Radius, Client/server model, Information exchange security mechanism – H3C Technologies H3C S6300 Series Switches User Manual
Page 17
2
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a distributed information interaction protocol that
uses a client/server model. The protocol can protect networks against unauthorized access and is often
used in network environments that require both high security and remote user access.
The RADIUS authorization process is combined with the RADIUS authentication process, and user
authorization information is piggybacked in authentication responses. RADIUS uses UDP port 1812 for
authentication and UDP port 1813 for accounting.
RADIUS was originally designed for dial-in user access, and has been extended to support additional
access methods, such as Ethernet and ADSL.
Client/server model
The RADIUS client runs on the NASs located throughout the network. It passes user information to
RADIUS servers and acts on the responses to, for example, reject or accept user access requests.
The RADIUS server runs on the computer or workstation at the network center and maintains information
related to user authentication and network service access.
The RADIUS server operates using the following process:
1.
Receives authentication, authorization, and accounting requests from RADIUS clients.
2.
Performs user authentication, authorization, or accounting.
3.
Returns user access control information (for example, rejecting or accepting the user access
request) to the clients.
The RADIUS server can also act as the client of another RADIUS server to provide authentication proxy
services.
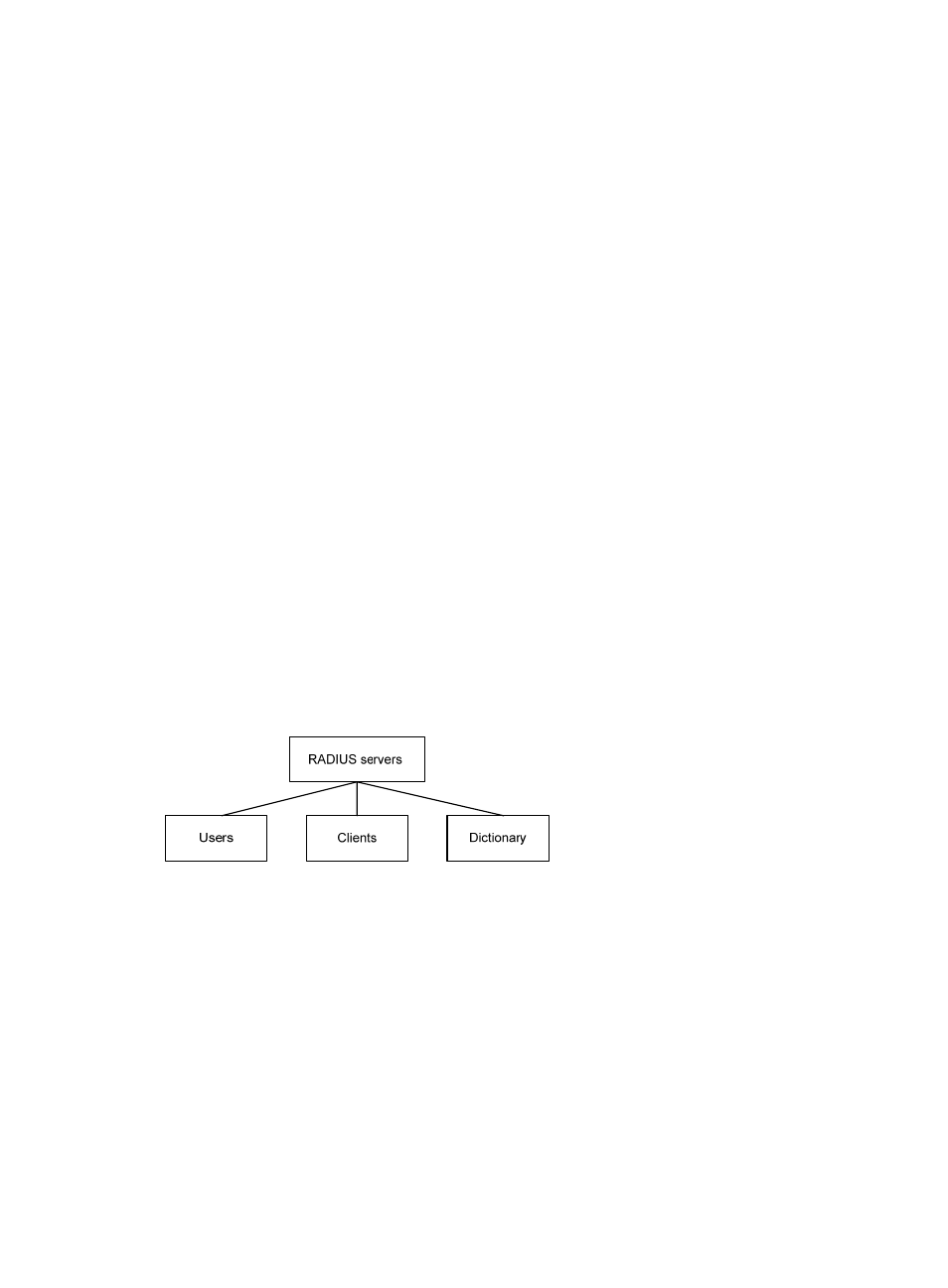
The RADIUS server maintains the following databases: Users, Clients, and Dictionary.
Figure 2 RADIUS server databases
•
Users—Stores user information, such as the usernames, passwords, applied protocols, and IP
addresses.
•
Clients—Stores information about RADIUS clients, such as shared keys and IP addresses.
•
Dictionary—Stores RADIUS protocol attributes and their values.
Information exchange security mechanism
The RADIUS client and server exchange information between them with the help of shared keys, which
are pre-configured on the client and server. A RADIUS packet has a 16-byte field called Authenticator.
This field includes a signature generated by using the MD5 algorithm, the shared key, and some other
information. The receiver of the packet verifies the signature and accepts the packet only when the
signature is correct. This mechanism ensures the security of information exchanged between the RADIUS
client and server.
The shared keys are also used to encrypt user passwords that are included in RADIUS packets.
