Altera Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration IP Core User Manual
Page 41
Specifications
Page 41
Phase-Locked Loop Reconfiguration (ALTPLL_RECONFIG) Megafunction
February 2012
Altera Corporation
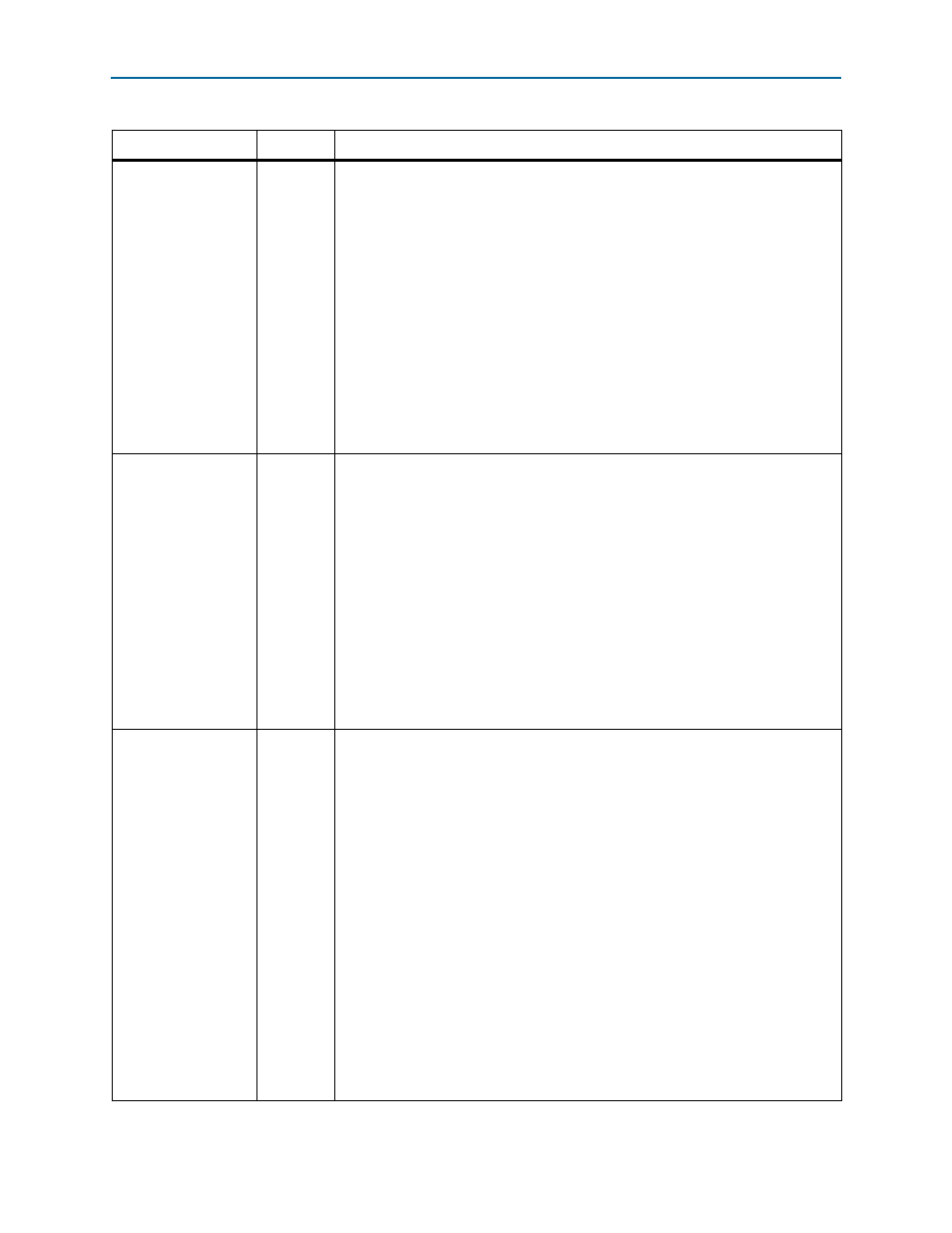
read_param
No
Reads the parameter specified with the
counter_type
and
counter_param
ports
from cache and fed to the
data_out[]
port.
When asserted, the
read_param
signal indicates that the scan cache should be read
and fed to
data_out[]
. The bit location of the scan cache and the number of bits
read and sent to
data_out[]
depend on the
counter_type
and
counter_param
values. The
read_param
signal is sampled at the rising clock edge. If it is asserted,
the parameter value is read from the cache. Assert the
read_param
signal for 1 clock
cycle only to prevent the parameter from being read twice.
The
busy
signal is asserted on the rising clock edge following the assertion of
read_param
. While the parameter is being read, the
busy
signal remains asserted.
After the
busy
signal is deasserted, the value on
data_out[]
is valid and the next
parameter can be loaded. While the
busy
signal is asserted, the value on
data_out[]
is not valid.
When the
read_param
signal is asserted, the
busy
signal is only asserted on the
following rising edge of the clock and not on the same clock cycle as
read_param
.
write_param
No
Writes the parameter specified with the
counter_type
and
counter_param
ports to
the cache with the value specified on the
data_in[]
port.
When asserted, the
write_param
signal indicates that the value on
data_in[]
should be written to the parameter specified by
counter_type[]
and
counter_param[]
. The number of bits read from the
data_in[]
port depends on
the parameter. The
write_param
signal is sampled at the rising clock edge. If it is
asserted, the parameter value is written to the cache. Assert the
write_param
signal
for 1 clock cycle only to prevent the parameter from being written twice.
The
busy
signal is asserted on the rising clock edge following the assertion of
write_param
. While the parameter is being written, the busy signal remains
asserted and input to
data_in[]
is ignored. After the
busy
signal is deasserted, the
next parameter can be written.
When the
write_param
signal is asserted, the
busy
signal is only asserted on the
following rising edge of the clock and not on the same clock cycle as
write_param
.
reconfig
Yes
Specifies that the phase-locked loop (PLL) should be reconfigured with the PLL
settings specified in the current cache.
When asserted, the
reconfig
signal indicates that the PLL should be reconfigured
with the values in the cache. The
reconfig
signal is sampled at the rising clock edge.
If it is asserted, the cached settings are loaded in the PLL. Assert the
reconfig
signal for 1 clock cycle only to prevent reloading the PLL configuration. The
busy
signal is asserted on the rising clock edge following the assertion of
reconfig
. While
the PLL is being loaded, the
busy
signal remains asserted. After the
busy
signal is
deasserted, the parameter values can be modified again.
During and after reconfiguration, the scan chain data cache remains unchanged. This
allows you to easily create a new set of reconfiguration settings that differs from the
previous one in only one parameter.
If
write_param
has not been asserted since the previous assertion of
reconfig
, in
Stratix II devices, the
pll_scanwrite
signal is pulsed during reconfiguration. This
feature supports burst-phase stepping. However, in Stratix III, Stratix IV, Cyclone III,
Cyclone IV, and Arria II GX devices, the entire scan chain is shifted in to the PLL
again.
When the
reconfig
signal is asserted, the
busy
signal is only asserted on the
following rising edge of the clock and not on the same clock cycle as
reconfig
.
Table 8. ALTPLL_RECONFIG Megafunction Input Ports (Part 2 of 3)
Port Name
Required?
Description
