Figure 59 – H3C Technologies H3C S5560 Series Switches User Manual
Page 251
235
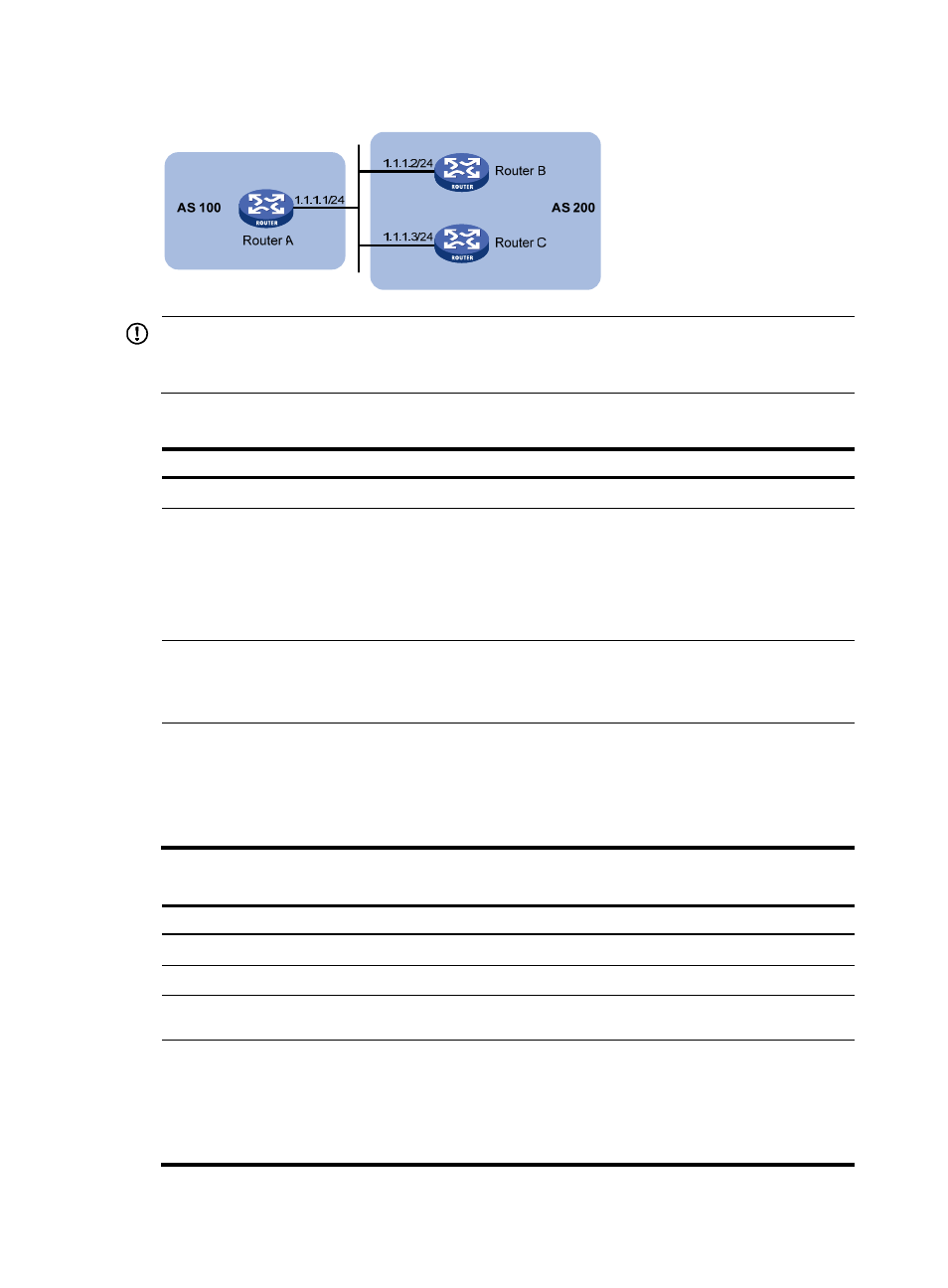
Figure 59 NEXT_HOP attribute configuration
IMPORTANT:
If you have configured BGP load balancing, the router sets itself as the next hop for routes sent to an IBGP
peer or peer group regardless of whether the peer next-hop-local command is configured.
To configure the NEXT_HOP attribute (IPv4):
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Enter BGP view or BGP-VPN
instance view.
•
Enter BGP view:
bgp as-number
•
Enter BGP-VPN instance view:
a.
bgp as-number
b.
ip vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name
N/A
3.
Enter BGP IPv4 unicast
address family view or
BGP-VPN IPv4 unicast
address family view.
address-family ipv4 [ unicast ]
N/A
4.
Specify the router as the next
hop for routes sent to a peer
or peer group.
peer { group-name | ip-address }
next-hop-local
By default, the router sets itself as
the next hop for routes sent to an
EBGP peer or peer group.
However, it does not set itself as
the next hop for routes sent to an
IBGP peer or peer group.
To configure the NEXT_HOP attribute (IPv6):
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Enter BGP view.
bgp as-number
N/A
3.
Enter BGP IPv6 unicast
address family view.
address-family ipv6 [ unicast ]
N/A
4.
Specify the router as the next
hop for routes sent to a peer
or peer group.
peer { group-name |
ipv6-address } next-hop-local
By default, the router sets itself as
the next hop for routes sent to an
EBGP peer or peer group.
However, it does not set itself as
the next hop for routes sent to an
IBGP peer or peer group.
