Siemens Simatic S7-300 CPU 31xC and CPU 31x S7-300 User Manual
Page 93
Cycle and reaction times
5.2 Cycle time
CPU 31xC and CPU 31x, Technical data
Manual, Edition 08/2004, A5E00105475-05
5-11
5.2.5
Cycle time extension as a result of testing and commissioning functions
Runtimes
The runtimes of the testing and commissioning functions are operating system runtimes, so
they are the same for every CPU. Initially, there is no difference between process mode and
testing mode. How the cycle time is extended as a result of active testing and commissioning
functions is shown in the table below.
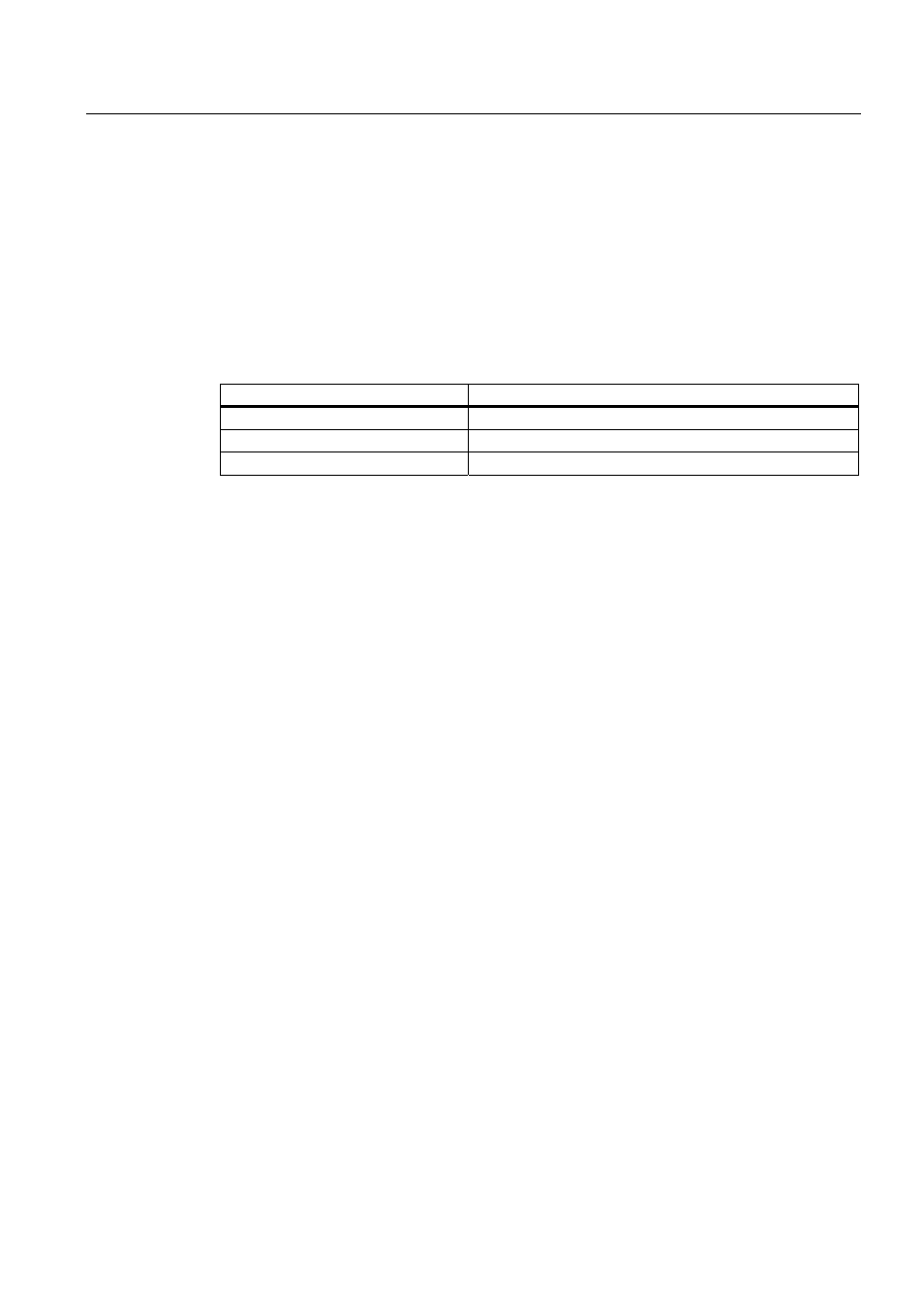
Table 5-9
Cycle time extension as a result of testing and commissioning functions
Function
CPU 31xC/ CPU 31x
Status variable
50 μs for each variable
Control variable
50 μs for each variable
Block status
200 μs for each monitored line
Configuration during parameter assignment
For process operation, the maximum permissible cycle load by communication is not
specified in "Cycle load by communication", but rather in "Maximum permitted increase of
cycle time as a result of testing functions during process operation". Thus, the configured
time is monitored absolutely in process mode and data acquisition is stopped if a timeout
occurs. This is how STEP 7 stops data requests in loops before a loop ends, for example.
When running in Testing mode, the complete loop is executed in every cycle. This can
significantly increase cycle time.
5.2.6
Cycle extension through component-based automation (CBA)
By default, the operating system of your CPU updates the PROFINET interface as well as
the DP interconnections at the cycle control point. However, if you deactivated these
automatic updates during configuration (e.g. to obtain improved capabilities of influencing the
time behavior of the CPU), you must perform the update manually. This is done by calling
SFCs 112 to 114 at the appropriate times.
Reference
Information about SFC 112 to 114 is available in the
STEP 7 Online Help.
Extending the OB1 cycle time
The OB1 cycle is extended by
•
Increasing the number of PROFINET interconnections,
•
Increasing the number of remote partners,
•
Increasing the data volume and
•
Incrasing the transfer frequency
