Care and use manual, D. eluting the derivatives from the sampler, Use hplc-grade water and hplc-grade acetonitrile – Waters Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler User Manual
Page 4: Waters symmetry, Sep-pak xposure aldehyde sampler
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
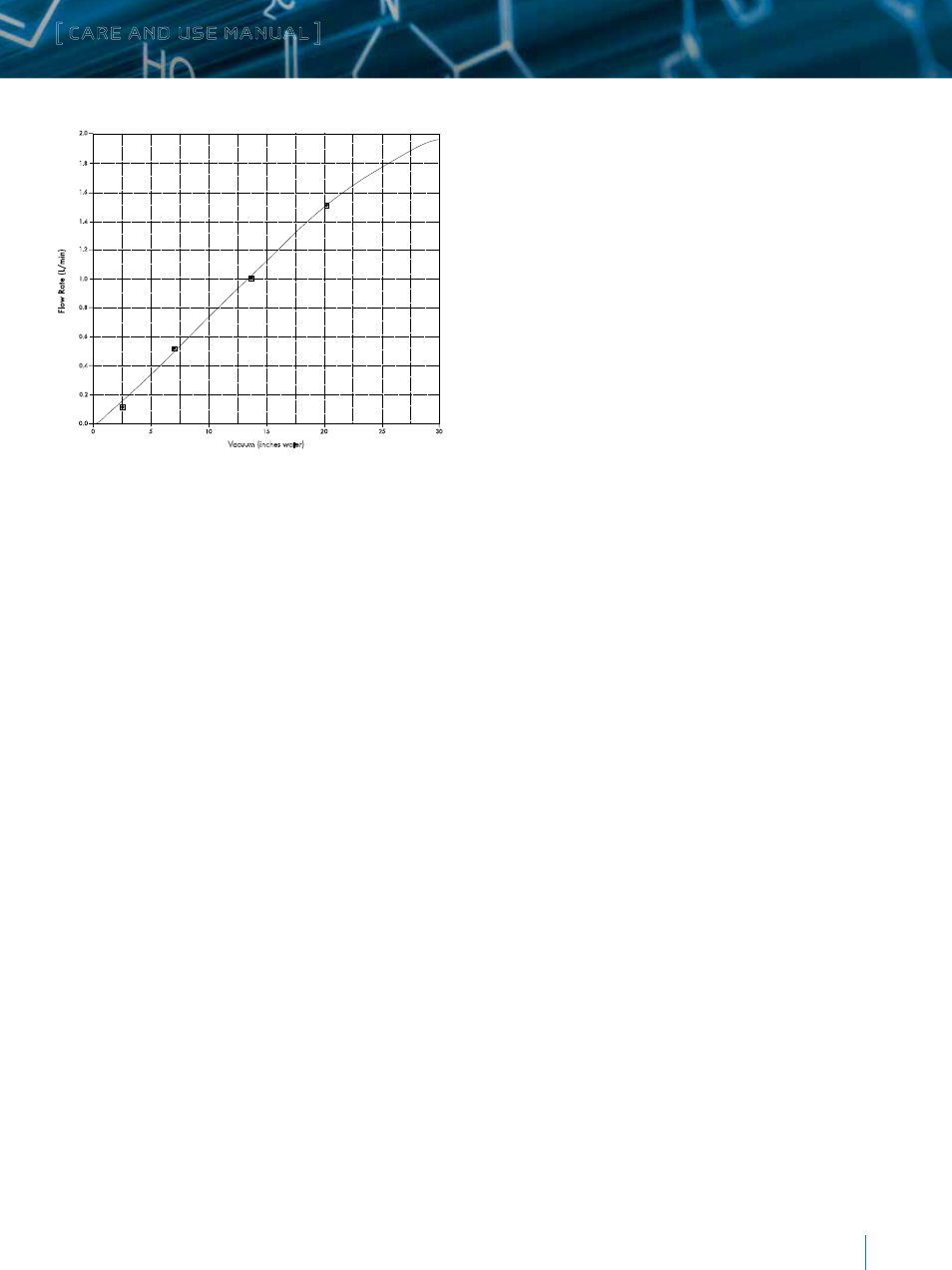
Figure 3: Typical Sampler Backpressure Profile.
Sample Collection – PEL (0.01 to 1.0 ppmv)
To collect the PEL air sample:
1. Calibrate the sampling pump with a representative sampler in
line. Set the flow to 100 mL/min. Figure 3 shows the flow rate
through a sampler versus applied vacuum. Once calibrated,
remove and store this representative sampler for future
calibrations.
2. Take a fresh sample from its pouch. Remove and save the end
cap and plugs.
3. Connect the sampler to a pump with flexible plastic tubing. The
sampler is bidirectional (flow can be in either direction).
4. Draw air for 8 hours, yielding a sample volume of 48 liters.
5. Reseal the sampler with its end cap and plug.
6. Store the sampler in the pouch provided with appropriate
identification. Seal the pouch by folding the edge over twice
and stapling it shut. Avoid exposing the samplers to heat.
A 48 L air sample is sufficient for quantifying formaldehyde in the
range of 0.01 to 1 ppmv. Formaldehyde concentrations lower than
0.01 ppmv in air will require longer sampling times and a larger
air sample. Conversely, formaldehyde concentrations that exceed
1.0 ppmv will require shorter sampling times or reduced sampling
flow rates in order to avoid overloading the sampler and obtaining
nonlinear results.
Note: The maximum recommended sampler capacity is 2.3 µmoles
total carbonyl species. This calculates to 50% of the DNPH consumed.
Contaminated air may contain significant concentrations of other
aldehydes and ketones and the total may exceed the capacity
of the sampling device. Follow the procedure in Appendix C,
Measuring Breakthrough for more information.
d. Eluting the Derivatives from the Sampler
To elute the derivatives from the sampler:
1. Remove the sampler from the stapled pouch.
2. Elute the DNPH derivatives from the sampler with pre-qualified
acetonitrile directly into a 10 mL volumetric flask. Use a flow
rate of <3 mL/min. Higher flow rates (>3 mL/min) can result in
reduced recovery.
3. Cap the volumetric flask and mix by inverting it several times.
4. Analyze the eluate using HPLC.
Note: Since background levels may change during storage, always
compare samples to a blank sampler from the same lot, stored
under the same conditions.
III. ANALYZING T HE DNPH DERIVATIV ES
a. Operating Guidelines
To ensure success in your HPLC analysis:
■
■
Use a pre-column filter between the injector and column.
■
■
Use HPLC-grade water and HPLC-grade acetonitrile.
■
■
Degas the mobile phases by simultaneously applying
vacuum and ultrasound to the mobile phases for 30 seconds.
If you are using a low-pressure mixing gradient system,
sparging with helium may be necessary.
■
■
Waters Symmetry
®
C
18
columns are shipped containing
water/acetonitrile. Before the first analysis, equilibrate the
column with mobile phase at 1.3 mL/min for 10 minutes in
mobile phase or until the baseline is stable. See Table 4 for
separation conditions.
Vacuum (inches water)
25
30
5
15
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
4
[ CARE AND USE MANUAL ]
Sep-Pak XPoSure Aldehyde Sampler
