Datamax-O'Neil Class Series Programmer’s Manual User Manual
Page 83
Extended System-Level Command Functions
Class Series Programmer’s Manual
69
(HB) Head Bias – This command instructs the printer to switch the dot zero position: as viewed
from the printer’s front panel (or label output side) – when dot zero occupies the left-most
location on the print head then printing is left justified; when dot zero occupies the right-most
location, printing is right justified.
(HC) Head Cleaning – This command controls the print head cleaning routine. The entered value
specifies the inch (or centimeter) count to reach before prompting a print head cleaning. If the
number specified is exceeded three times, the printer will fault until cleaning is initiated.
Note: The number specified is multiplied by one thousand. Zero disables this function.
(HE) Heat – See Hnn for command details.
(HT) Host Timeout – This command controls the number of seconds a communications port must
be idle before the printer may process data from a different port. The value is also used to
“timeout” an image / label format download (i.e., if, at any time, data flow stops before a
complete label format is received, the data will be ignored).
(IC) Ignore Control Codes – This command allows the user to remove control codes (< 20 Hex)
in the data field. The selected line terminator is processed. When enabled, DPL Control Code
(SOH, STX, CR, ESC, and ^) characters are removed from the data string. (Note that some fonts
do have printable characters in this range and they will not be printed when enabled.)
(IE) Ignore Distances – This command, when enabled, prevents
change the start of print position.
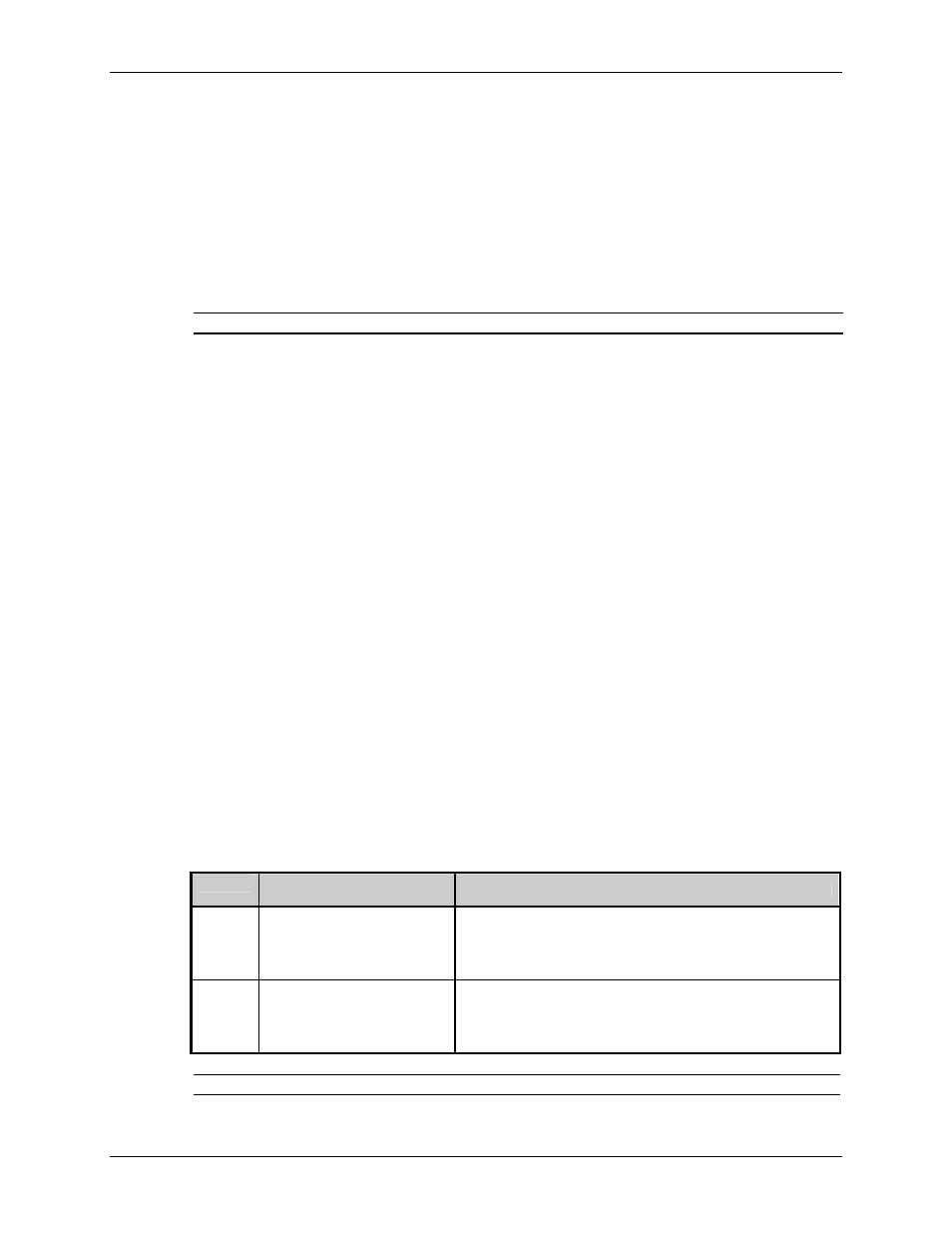
(IL) Imaging Mode – This command instructs the printer whether to pre-image the label format:
Value
Units / Interpretation
Imaging Mode Definition
M
Multiple Label
The printer images multiple labels as memory permits,
achieving the fastest throughput; however, if time-
stamping, the time will reflect the moment the label is
imaged rather than when actually printed.
S
Single Label
The printer images the next label only after the previous
label has been successfully printed. Single processing
provides time-stamps that are more accurate, but it slows
label throughput time.
Note: This selection can affect the accuracy of time-stamped labels and label throughput.
