Figure 41, Atmega16(l) – Rainbow Electronics ATmega64L User Manual
Page 89
89
ATmega16(L)
2466B–09/01
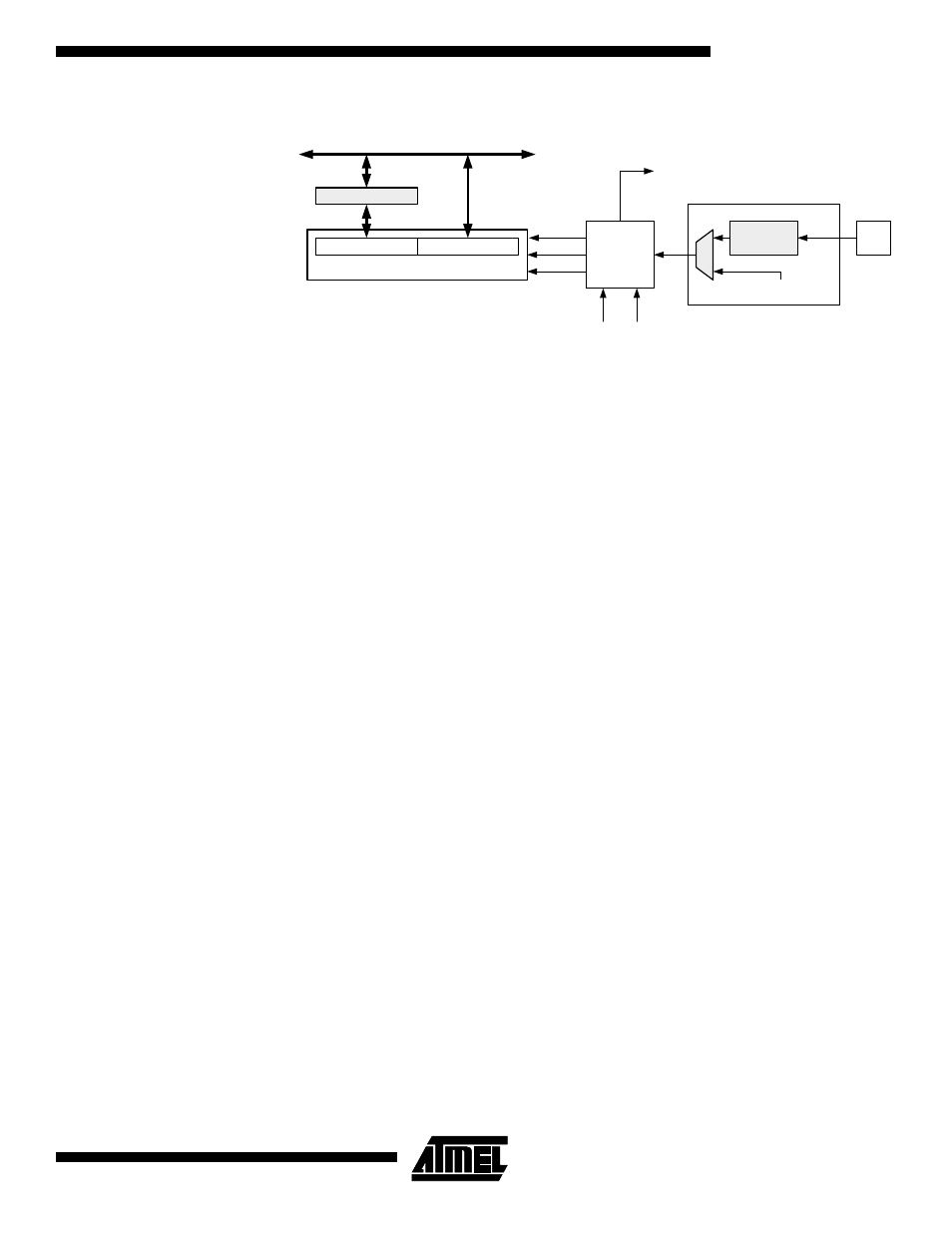
Figure 41. Counter Unit Block Diagram
Signal description (internal signals):
Count
Increment or decrement TCNT1 by 1.
Direction
Select between increment and decrement.
Clear
Clear TCNT1 (set all bits to zero).
clk
T
1
Timer/counter clock.
TOP
Signalize that TCNT1 has reached maximum value.
BOTTOM
Signalize that TCNT1 has reached minimum value (zero).
The 16-bit counter is mapped into two 8-bit I/O memory locations: counter high
(TCNT1H) containing the upper 8 bits of the counter, and counter low (TCNT1L) con-
taining the lower 8 bits. The TCNT1H register can only be indirectly accessed by the
CPU. When the CPU does an access to the TCNT1H I/O location, the CPU accesses
the high byte temporary register (TEMP). The temporary register is updated with the
TCNT1H value when the TCNT1L is read, and TCNT1H is updated with the temporary
register value when TCNT1L is written. This allows the CPU to read or write the entire
16-bit counter value within one clock cycle via the 8-bit data bus. It is important to notice
that there are special cases of writing to the TCNT1 register when the counter is count-
ing that will give unpredictable results. The special cases are described in the sections
where they are of importance.
Depending on the mode of operation used, the counter is cleared, incremented, or dec-
remented at each timer clock (clk
T
1
). The clk
T
1
can be generated from an external or
internal clock source, selected by the clock select bits (CS12:0). When no clock source
is selected (CS12:0 = 0) the timer is stopped. However, the TCNT1 value can be
accessed by the CPU, independent of whether clk
T
1
is present or not. A CPU write over-
rides (has priority over) all counter clear or count operations.
The counting sequence is determined by the setting of the waveform generation mode
bits (WGM13:0) located in the Timer/Counter control registers A and B (TCCR1A and
TCCR1B). There are close connections between how the counter behaves (counts) and
how waveforms are generated on the output compare outputs OC1x. For more details
about advanced counting sequences and waveform generation, see “Modes of Opera-
tion” on page 94.
The Timer/Counter overflow (TOV1) flag is set according to the mode of operation
selected by the WGM13:0 bits. TOV1 can be used for generating a CPU interrupt.
TEMP (8-bit)
DATABUS
(8-bit)
TCNTn (16-bit Counter)
TCNTnH (8-bit)
TCNTnL (8-bit)
Control Logic
Count
Clear
Direction
TOVn
(Int.Req.)
Clock Select
TOP
BOTTOM
Tn
Edge
Detector
( From Prescaler )
clk
Tn
