Configuring atm, Overview, Introduction to atm – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 9: Atm connection
1
Configuring ATM
Overview
Introduction to ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a technology based on packet transmission mode while
incorporating the high speed of circuit transmission mode. It can satisfy the needs of various
communication services. ATM was specified as a broadband ISDN transmission and switching mode by
the ITU-T in June 1992. Due to its flexibility and support for multimedia services, it is regarded as the core
technology for broadband communications.
As defined by the ITU-T, ATM encapsulates data in cells. Each ATM cell is 53 bytes long, among which
5 bytes are the cell header and the remaining 48 bytes are the payload. The major function of the cell
header is to identify virtual connection, with limited functions regarding flow control, congestion control,
and error control.
ATM connection
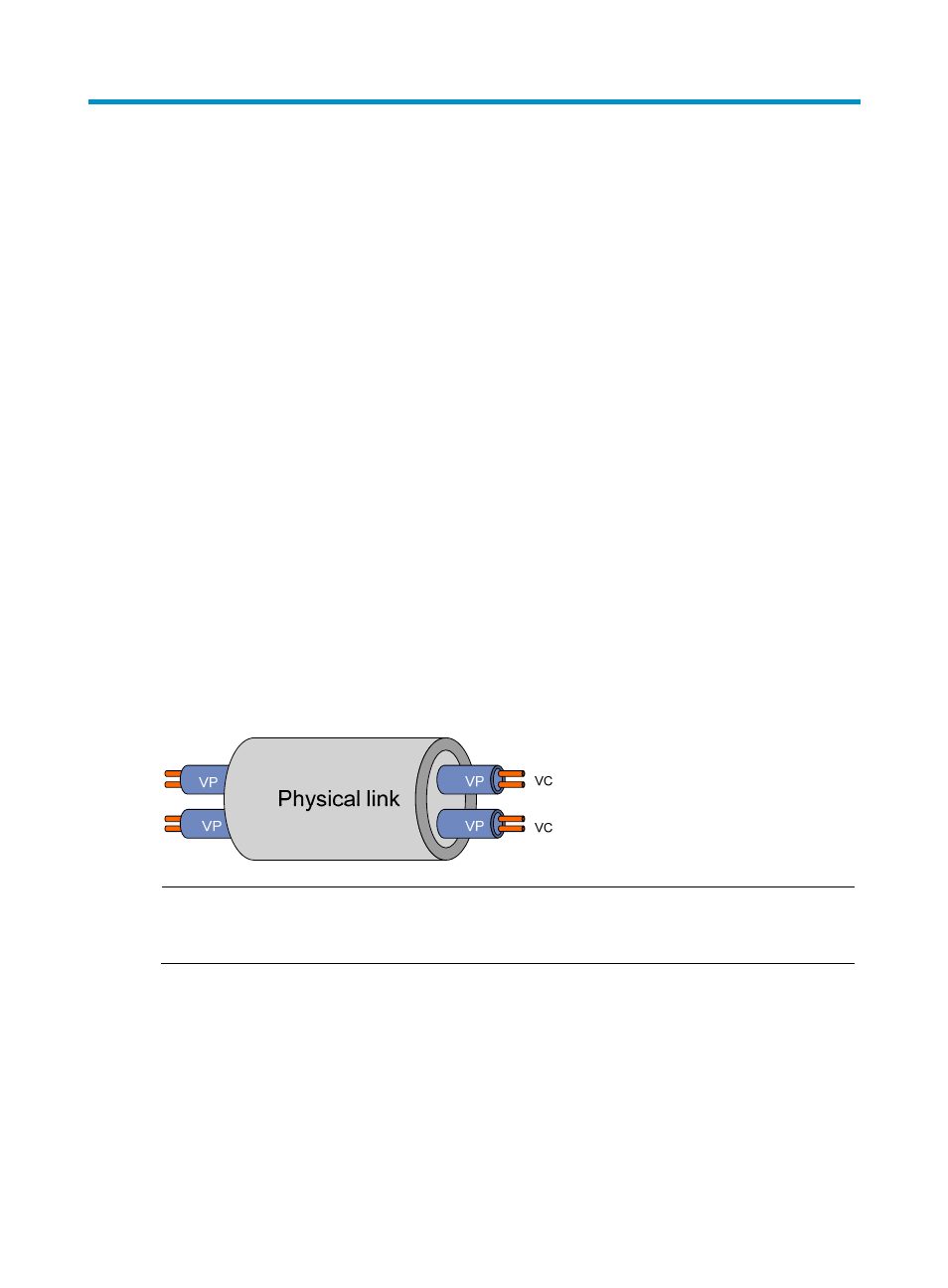
ATM is connection-oriented and ATM connections are logical connections, or virtual circuits. In an ATM
network, you can create logical connections called virtual paths (VPs) and virtual circuits (VCs) on
physical links. As shown in
, you can create multiple VPs on a physical link, and each VP can be
demultiplexed into multiple VCs. Cells from different users are transmitted over different VPs and VCs,
which are identified by virtual path identifier (VPI) and virtual channel identifier (VCI).
Figure 1 Physical link, VP, and VC
NOTE:
ATM uses VPI/VCI pairs to identify a logical connection. When a connection is released, all the involved
VPI/VCI pairs are reclaimed for new connections.
ATM interfaces of the router support permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) only.
- H3C SR6600-X H3C SR6600 H3C MSR 5600 H3C MSR 50 H3C MSR 3600 H3C MSR 30 H3C MSR 2600 H3C MSR 20-2X[40] H3C MSR 20-1X H3C MSR 930 H3C MSR 900 H3C WX6000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX5000 Series Access Controllers H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches H3C LSWM1WCM10 Access Controller Module H3C LSWM1WCM20 Access Controller Module H3C LSQM1WCMB0 Access Controller Module H3C LSRM1WCM2A1 Access Controller Module H3C LSBM1WCM2A0 Access Controller Module
