Intersecting-ring load balancing, Protocols and standards, N in – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 67: Figure
58
Figure 18 Schematic diagram for a single-ring load balancing network
Domain 1
Ring 1
Device A
Device B
Device D
Device C
Domain 2
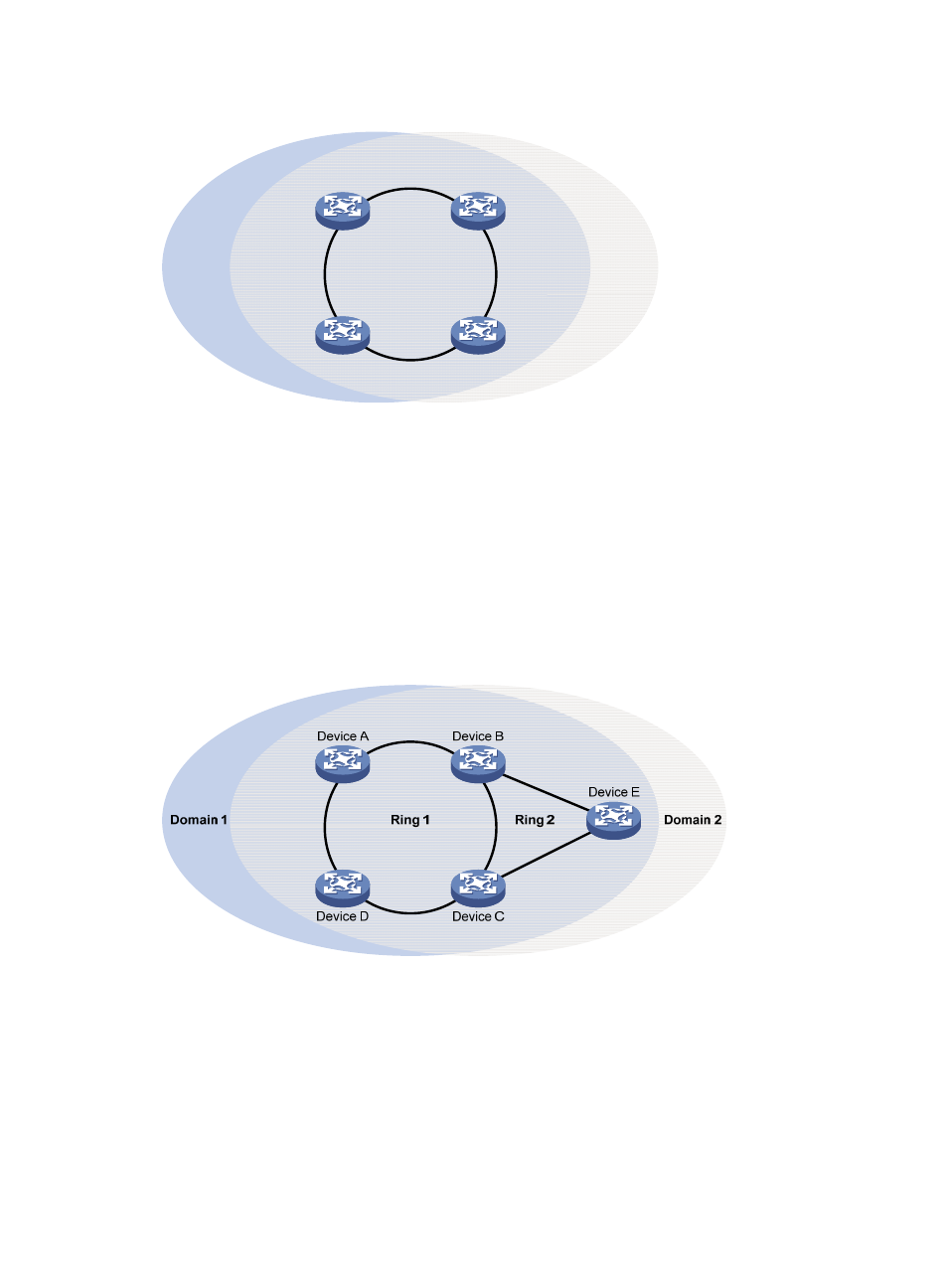
Intersecting-ring load balancing
In an intersecting-ring network, you can also achieve load balancing by configuring multiple domains.
As shown in
, Ring 1 is the primary ring, and Ring 2 is the subring in both Domain 1 and
Domain 2. Domain 1 and Domain 2 are configured with different protected VLANs. Device A is
configured as the master node of Ring 1 in Domain 1. Device D is configured as the master node of Ring
1 in Domain 2. Device E is configured as the master node of Ring 2 in both Domain 1 and Domain 2.
However, different ports on Device E are blocked in Domain 1 and Domain 2. With the configurations,
you can enable traffic of different VLANs to travel over different paths in the subring and primary ring to
achieve intersecting-ring load balancing.
Figure 19 Schematic diagram for an intersecting-ring load balancing network
Protocols and standards
RFC 3619 Extreme Networks' Ethernet Automatic Protection Switching (EAPS) Version 1 is related to
RRPP.
- H3C S5800 Series Switches H3C S5820X Series Switches H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches H3C SecPath F1000-E H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS
