Eap relay, Relay – H3C Technologies H3C S6300 Series Switches User Manual
Page 82
67
EAP relay
shows the basic 802.1X authentication procedure in EAP relay mode, assuming that EAP-MD5
is used.
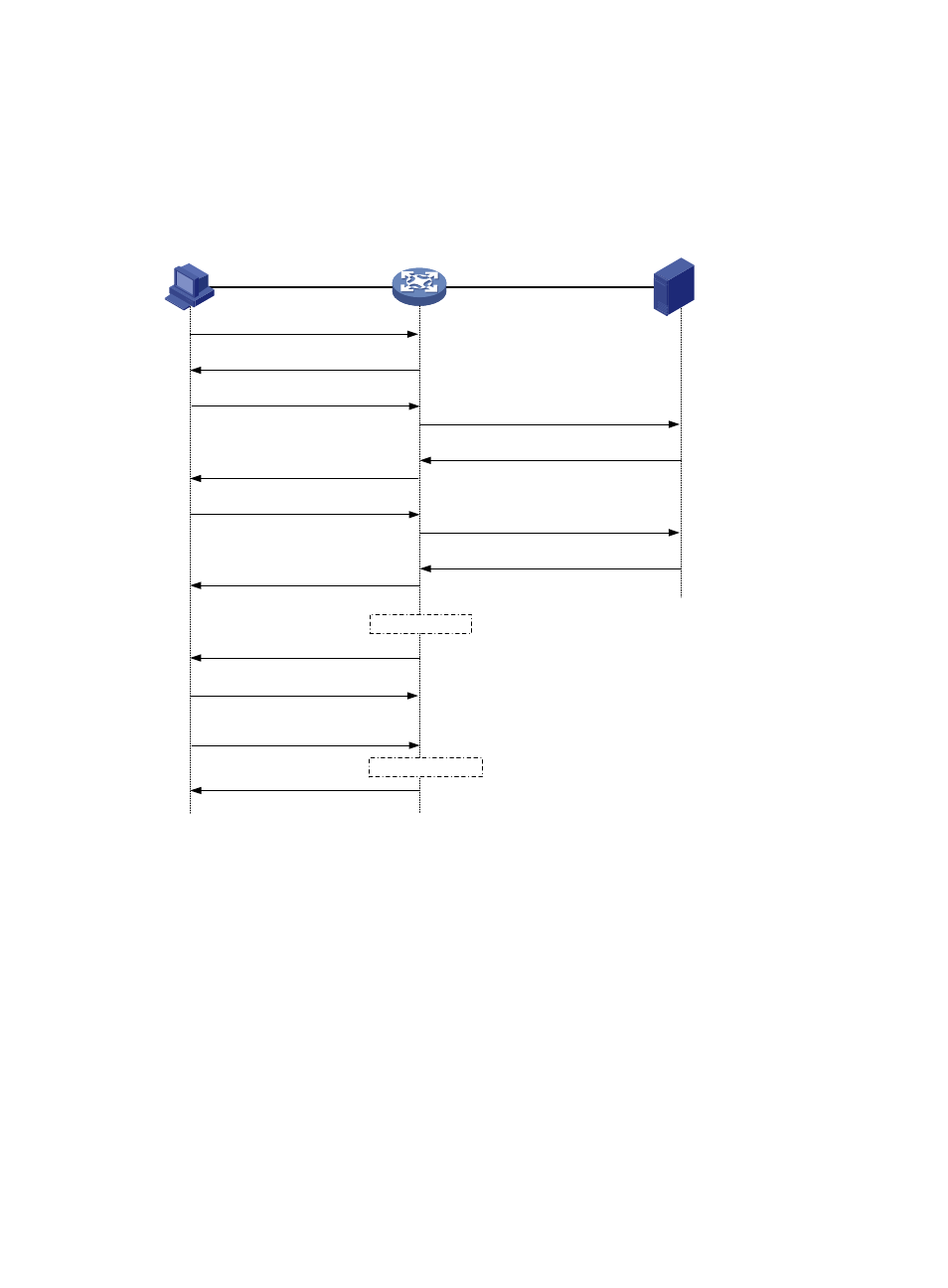
Figure 28 802.1X authentication procedure in EAP relay mode
1.
When a user launches the 802.1X client software and enters a registered username and password,
the 802.1X client software sends an EAPOL-Start packet to the network access device.
2.
The network access device responds with an Identity EAP-Request packet to ask for the client
username.
3.
In response to the Identity EAP-Request packet, the client sends the username in an Identity
EAP-Response packet to the network access device.
4.
The network access device relays the Identity EAP-Response packet in a RADIUS Access-Request
packet to the authentication server.
5.
The authentication server uses the identity information in the RADIUS Access-Request to search its
user database. If a matching entry is found, the server uses a randomly generated challenge
(EAP-Request/MD5 challenge) to encrypt the password in the entry, and sends the challenge in a
RADIUS Access-Challenge packet to the network access device.
6.
The network access device relays the EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge packet in a RADIUS
Access-Request packet to the client.
EAPOL
EAPOR
(1) EAPOL-Start
(2) EAP-Request/Identity
(3) EAP-Response/Identity
(6) EAP-Request/MD5 challenge
(10) EAP-Success
(7) EAP-Response/MD5 challenge
(4) RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response/Identity)
(5) RADIUS Access-Challenge
(EAP-Request/MD5 challenge)
(9) RADIUS Access-Accept
(EAP-Success)
(8) RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response/MD5 challenge)
(11) EAP-Request/Identity
(12) EAP-Response/Identity
(13) EAPOL-Logoff
...
Client
Device
Authentication server
Port authorized
Port unauthorized
(14) EAP-Failure
