Appendix, cont’d, Test patterns in detail – Extron Electronics VTG 400D_400 DVI User Guide User Manual
Page 72
Appendix, cont’d
VTG 400D/400 DVI • Appendix
A-8
Test Patterns in Detail
The following test patterns descriptions are helpful in determining how and when
the VTG’s array of test patterns can be used. The numbers correspond to the test
patterns in the previously described Test Patterns Chart.
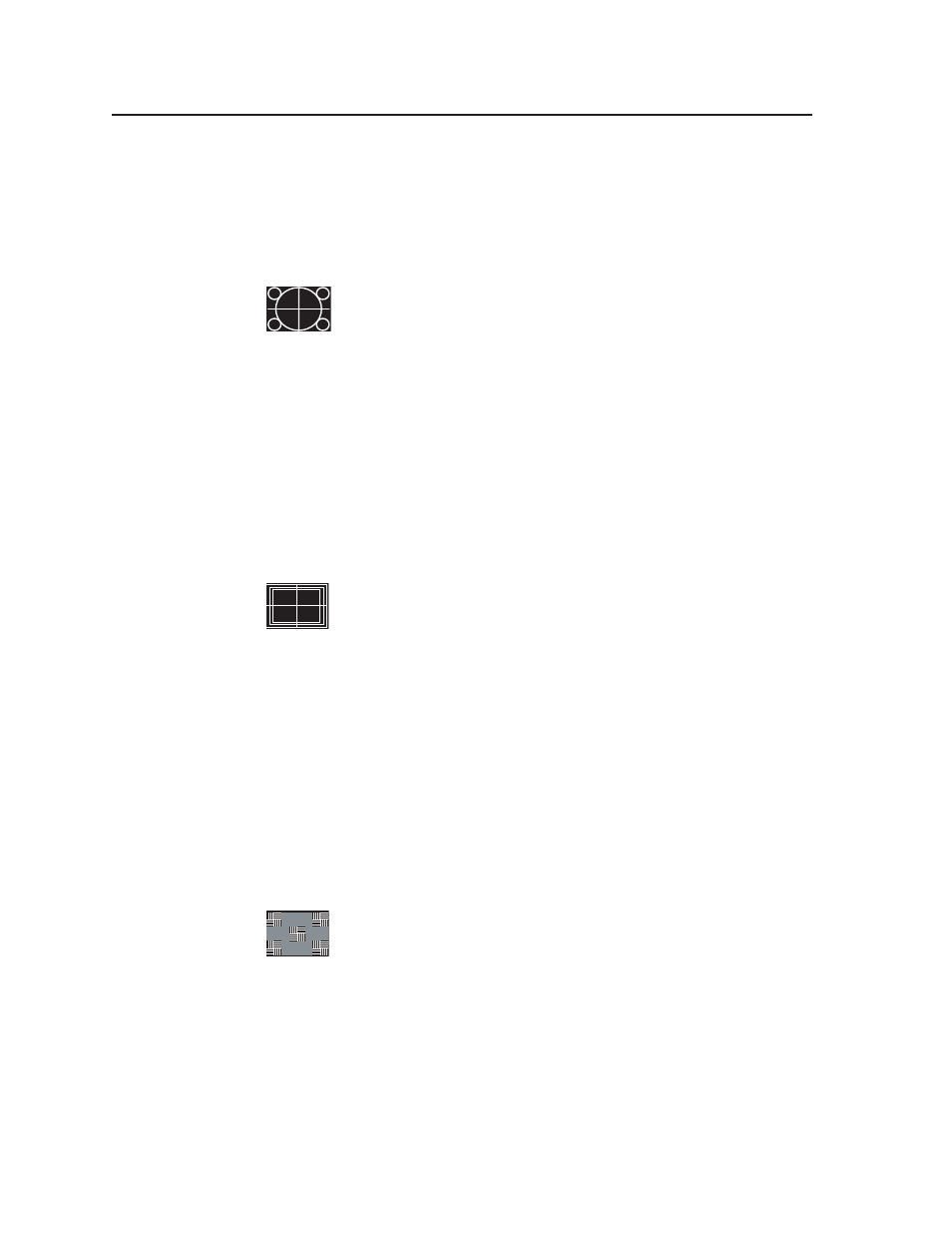
1. Circles
White circles on a black background are useful for checking overall
image geometry and linearity. The invert feature converts the pattern
to predominantly white, which may also be used to evaluate white
field uniformity as well as geometry across the screen. Projectors
having low quality optics may show chromatic aberrations of the test pattern,
especially in the corners. Chromatic aberrations manifest when the projection lens
functions as a prism and separates light into its component colors. Utilizing this
pattern, chromatic aberration is seen as a separation of red, green, and blue typically
toward the corners of the image area.
When used in the 16:9 format, the pattern shows the small circles in the extreme
corners of the test pattern. The 4:3 format version, if displayed on a 16:9 display in
the widescreen mode, shows the circles as being more egg-shaped. The centered
vertical line and horizontal line form a crosshair target indicating the exact center of
the image.
2. Safe Area (5%/10%)
Television receivers (typically CRT-based types) commonly extend the
image raster beyond the edges of the display, which is a practice called
overscanning.
Overscanning hides image nonlinearities and raster scan
artifacts as well as production test patterns typically hidden within the
last few lines of the vertical blanking interval.
The safe area pattern thus becomes a guide for the technicians in the television
production environment to show the likely amount of cropped display area on a
typical consumer television receiver. The outer rectangle indicates a 5% crop area,
which is the minimum amount of overscan for picture information. The inner
rectangle represents a 10% crop area and is referred to as the “safe title area”.
By maintaining all key action within the rectangle representing the 5% crop area,
the producer can guarantee that the viewer will be able to see all of the intended
information. By maintaining all titles inside the area bounded by the 10% safe area
marker, all text and titling will be seen by the viewer. The centered vertical line and
horizontal line form a crosshair target indicating the exact center of the image.
3. Focus
The focus test pattern tests the depth of field of the projector lens. Low
quality lenses do not display the corners of the test pattern with equal
sharpness to the center; or, the corners do not appear the same as the
center. The focus patches represent a combination of high frequency
detail (vertical lines) as compared to low frequency information (horizontal lines).
These patches should be equal in brightness and color hue when a video system has
an overall flat frequency response.
When high frequency response suffers significantly, the patches of vertical
alternating pixels blend toward a 50% gray level. Since the background is 50% gray,
the patches tend to disappear within the background. Comparing the patches to
the background assists in making this evaluation.
