Stick welding problems – Tweco 400 MST Arc Master User Manual
Page 31
400MST
6
BASIC TROUBLE SHOOTING
6 – 4
4
Stick Welding Problems
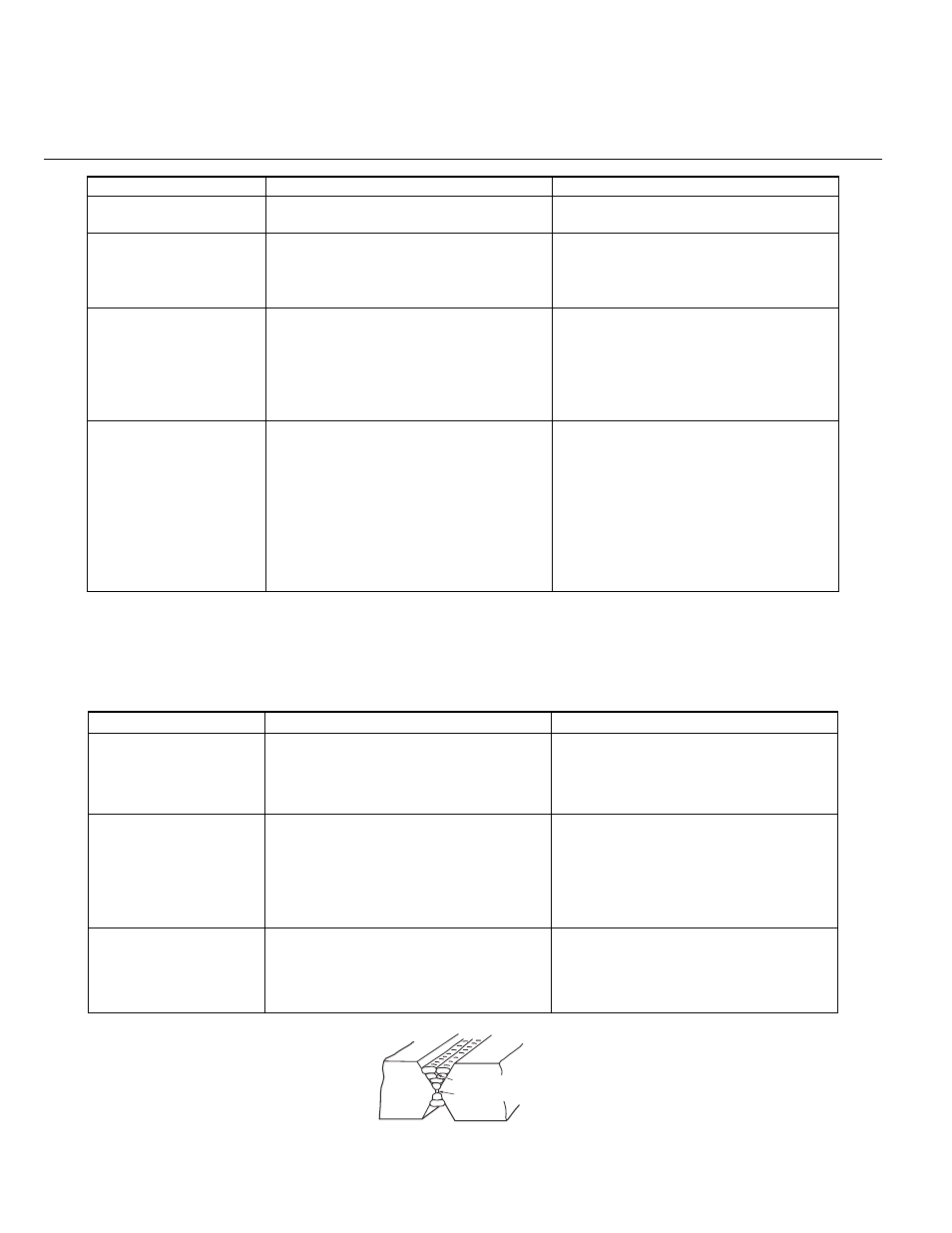
Figure 6-1: Example of insufficient gap or incorrect sequence
9 Poor weld finish.
Inadequate shielding gas.
Increase gas flow or check gas line for gas
flow problems.
10 Arc flutters during TIG
welding.
A Tungsten electrode is too large for the
welding current.
B Absence of oxides in the weld pool.
A Select the right size electrode. Refer to
Basic TIG Welding guide.
B Refer Basic TIG Welding Guide for ways
to reduce arc flutter.
11 Welding arc can not be
established.
A Work clamp is not connected to the work
piece or the work/torch leads are not
connected to the right welding terminals.
B Torch lead is disconnected.
C Gas flow incorrectly set, cylinder empty
or the torch valve is off.
A Connect the work clamp to the work
piece or connect the work/torch leads to
the right welding terminals.
B Connect it to the '-' terminal.
C Select the right flow rate, change
cylinders or turn torch valve on.
12 Arc start is not smooth. A Tungsten electrode is too large for the
welding current.
B The wrong electrode is being used for the
welding job.
C Gas flow rate is too high.
D Incorrect shielding gas is being used.
E Poor work clamp connection to work
piece.
A Select the right size electrode. Refer to
Basic TIG Welding Guide.
B Select the right electrode type. Refer to
Basic TIG Welding Guide.
C Select the correct rate for the welding job.
Refer to Basic TIG Welding Guide.
D Select the right shielding gas. Refer to
Basic TIG Welding Guide.
E Improve connection to work piece.
Description
Possible Cause
Remedy
Description
Possible Cause
Remedy
1 Gas pockets or voids in
weld metal (Porosity).
A Electrodes are damp.
B Welding current is too high.
C Surface impurities such as oil, grease,
paint, etc.
A Dry electrodes before use.
B Reduce welding current.
C Clean joint before welding.
2 Crack occurring in weld
metal soon after
solidification
commences.
A Rigidity of joint.
B Insufficient throat thickness.
C Cooling rate is too high.
A Redesign to relieve weld joint of severe
stresses or use crack resistance
electrodes.
B Travel slightly slower to allow greater
build up in throat.
C Preheat plate and cool slowly.
3 A gap is left by failure
of the weld metal to fill
the root of the weld.
A Welding current is too low.
B Electrode too large for joint.
C Insufficient gap.
D Incorrect sequence.
A Increase welding current.
B Use smaller diameter electrode.
C Allow wider gap.
D Use correct build-up sequence.
Incorrect sequence
Insufficient gap
