Siemens Simatic S7-300 CPU 31xC and CPU 31x S7-300 User Manual
Page 92
Cycle and reaction times
5.2 Cycle time
CPU 31xC and CPU 31x, Technical data
5-10
Manual, Edition 08/2004, A5E00105475-05
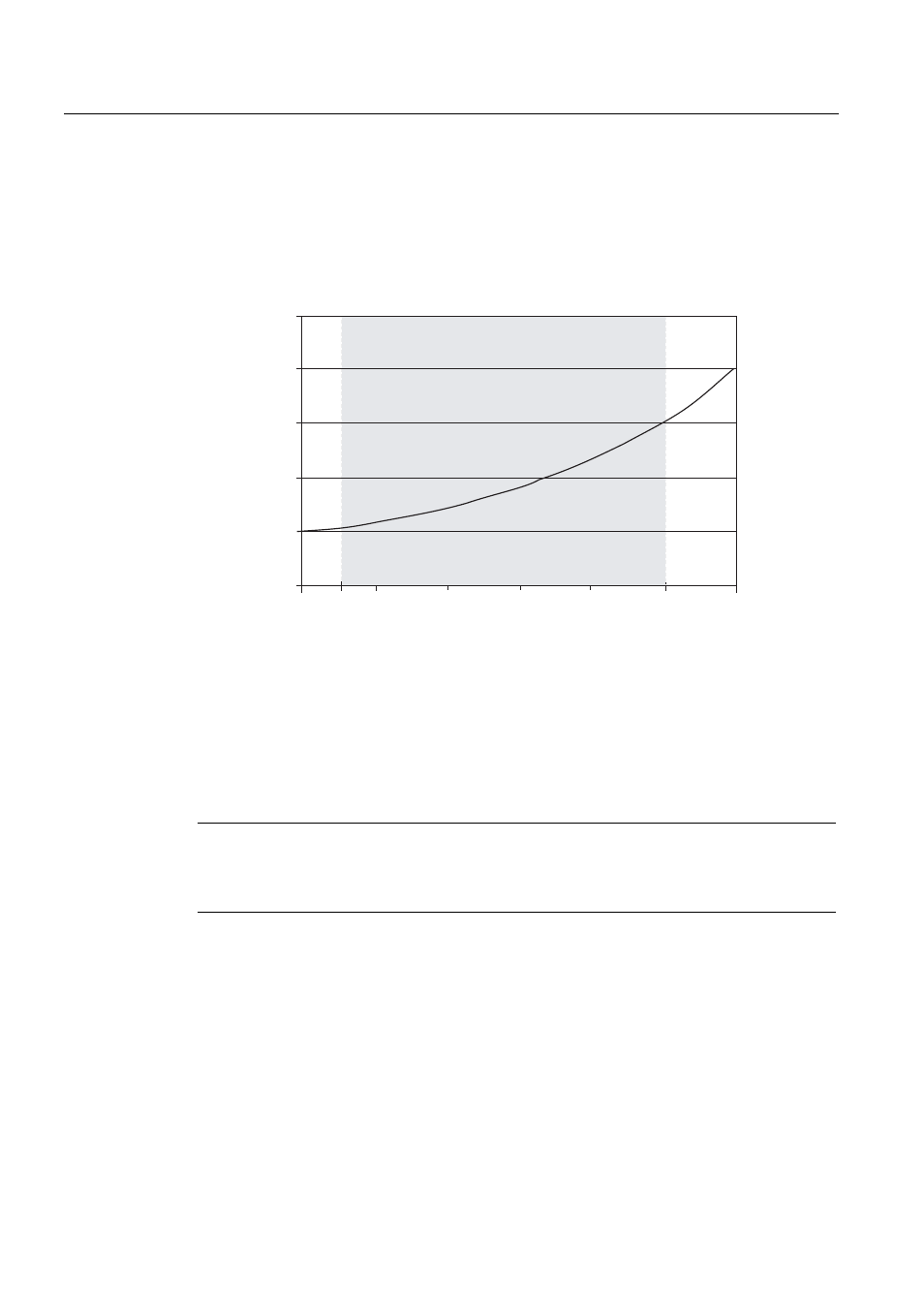
Physical cycle time depending on communication load
The figure below describes the non-linear dependency of the physical cycle time on
communication load. In our sample we have chosen a cycle time of 10 ms.
0 %
10 %
20 %
30 %
40 %
50 %
60 %
Cycle time
10 ms
20 ms
25 ms
15 ms
5 ms
30 ms
5 %
Communication load
The communication load can
be defined in this area.
Influence on the physical cycle time
From the statistical viewpoint, asynchronous events—such as interrupts—occur more
frequently within the OB1 cycle when the cycle time is extended as a result of
communication load. This further extends the OB1 cycle. This extension depends on the
number of events that occur per OB1 cycle and the time required to process these events.
Note
Change the value of the "communication load" parameter to check the effects on the cycle
time at system runtime. You must consider the communication load when you set the
maximum cycle time, otherwise timing errors may occur.
Tips
•
Use the default setting wherever possible.
•
Increase this value only if the CPU is used primarily for communications and if the user
program is not time critical.
•
In all other situations you should only reduce this value.
