Care and use manual, Short elution gradient 2.1 x 50 mm, Iv. typical chromatographic conditions – Waters XBridge Direct Connect HP 2.1 x 30 mm Column for Automated Sample Preparation with Waters UPLC with Online SPE Technology User Manual
Page 2
[ Care and Use ManUal ]
XBridge Direct Connect HP 2.1 x 30 mm Column
2
IV. TyPICAl CHROmATOgRAPHIC CONDITIONS
The analytical process begins with loading a sample on to the
XBridge Direct Connect extraction column (Extraction Column A)
via the SPE injector port (valve A). The loading pump (QSM) using
100% aqueous mobile phase (with or without additives) at a flow
rate of 2 mL/min moves the sample from the injection loop on to
extraction column A. During the loading step, analytes of interest
will be trapped on the extraction column, while un-retained inter-
ferences will be discarded to waste. After completing the loading
step, the extraction column is washed to remove mildly retained
interferences. After the wash step, the trapped analytes on extrac-
tion column A are eluted with a gradient from the ACQUITY BSM on
to a UPLC analytical column for peak re-focusing. During the elution
step of extraction column A, extraction column B is regenerated
then re-equilibrated (using the QSM) to original conditions for the
next analysis. The events on each of the parallel extraction columns
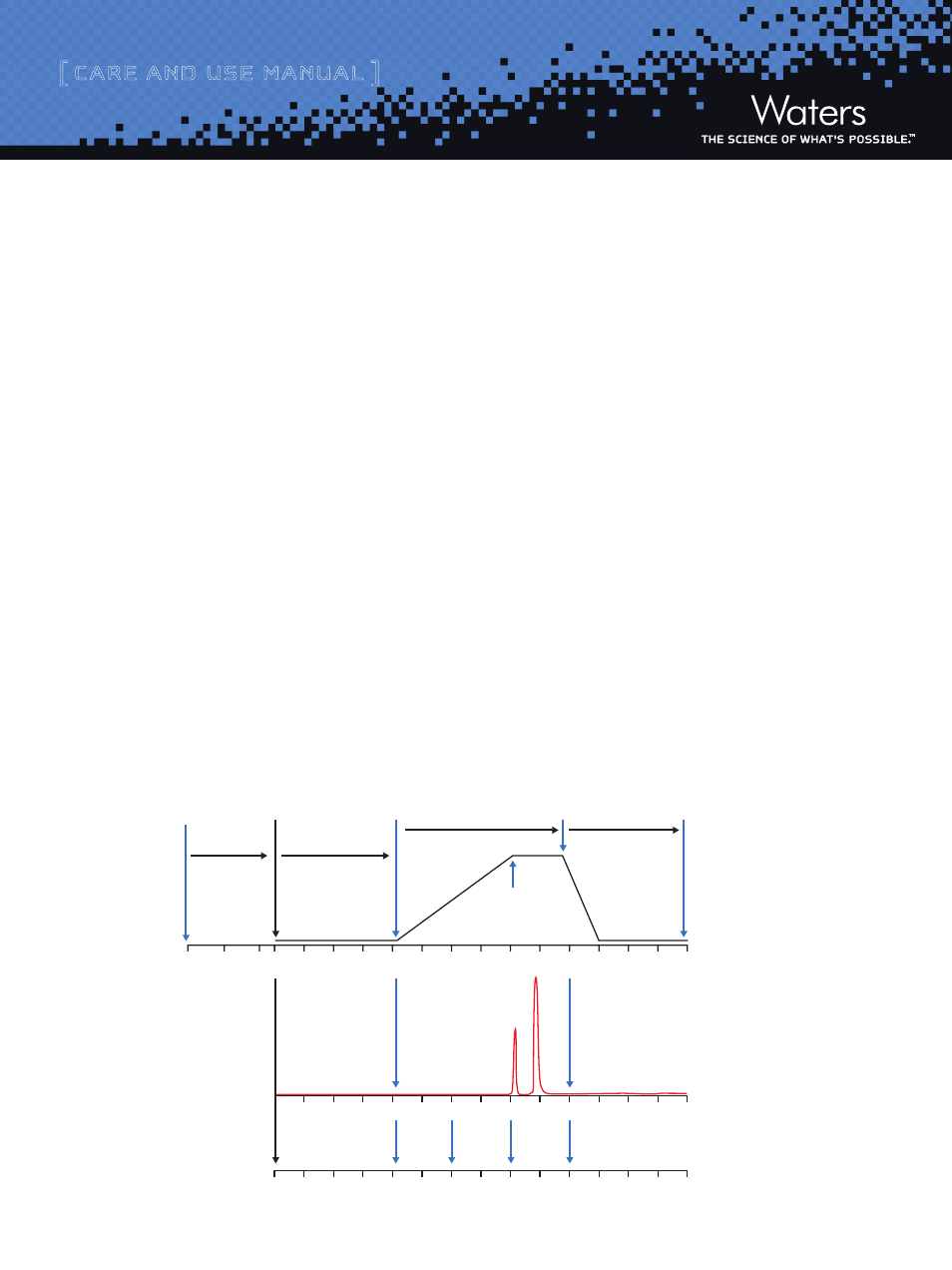
are shown in Figure 2.
Typical mobile phase conditions to use for the load, wash and elution
of the XBridge Direct Connect HP 2.1 x 30 mm column will depend
on the analytes of interest. The pH of the mobile phase will affect
the retention behavior of analytes.
For a typical application consisting primarily of basic compounds,
such as the analysis of pharmaceuticals in water, a loading condi-
tion using a high pH aqueous mobile phase would usually provide
good retention of the analytes of interest. An example of this type
of loading mobile phase is 2% ammonium hydroxide in water,
pH 10. To wash mildly retained interferences from the extraction
column without eluting the compounds of interest the percentage
of organic in the mobile phase can be increased without changing
the pH. For the example of basic pharmaceuticals in water, the wash
could be set at 20% methanol with 2% ammonium hydroxide.
Once the wash is completed, the next phase is the elution of the
trapped analyte from the extraction column on to the analytical
column. A suitable mobile phase for the example of basic pharma-
ceuticals is a gradient elution using 20 mM ammonium formate in
water, pH 3.2 for solvent A and 50/50 methanol/acetone with 20
mM ammonium formate, pH 3.2 for solvent B.
Figure 2: Timeline showing the events occurring on each of the extraction columns during an online SPE UPLC analysis
6
Time
Time
Time
5
4
3
2
1
0
-2
-4
-6
Acquisition
Start
Loading
SPE
wash
Flush
Flush
Re-equilibration
Recon.
5%
95%
SPE A
SPE B
Elution
Re-equilibration
6
5
4
4.04
4.36
3
2
1
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Short Elution Gradient
2.1 x 50 mm
