Redirection, Ipv6 pmtu discovery, Ipv6 transition technologies – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 118
107
Redirection
A newly started host may contain only a default route to the gateway in its routing table. When certain
conditions are satisfied, the gateway sends an ICMPv6 Redirect message to the source host so that the
host can select a better next hop to forward packets (similar to the ICMP redirection function in IPv4).
The gateway sends an ICMPv6 Redirect message when the following conditions are satisfied.
•
The receiving interface is the forwarding interface.
•
The selected route itself is not created or modified by an ICMPv6 Redirect message.
•
The selected route is not the default route.
•
The IPv6 packet to be forwarded does not contain any routing header.
IPv6 PMTU discovery
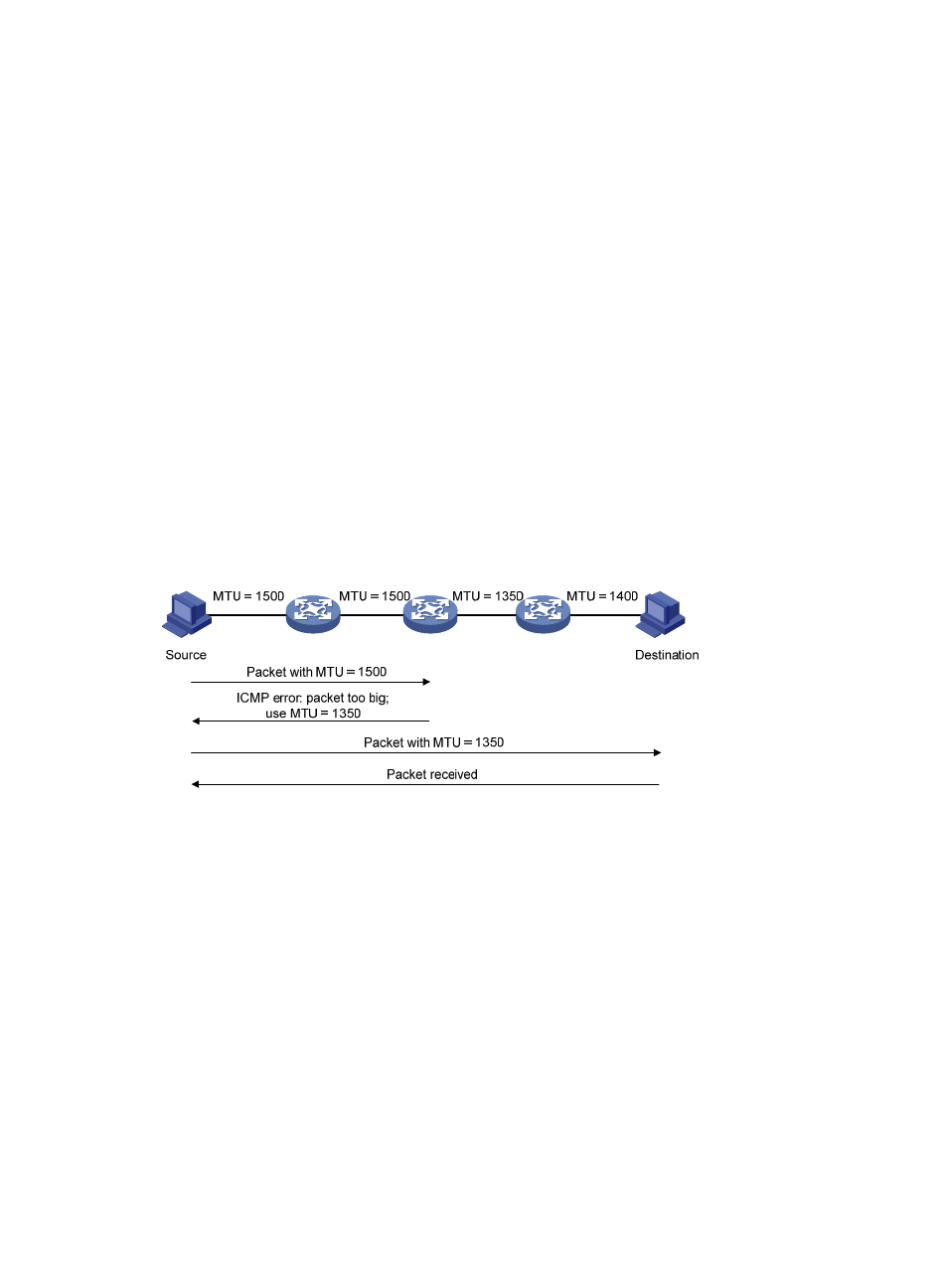
The links that a packet passes from a source to a destination may have different MTUs. In IPv6, when the
packet size exceeds the path MTU of a link, the packet is fragmented at the source end of the link to
reduce the processing pressure on intermediate devices and use network resources effectively.
The path MTU (PMTU) discovery mechanism is designed to find the minimum MTU of all links in the path
between a source and a destination.
shows how a source host discovers the PMTU to a
destination host.
Figure 48 PMTU discovery process
1.
The source host compares its MTU with the packet to be sent, performs necessary fragmentation,
and sends the resulting packet to the destination host.
2.
If the MTU supported by a forwarding interface is smaller than the packet, the device discards the
packet and returns an ICMPv6 error packet containing the interface MTU to the source host.
3.
After receiving the ICMPv6 error packet, the source host uses the returned MTU to limit the packet
size, performs fragmentation, and sends the resulting packet to the destination host.
4.
Step 2 and step 3 are repeated until the destination host receives the packet. In this way, the
source host decides the minimum MTU of all links in the path to the destination host.
IPv6 transition technologies
Before IPv6 dominates the Internet, high-efficient, seamless IPv6 transition technologies are needed to
enable communication between IPv4 and IPv6 networks. Several IPv6 transition technologies can be
used in different environments and periods, such as dual stack (RFC 2893), tunneling (RFC 2893), and
NAT-PT (RFC 2766).
- H3C WX5500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX3500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX2500E Series Access Controllers H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM3WCMD0 Access Controller Module H3C LSUM1WCME0 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module H3C WA3600 Series Access Points H3C WA2600 Series WLAN Access Points
