculated force based on the vector model compare to your measured force?
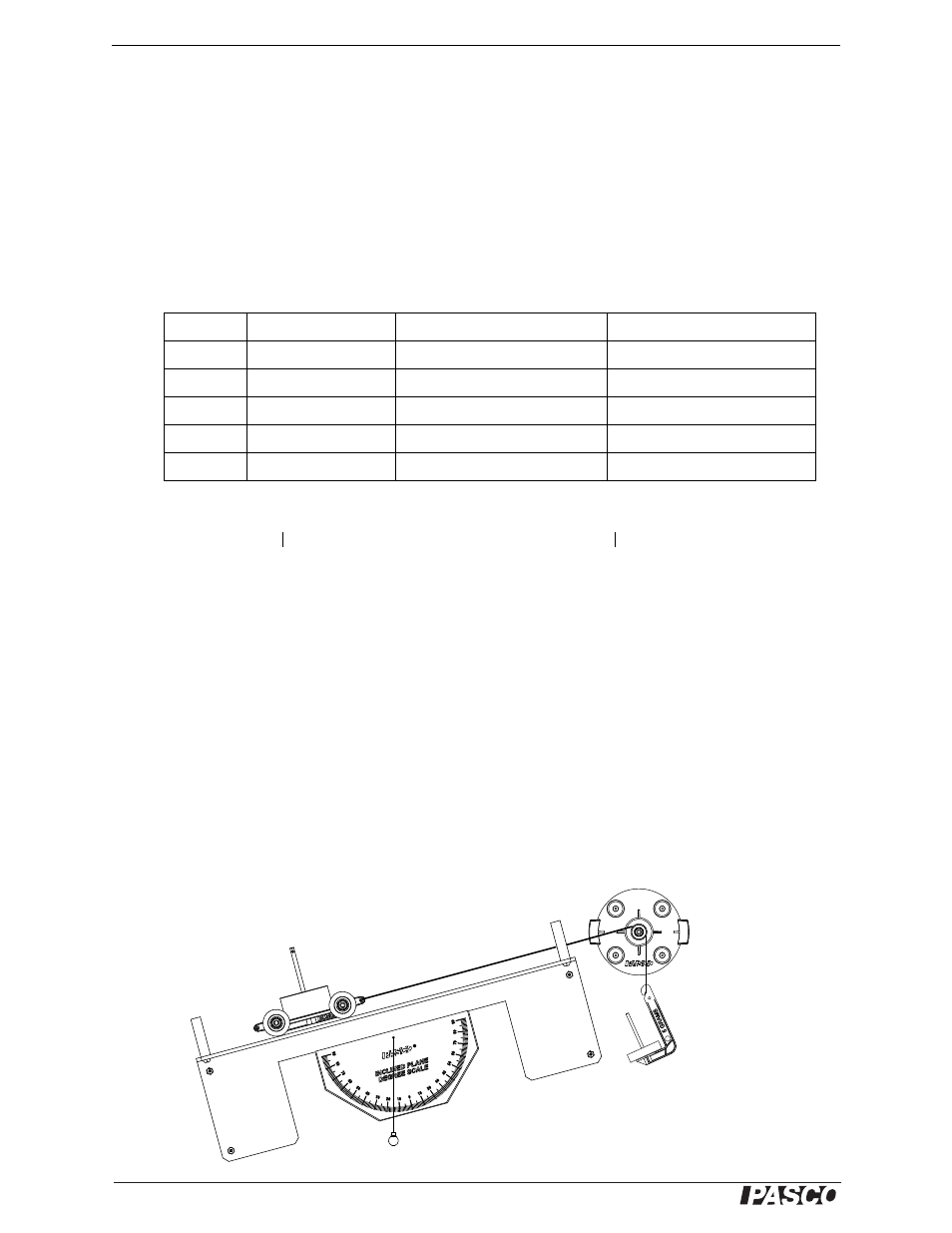
Normal Force
The force that the Inclined Plane provides to support the cart is called the normal force (a force perpendicular –
“normal” – to the surface.) In the vector model of the force, the component of force that is perpendicular to the
plane, F
, is F cos
. The normal force is equal to the force of the cart on the Inclined Plane, perpendicular to its
surface.
To measure the force of the cart on the Inclined Plane, reset the Inclined Plane to 15°. Replace the Spring Scale
with a mass hanger connected by a thread over the pulley to the cart. Add masses to the mass hanger until the cart
and the hanging mass are in equilibrium. (In other words, the force provided by the tension in the thread equals the
component of the cart’s weight that is parallel to the plane.)
Angle
F
measured
F
calculated
= F sin
Percent Difference*
15°
30°
45°
60°
75°
measured - calculated
measured + calculated
2
x 100%
Figure 7.3: Normal Force Equipment Setup
