Figure 8: general topology of a chopped amplifier, Figure 9: cross signal with chop_e = 00, Hown in – Rainbow Electronics 71M6542G User Manual
Page 21: Figure 8
v1.1
© 2008–2011 Teridian Semiconductor Corporation
21
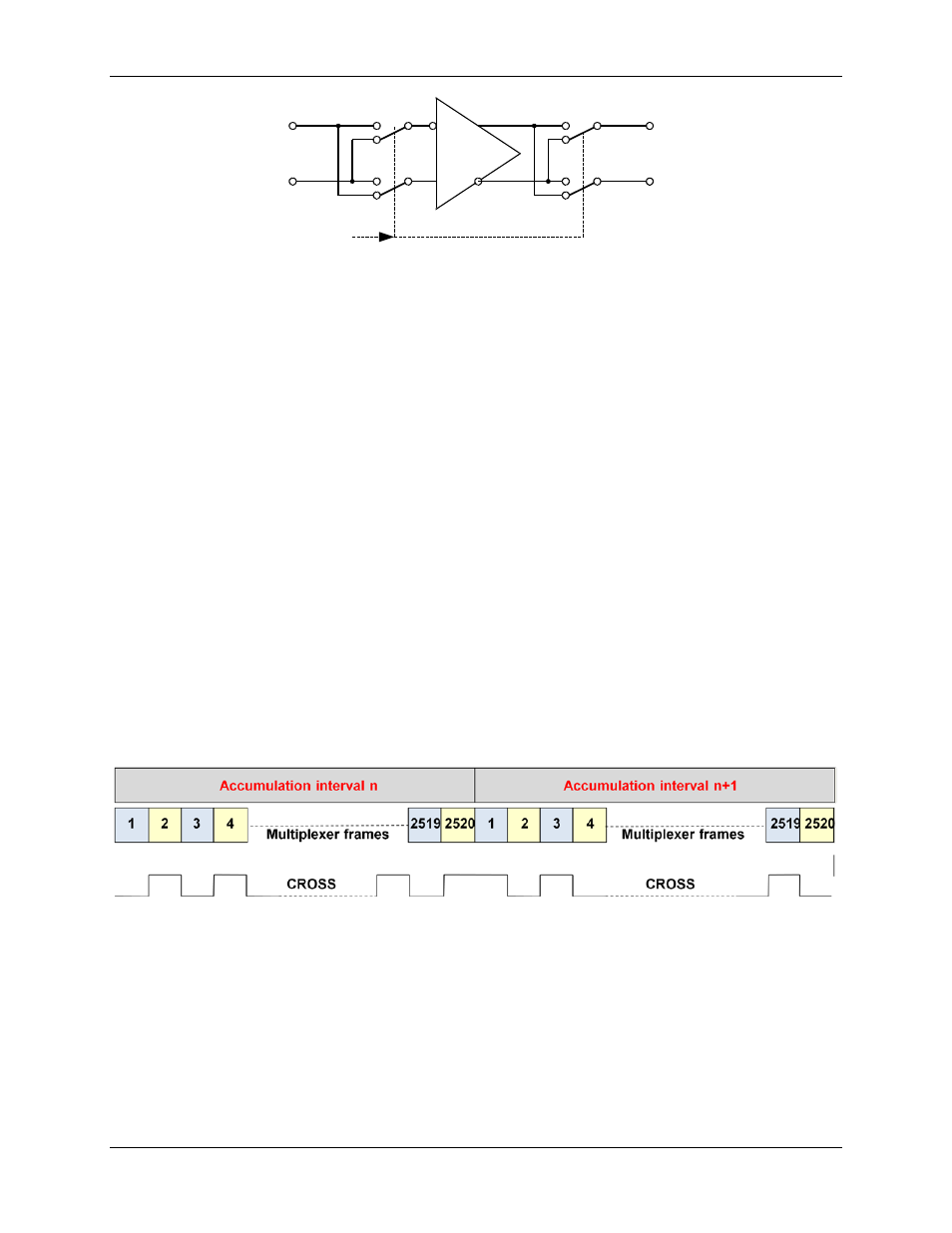
Figure 8: General Topology of a Chopped Amplifier
It is assumed that an offset voltage Voff appears at the positive amplifier input. With all switches, as
controlled by CROSS (an internal signal), in the A position, the output voltage is:
Voutp – Voutn = G (Vinp + Voff – Vinn) = G (Vinp – Vinn) + G Voff
With all switches set to the B position by applying the inverted CROSS signal, the output voltage is:
Voutn – Voutp = G (Vinn – Vinp + Voff) = G (Vinn – Vinp) + G Voff, or
Voutp – Voutn = G (Vinp – Vinn) - G Voff
Thus, when CROSS is toggled, e.g., after each multiplexer cycle, the offset alternately appears on the
output as positive and negative, which results in the offset effectively being eliminated, regardless of its
polarity or magnitude.
When CROSS is high, the connection of the amplifier input devices is reversed. This preserves the overall
polarity of that amplifier gain; it inverts its input offset. By alternately reversing the connection, the amplifier’s
offset is averaged to zero. This removes the most significant long-term drift mechanism in the voltage
reference. The CHOP_E[1:0] (I/O RAM 0x2106[3:2]) control field controls the behavior of CROSS. The
CROSS signal reverses the amplifier connection in the voltage reference in order to negate the effects of its
offset. On the first CK32 rising edge after the last multiplexer state of its sequence, the multiplexer waits
one additional CK32 cycle before beginning a new frame. At the beginning of this cycle, the value of
CROSS is updated according to the CHOP_E[1:0] field. The extra CK32 cycle allows time for the
chopped VREF to settle. During this cycle, MUXSYNC is held high. The leading edge of MUXSYNC initiates
a pass through the CE program sequence. The beginning of the sequence is the serial readout of the four
RTM words.
CHOP_E[1:0] has four states: positive, reverse, and two toggle states. In the positive state, CHOP_E[1:0]
= 01, CROSS is held low. In the reverse state, CHOP_E[1:0] = 10, CROSS is held high.
Figure 9: CROSS Signal with CHOP_E = 00
shows CROSS over two accumulation intervals when CHOP_E[1:0] = 00: At the end of the
first interval, CROSS is high, at the end of the second interval, CROSS is low. Operation with
CHOP_E[1:0] = 00 does not require control of the chopping mechanism by the MPU.
In the second toggle state, CHOP_E[1:0] = 11, CROSS does not toggle at the end of the last multiplexer
cycle in an accumulation interval.
A second, low-power voltage reference is used in the LCD system and for the comparators that support
transitions to and from the battery modes.
G
-
+
V
inp
V
outp
V
outn
V
inn
CROSS
A
B
A
B
A
B
A
B
