Exp. 5b: equilibrium of physical bodies, Theory, Setup – PASCO ME-9502 Statics System User Manual
Page 33: Experiment
®
M o d e l N o . M E - 9 5 0 2
E x p . 5 B : E q u i l i b r i u m o f P h y s i c a l B o d i e s
0 1 2 - 1 2 8 7 6 B
29
Exp. 5B: Equilibrium of Physical Bodies
Equipment Needed
Theory
Any force acting on a body may produce both translational motion
(movement of the center of mass of the body in the direction of the force)
and rotational motion (rotation about a pivot point).
In this part of the experiment you will investigate the interplay between
forces and torques by examining all the forces acting on a body in physi-
cal equilibrium.
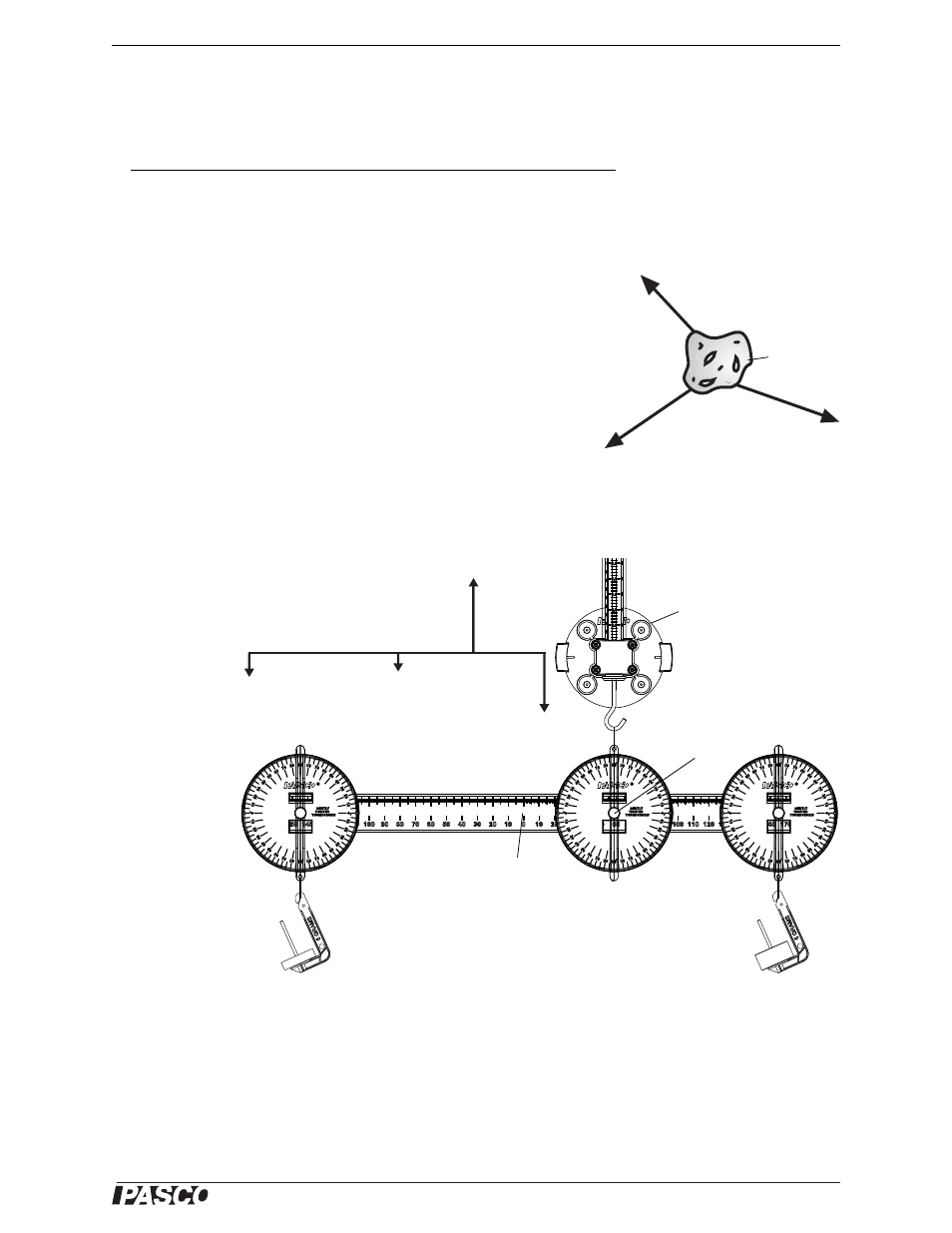
Setup
Find the center of mass of the balance beam and mark it with a pencil. Use the Spring Scale, mass hangers, and
three protractors on the Balance Arm to set up the equipment as shown.
By supporting
the Balance
Arm from the
Spring Scale,
you can now
determine all
the forces act-
ing on the Bal-
ance Arm.
As shown in
the diagram,
these forces
include F
1
, the
weight of the
mass, M
1
, F
2
,
the weight of
the mass M
2
,
F
3
, the weight
of the balance
beam acting
through its cen-
ter of mass, and
F
4
, the upward pull of the Spring Scale.
Experiment
Fill in the data table listing M (in kilograms), F (in newtons), d (the distance in meters from the applied force to the
suspension point), and
(the torque acting about the point of suspension in newton • meters. Indicate whether each
torque is clockwise (cw) or counterclockwise (ccw)
Item
Item
Statics Board
Balance Arm and Protractors
Pulley (1)
Mounted Spring Scale
Mass and Hanger Set
Thread
Figure 5.4: Non-concurrent,
non-parallel forces
Object
F
1
F
2
F
3
M
1
M
2
F
1
F
2
F
3
F
4
Spring
Scale
Force
diagram
Point of
suspension
Center of mass
of the beam
C.O.M.
Figure 5.5: Equipment Setup
