Eap authentication, Eap characteristics – AMX MVP-5100 User Manual
Page 168
Appendix B: Wireless Technology
160
MVP-5100/5150 Modero Viewpoint Touch Panels
EAP Authentication
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an Enterprise authentication protocol that can be used in
both a wired and wireless network environment. EAP requires the use of an 802.1x Authentication
Server, also known as a RADIUS server. Although over 40 different EAP methods are currently defined,
the current internal Modero 802.11g wireless card and accompanying firmware only support the
following EAP methods (listed from simplest to most complex):
EAP-LEAP (Cisco Light EAP)
EAP-FAST (Cisco Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling, a.k.a. LEAPv2)
The following use certificates:
EAP-PEAP (Protected EAP)
EAP-TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Security)
EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security)
EAP requires the use of an 802.1x authentication server (also known as a RADIUS server). Sophisticated
Access Points (such as Cisco) can use a built-in RADIUS server. The most common RADIUS servers
used in wireless networks today are:
Microsoft Sever 2003
Juniper Odyssey (once called Funk Odyssey)
Meetinghouse AEGIS Server
DeviceScape RADIUS Server
Cisco Secure ACS
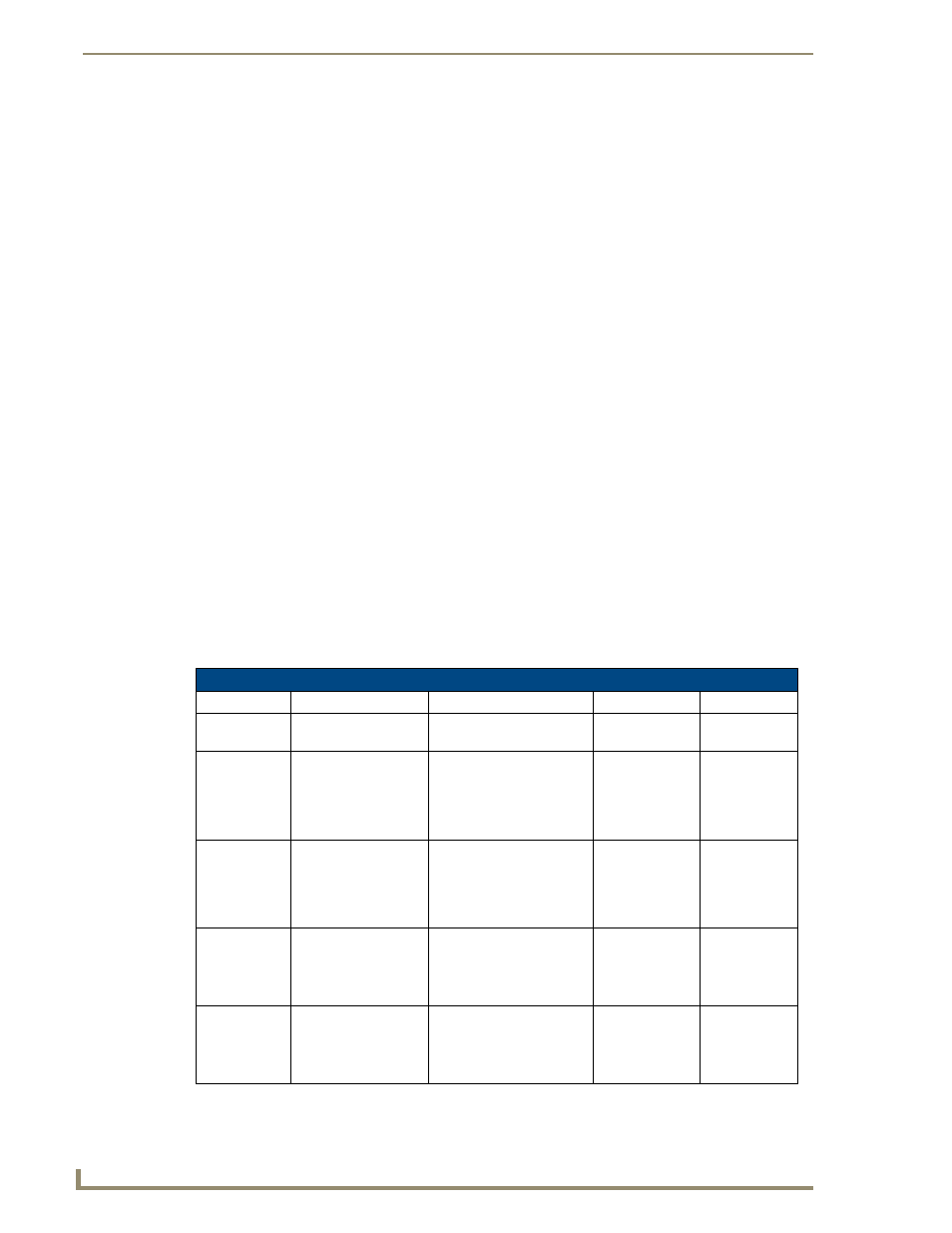
EAP characteristics
The following table outlines the differences among the various EAP Methods from most secure (at the
top of the list) to the least secure (at the bottom of the list):
EAP Method Characteristics
Method:
Credential Type:
Authentication:
Pros:
Cons:
EAP-TLS
• Certificates
• Certificate is based on a
two-way authentication
• Highest
Security
• Difficult to
deploy
EAP-TTLS
• Certificates
• Fixed Passwords
• One-time passwords
(tokens)
• Client authentication is
done via password and
certificates
• Server authentication is
done via certificates
• High Security
• Moderately
difficult to
deploy
EAP-PEAP
• Certificates
• Fixed Passwords
• One-time passwords
(tokens)
• Client authentication is
done via password and
certificates
• Server authentication is
done via certificates
• High Security
• Moderately
difficult to
deploy
EAP-LEAP
• Certificates
• Fixed Passwords
• One-time passwords
(tokens)
• Authentication is based on
MS-CHAP and
MS-CHAPv2
authentication protocols
• Easy
deployment
• Susceptible to
dictionary
attacks
EAP-FAST
• Certificates
• Fixed Passwords
• One-time passwords
(tokens)
• N/A
• N/A
• N/A
