Kipp&Zonen BSRN Scientific Solar Monitoring System User Manual
Page 133
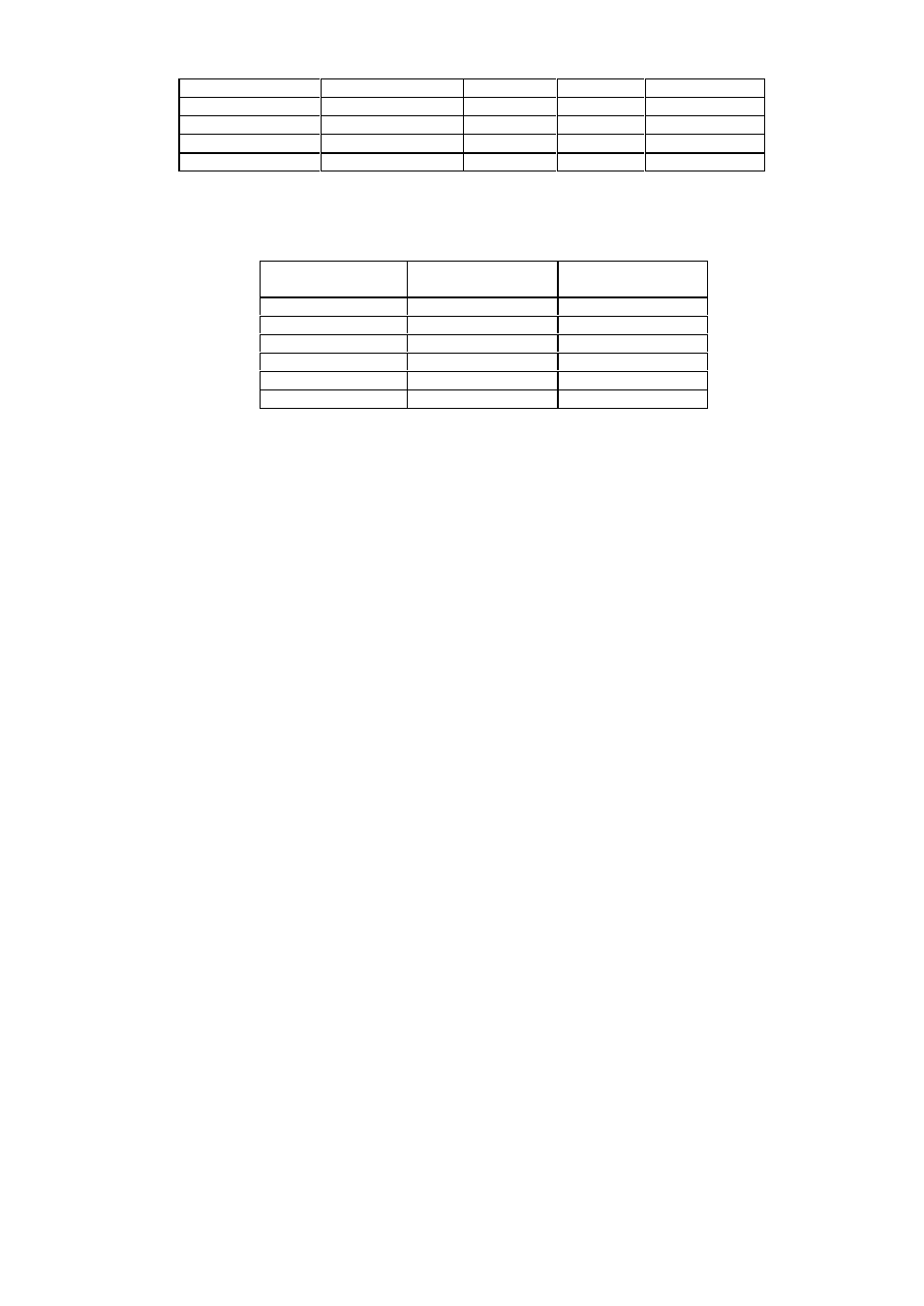
121
Pyrheliometer
Direct radiation
Circum 1
Circum 2
“Measured”
CRO3
770
2.92
7.74
780.7
ABS
770
3.05
8.04
781.1
KIPP
770
3.11
8.65
781.8
NIP
770
3.11
10.92
784.0
Table C 2.2b. Pyrheliom eter irradiances in W m
-2
CRO3 is the absolute pyrheliometer designed by D. Crommelynck. ABS is a group of absolute
pyrheliometers (HF, PMO5, etc), KIPP and NIP are thermoelectric station pyrheliometers
Instrum ent
Deficit
percent
Deficit
norm alized to HunIII
Austria
6.1
2.54
Germ any I
5.4
2.25
Germ any III
1.0
0.42
Hungary II
1.3
0.54
Hungary III
2.4
1.00
USA
1.0
0,42
Table C 2.3. Com parison to the standard group.
There exists a group of diffusom eters, the 4 m em bers of the group give sam e diffuse radiation value
according to the calculations, therefore it is suggested that this group could be regarded as geom etrical
standard of diffusom etry.
C 2.3.1
Intercalibration of pyranom eters
Kipp & Zonen CM5 pyranom eters were used. Their intercalibration were made for each m onth. In overcast
conditions the three diffusom eters should provide the sam e value, since then the circum solar effect
is quite negligible. The ratio of HunI/HunII and of HunI/HunIII have different standard deviation, nam ely
0.011 and 0.006. This m eans that the “m iddle” pyranom eter is m ore uncertain than the other two. This
was recognized during the data processing, so the change of the uncertain pyranom eter could not
be m ade. It is lucky, that not the other pyranom eters were problem atic.
C 2.3.2
Dependence of ratios of m easured diffuse radiation values on other param eters
For the whole data series the HunI/HunII and HunI/HunIII ratios had been calculated and their connection
to other radiation m easurem ents were looked for. A special “dem onstration sam ple” of
50 observations has been selected to present here the relations. In this sam ple the cases of high direct
radiation are over-represented.
Figure C 2.4 shows the connection between the ratio and the diffuse radiation itself. The upgoing part
of the plot is the clear weather part. Figure C 2.5 shows the connections with the direct radiation. The
highest ratios belong to the clearest atm ospheric situations. The dependence on the diffuse per global
ratio is seen in Figure C 2.6.
To estim ate the deviation from the standard, the following type of equation is suggested:
H u n III
RATIO
= a + b/(X-c)
W here
a, b,c = regression param eters,
X
= either the direct radiation or the diffuse/global ratio.
For the direct radiation
a = 0.98621
b = - 14.9824
c = 1086.5
For the diffuse/global ratio a = 0.99419
b = 0.00537
c = -0.07553.
