Self-programming the flash, Atmega8515(l) – Rainbow Electronics ATmega8515L User Manual
Page 168
168
ATmega8515(L)
2512A–AVR–04/02
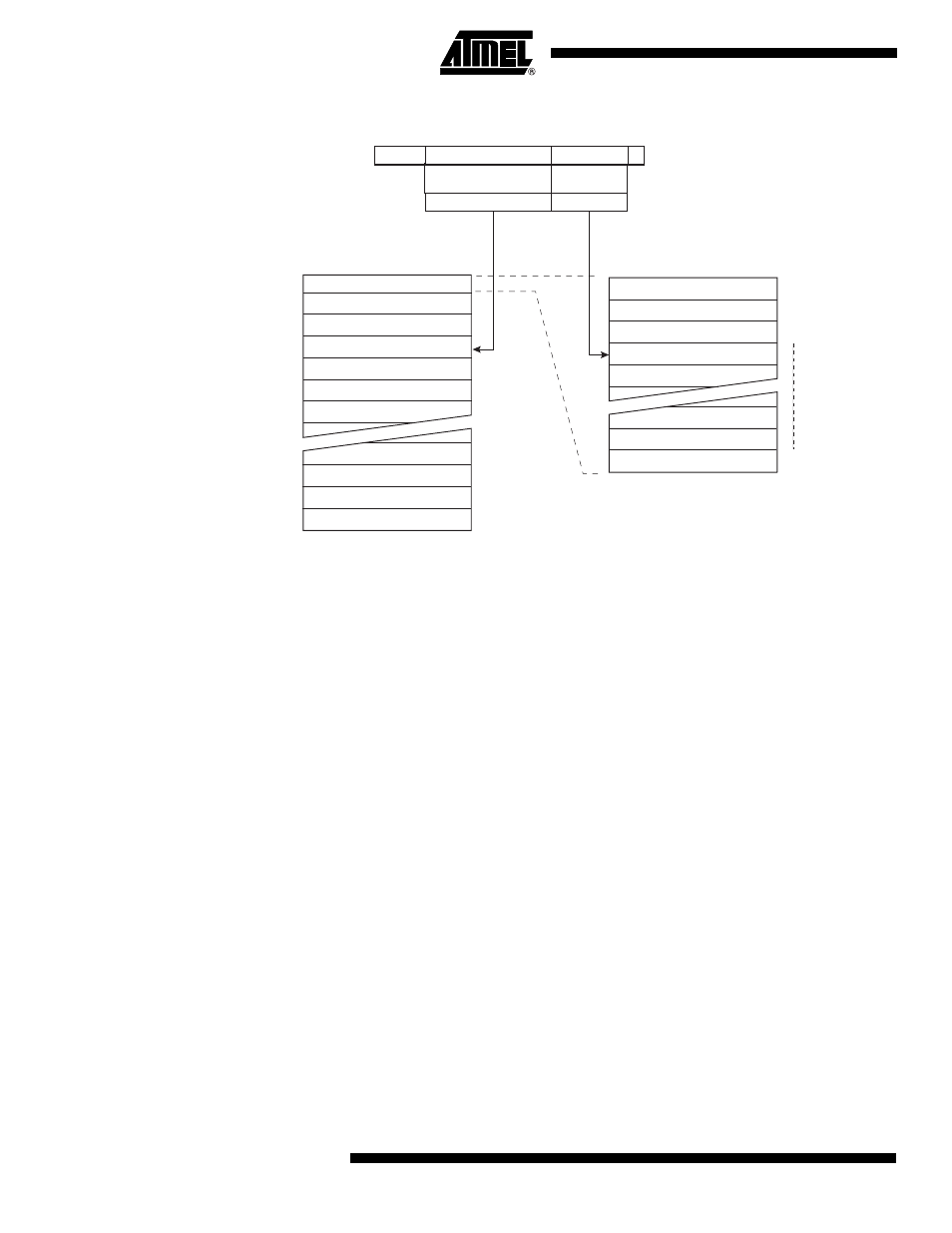
Figure 73. Addressing the Flash during SPM
Note:
1. The different variables used in Figure 73 are listed in Table 80 on page 174.
Self-Programming the
Flash
The program memory is updated in a page by page fashion. Before programming a
page with the data stored in the temporary page buffer, the page must be erased. The
temporary page buffer is filled one word at a time using SPM and the buffer can be filled
either before the page erase command or between a Page Erase and a Page Write
operation:
Alternative 1, fill the buffer before a Page Erase:
•
Fill temporary page buffer.
•
Perform a Page Erase.
•
Perform a Page Write.
Alternative 2, fill the buffer after Page Erase:
•
Perform a Page Erase.
•
Fill temporary page buffer.
•
Perform a Page Write.
If only a part of the page needs to be changed, the rest of the page must be stored (for
example in the temporary page buffer) before the erase, and then be rewritten. When
using alternative 1, the Boot Loader provides an effective Read-Modify-Write feature
which allows the user software to first read the page, do the necessary changes, and
then write back the modified data. If alternative 2 is used, it is not possible to read the
old data while loading since the page is already erased. The temporary page buffer can
be accessed in a random sequence. It is essential that the page address used in both
the Page Erase and Page Write operation is addressing the same page. See “Simple
Assembly Code Example for a Boot Loader” on page 171 for an assembly code
example.
PROGRAM MEMORY
0
1
15
Z - REGISTER
BIT
0
ZPAGEMSB
WORD ADDRESS
WITHIN A PAGE
PAGE ADDRESS
WITHIN THE FLASH
ZPCMSB
INSTRUCTION WORD
PAGE
PCWORD[PAGEMSB:0]:
00
01
02
PAGEEND
PAGE
PCWORD
PCPAGE
PCMSB
PAGEMSB
PROGRAM
COUNTER
