Data table, Calculations, Using a spring scale to measure force – PASCO ME-9502 Statics System User Manual
Page 16: Questions, Data table calculations
S t a t i c s S y s t e m
E x p . 1 : H o o k e ’ s L a w — M e a s u r i n g F o r c e
®
12
012-12876B
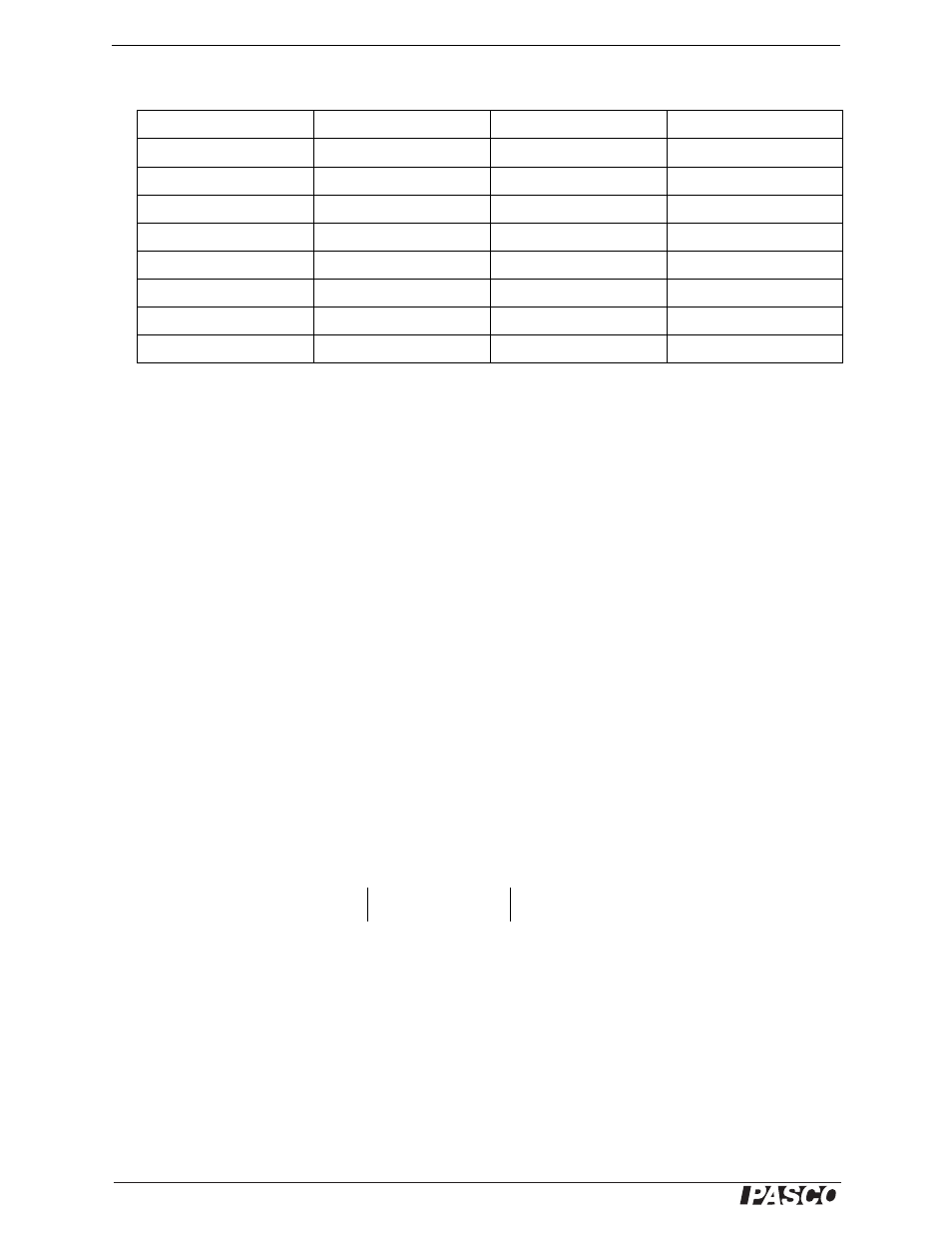
Data Table
Calculations
1.
Using the formula F = mg, where m is the mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity, calculate the weight in
newtons for each trial. Record the weight in the data table. (To get the correct force in newtons, you must con-
vert the mass value to kilograms.)
2.
On a sheet of graph paper, construct a graph of Weight (N) versus Spring Displacement (m) with Spring Dis-
placement on the x-axis.
3.
Draw the line that best fits your data points on the graph. The slope of this line on the graph is the ratio of the
force that stretched the spring divided by the amount of stretch. In other words, the slope is the spring con-
stant, k, for the spring in the Spring Scale.
4.
Determine the spring constant, k, from your graph and record the result. Remember to include the units (new-
tons per meter).
Spring constant = _____________________________
Using a Spring Scale to Measure Force
•
Hang 160 g (0.160 kg) on the Spring Scale. Calculate the weight based on F = mg. Read the force in newtons
from the Spring Scale.
Weight = _______________
Spring Scale reading = ______________
•
How does the measurement from the Spring Scale compare to the actual weight?
•
Calculate the percent difference:
Percent Difference = _______________
Questions
1.
Hooke’s Law states that the relationship between force and displacement in springs is a linear relationship. If
Hooke’s Law was not valid, could a spring still be used successfully to measure forces? If so, how?
2.
In what way is Hooke’s Law useful when calibrating a spring for measuring forces?
3.
On your graph of Weight versus Spring Displacement, did the best fit line go through the origin (zero)? If it
didn’t, what does that mean?
Spring Displacement (m)
Mass (kg)
Uncertainty
Weight (N)
0.010 m (10 mm)
0.020 m (20 mm)
0.030 m (30 mm)
0.040 m (40 mm)
0.050 m (50 mm)
0.060 m (60 mm)
0.070 m (70 mm)
0.080 m (80 mm)
Weight - Spring Scale
Weight
----------------------------------------------------- X100
