Care and use manual – Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler User Manual
Page 9
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
c. Appendix C: Measuring Breakthrough
Note: If several aldehydes and ketones are present in significant
concentration, estimate the maximum sample size from the total
concentration of all species. Collection efficiency determinations
are best made during times expected to yield peak formaldehyde
concentrations. This will enable appropriate sampling rates and
intervals to be selected to avoid breakthrough.
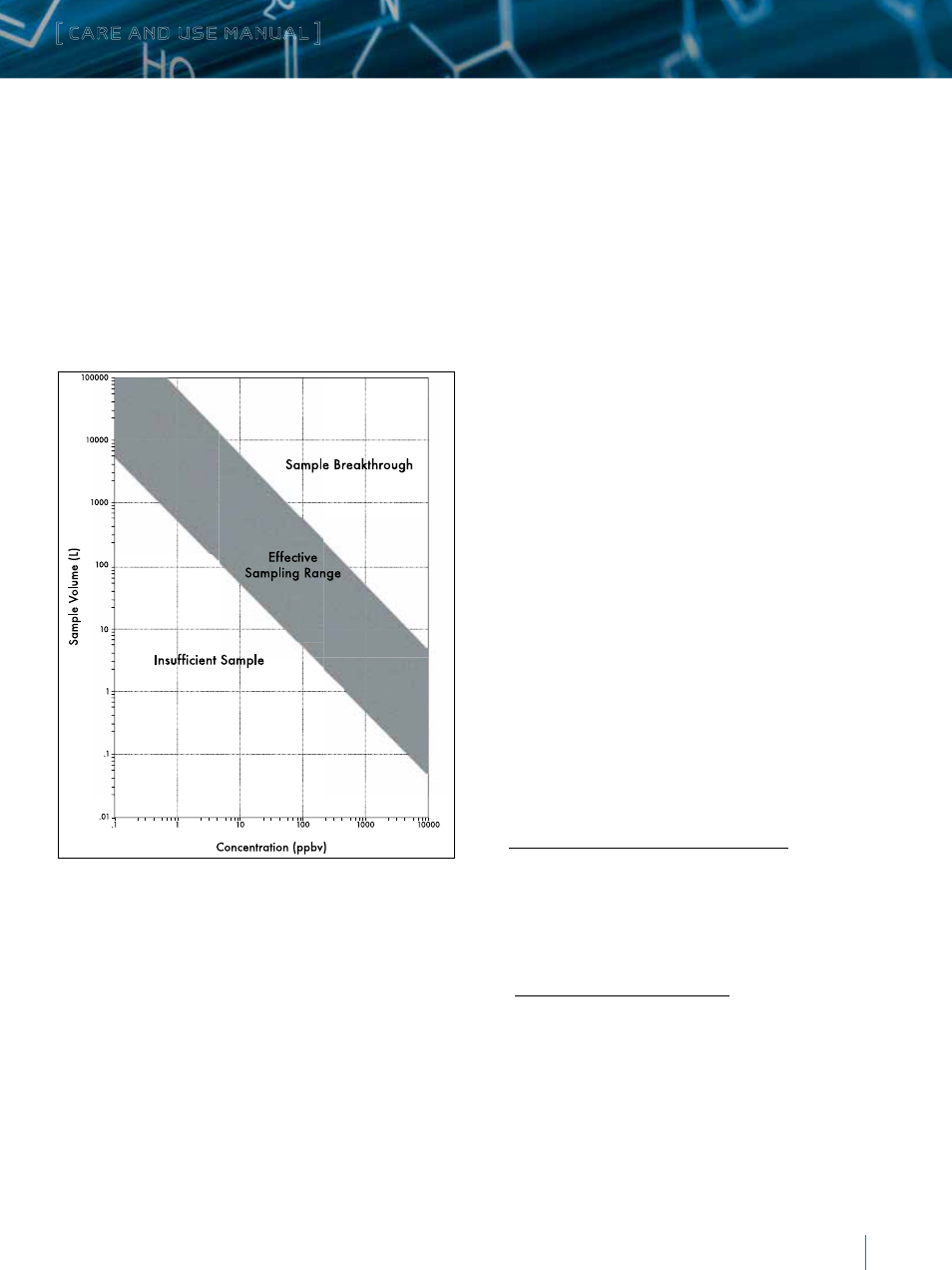
Figure 8 shows the predicted total carbonyl concentration versus
the range of sample volumes.
Figure 8. Total Carbonyl Concentration vs. Range of Sample Volumes.
Collection efficiency for Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde
Sampler is greater than 95% for air sampling rates of up to
1.5 L/min. The sampler may exhibit breakthrough if:
■
■
The sampling flow rate is greater than 1.5 L/min
■
■
The amount of sample collected is enough to react with
more than 50% of the DNPH (~2.3 µmoles)
To measure Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler for
collection efficiency:
1. Connect two unused cartridges together by the Luer fittings
and mark each cartridge for identification.
2. Connect the cartridges to a calibrated pump with a short
length of flexible tubing.
3. Collect the sample.
4. Elute both cartridges and a third blank cartridge.
5. Analyze all three cartridges by HPLC.
6. Subtract the blank value from the values determined from the
other two cartridges.
7. Calculate and sum of the total captured DNPH-derivative from
both cartridges.
8. Divide the amount of DNPH-derivative determined from
the first cartridge by the total amount determined form
cartridges 1 and 2. Multiply by 100. This is the percentage of
DNPH-derivatives captured on the first cartridge. This value
should exceed 95%; otherwise, some of the sample broke
through to the second cartridge.
Example: Measuring Sample Breakthrough
The expected concentration of formaldehyde is 0.66 ppmv (µL/L).
Flow rate is 1.25 L/min for 80 minutes. A sample volume of 100
liters is collected. The theoretical quantity of carbonyl is:
Analyte ppmv Carbonyl Collected
concentration x molecular x air volume = µg Carbonyl
weight
Analyte molar volume at 1 atm/25 °C
This calculates to:
0.66 µL x 30.03 g/mole x 100 L = 81 µg formaldehyde
24.46 L/mole
The actual results are shown in Table 7. To calculate the percent
captured on the first sampler, divide the quantity captured on
sampler 1 by the total quantity captured, then multiply by 100.
Since this value is less than 95%, and the total carbonyl amount
exceeded 2.3 µmoles, breakthrough occurred.
9
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
