Atmega16 boundary- scan order, Atmega16(l) – Rainbow Electronics ATmega64L User Manual
Page 235
235
ATmega16(L)
2466B–09/01
ATmega16 Boundary-
scan Order
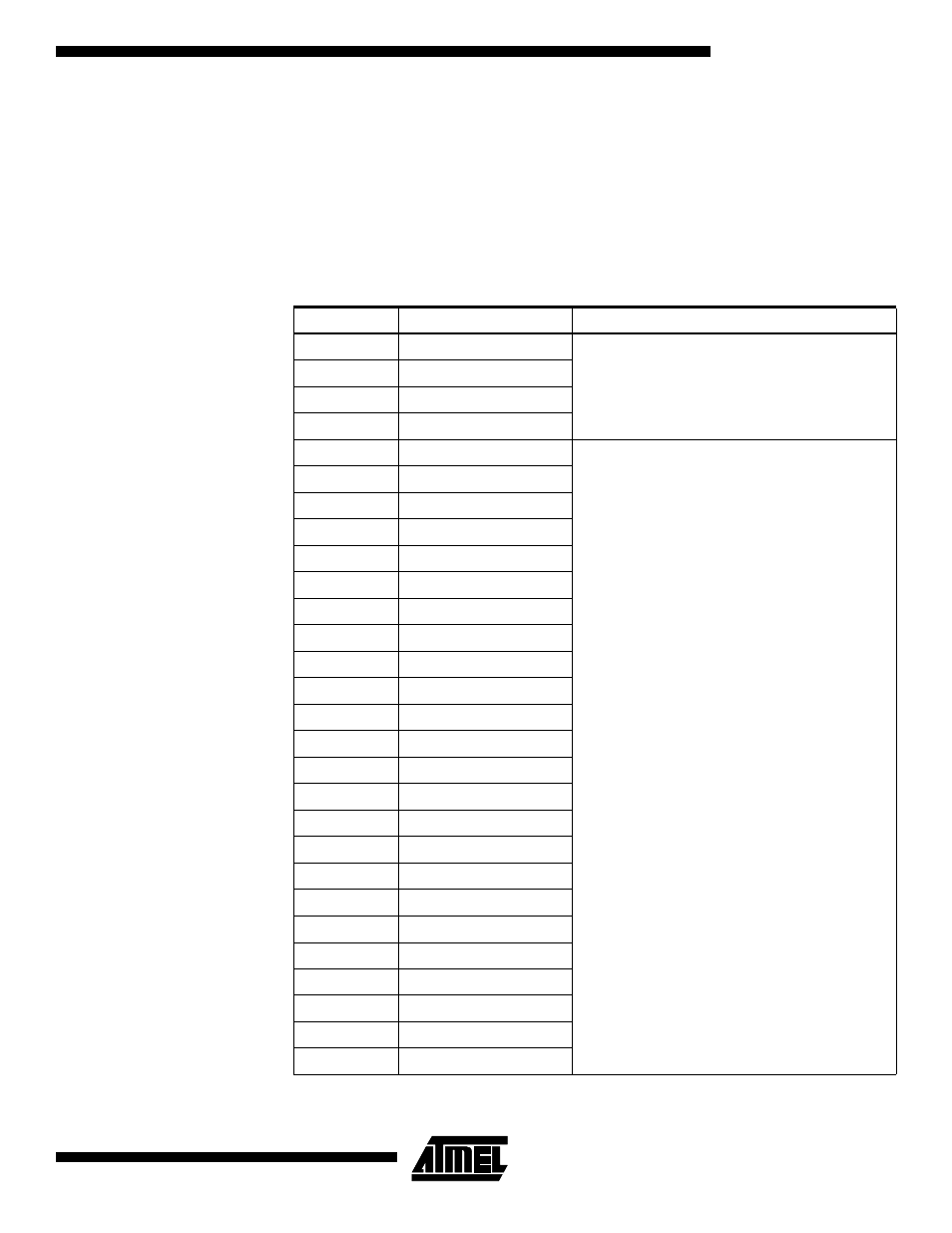
Table 94 shows the Scan order between TDI and TDO when the Boundary-scan chain
is selected as data path. Bit 0 is the LSB; the first bit scanned in, and the first bit
scanned out. The scan order follows the pin-out order as far as possible. Therefore, the
bits of Port A is scanned in the opposite bit order of the other ports. Exceptions from the
rules are the Scan chains for the analog circuits, which constitute the most significant
bits of the scan chain regardless of which physical pin they are connected to. In Figure
116, PXn. Data corresponds to FF0, PXn. Control corresponds to FF1, and PXn.
Pullup_enable corresponds to FF2. Bit 2, 3, 4, and 5 of Port C is not in the scan chain,
since these pins constitute the TAP pins when the JTAG is enabled.
Table 94. ATmega16 Boundary-scan Order
Bit Number
Signal Name
Module
140
AC_IDLE
Comparator
139
ACO
138
ACME
137
ACBG
136
COMP
ADC
135
PRIVATE_SIGNAL1
134
ACLK
133
ACTEN
132
ADHSM
131
ADCBGEN
130
ADCEN
129
AMPEN
128
DAC_9
127
DAC_8
126
DAC_7
125
DAC_6
124
DAC_5
123
DAC_4
122
DAC_3
121
DAC_2
120
DAC_1
119
DAC_0
118
EXTCH
117
G10
116
G20
115
GNDEN
114
HOLD
113
IREFEN
