9 validation tools, Validation tools, 9validation tools – Metrohm NIRS XDS Transmission OptiProbe Analyzer User Manual
Page 79
▪▪▪▪▪▪▪
77
9
Validation Tools
Validation is an overriding concern in the pharmaceutical marketplace. In the United States,
manufacturers must follow Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations, also known as CFR 21. Each
country has its own regulations or has adopted a set from another source; therefore, the requirement
for validation is worldwide.
The requirements are very detailed, and will not be recounted here. For every instrument used to
measure, qualify, or release materials at any stage of the pharmaceutical manufacturing process,
there must be a thorough validation package to support it. This is an onerous but necessary task.
In the chemical and polymer industries there is a heightened awareness of Q9000, often referred to
as ISO9000. This regulation is similar in scope and intent to CFR 21, but has not been uniformly
enforced with analytical instrumentation. There are many reasons for this, including assessor
familiarity with NIR instrumentation. However, the enforcement is beginning to be applied more
commonly.
In summary, validation is or will be the concern of every analytical instrument user, sooner or later.
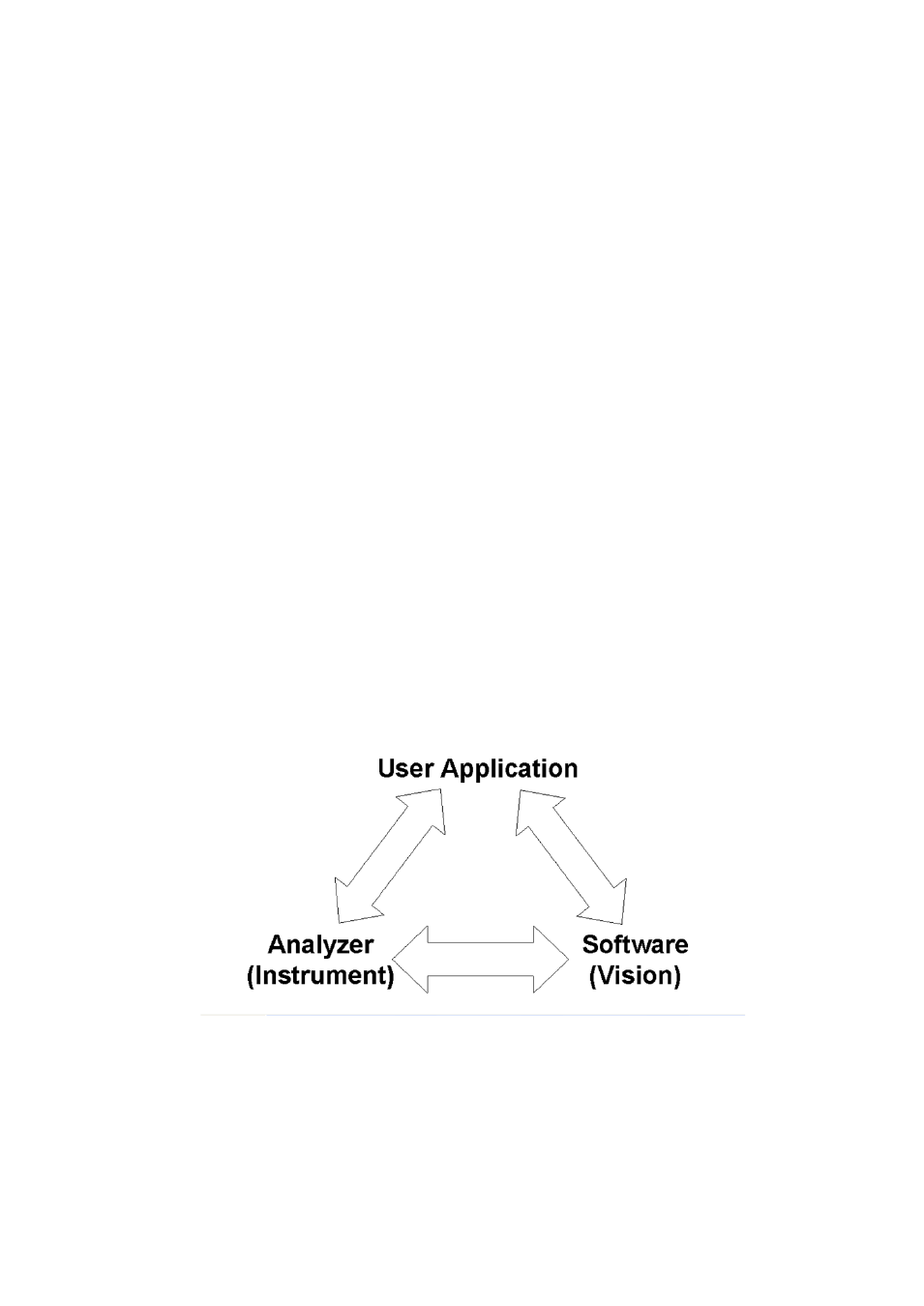
Validation is generally broken down into three categories:
•
Hardware (Analyzer and sampling accessories)
•
Software (Vision Spectral Analysis Software)
•
User Application (Customer samples, limits detection, range of calibration set, calibration
precision, and other factors.)
Users have requested specific tools and techniques to achieve validation. Metrohm has provided the
following tools to assist and expedite the task. Each item is described.
Successful validation must include all three elements: The Analyzer, Vision Software, and the User
Application.
