To identify a faulty rmc module – Cub Cadet 2000 Series User Manual
Page 103
Electrical System
97
To identify a faulty RMC module:
If the RMC module does not function as described, the
RMC plug test should be the first step in diagnosis.
• If the RMC plug test confirms that the safety cir-
cuits (inputs) work as designed, yet the RMC mod-
ule does not work properly, the RMC module is
faulty.
• The RMC plug test will give an indication of what
the problem is if it is not a faulty RMC module. If
the problem is identified in a particular circuit,
check the safety switch that is associated with that
circuit. If the switch is good, then the problem lies
within the wiring harness.
NOTE: Like the electronic components found on most
cars, the RMC module requires a fully charged
battery to work properly. If the system voltage falls
below 12 V, an accurate diagnosis of the RMC
module is impossible because the module will be
temporarily disabled by low voltage.
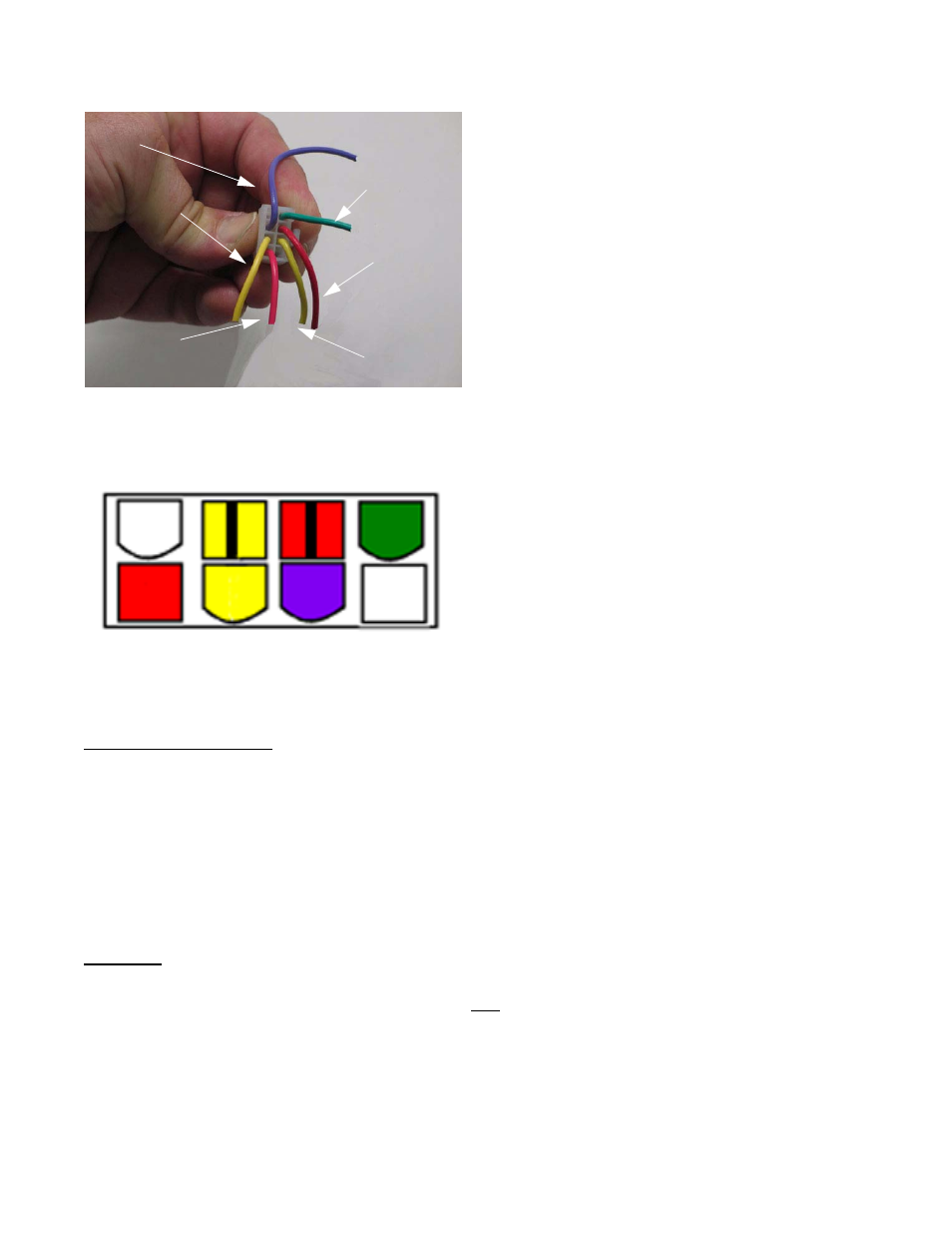
1. Disconnect the molded 8-pin plug from the RMC mod-
ule. See Figure 7.5.
2.
Looking at the plug head-on, it will be configured as
shown in the diagram: There will be 8 female pin ter-
minals. When probed, they should yield the results
described in the following sections. See Figure 7.5.
3.
Check the PTO and seat safety circuits with the 8-pin
pigtail connector unplugged, then reconnect it and
continue with the RMC plug test.
Yellow wire with black trace
•
Behavior: When the female pin terminal leading into the main harness is probed (yellow wire with black
trace), it should show DC power with the key on and the PTO switch off.
•
Circuitry: The yellow wire with a black trace is the ground side of the PTO relay coil. It splits with one lead
going to the PTO switch and the other going to the RMC module.
•
If there is continuity to ground when the PTO is OFF, the switch may be inoperative or there may be a
short to ground in the wire leading to it. If there is not continuity to ground when the PTO switch is ON, the
PTO switch may be inoperative, or there may be an open condition in the wire that leads to it.
•
Interpretation: If behavior is correct, the N.C. side of the PTO switch /circuit is functioning properly
Yellow wire
•
Behavior: When the female pin terminal leading into the main harness is probed (yellow wire), there
should be continuity to ground only when the seat is empty.
•
Circuitry: The yellow wire with white trace leads to the seat safety switch, where it finds a path to ground
when the seat is empty.
•
Interpretation: If behavior is correct, the seat safety circuit is good. If there is continuity to ground when
the seat is occupied, the switch may be inoperative, or there may be a short to ground in the wire leading
to it. If there is not continuity to ground when the seat is empty, the switch may be inoperative or there may
be an open condition in the wire leading to it.
Figure 7.5
Purple
Yellow/White
Red
Green
Red/Black
Yellow/Black
Figure 7.5
