03 basics of pulsed arc welding, 03 basics of pulsed arc welding -4 – Tweco 500SP PowerMaster Automation User Manual
Page 64
POWERMASTER 400SP, 500SP AUTOMATION
6-4
March 16, 2007
6.03 Basics of Pulsed Arc Welding
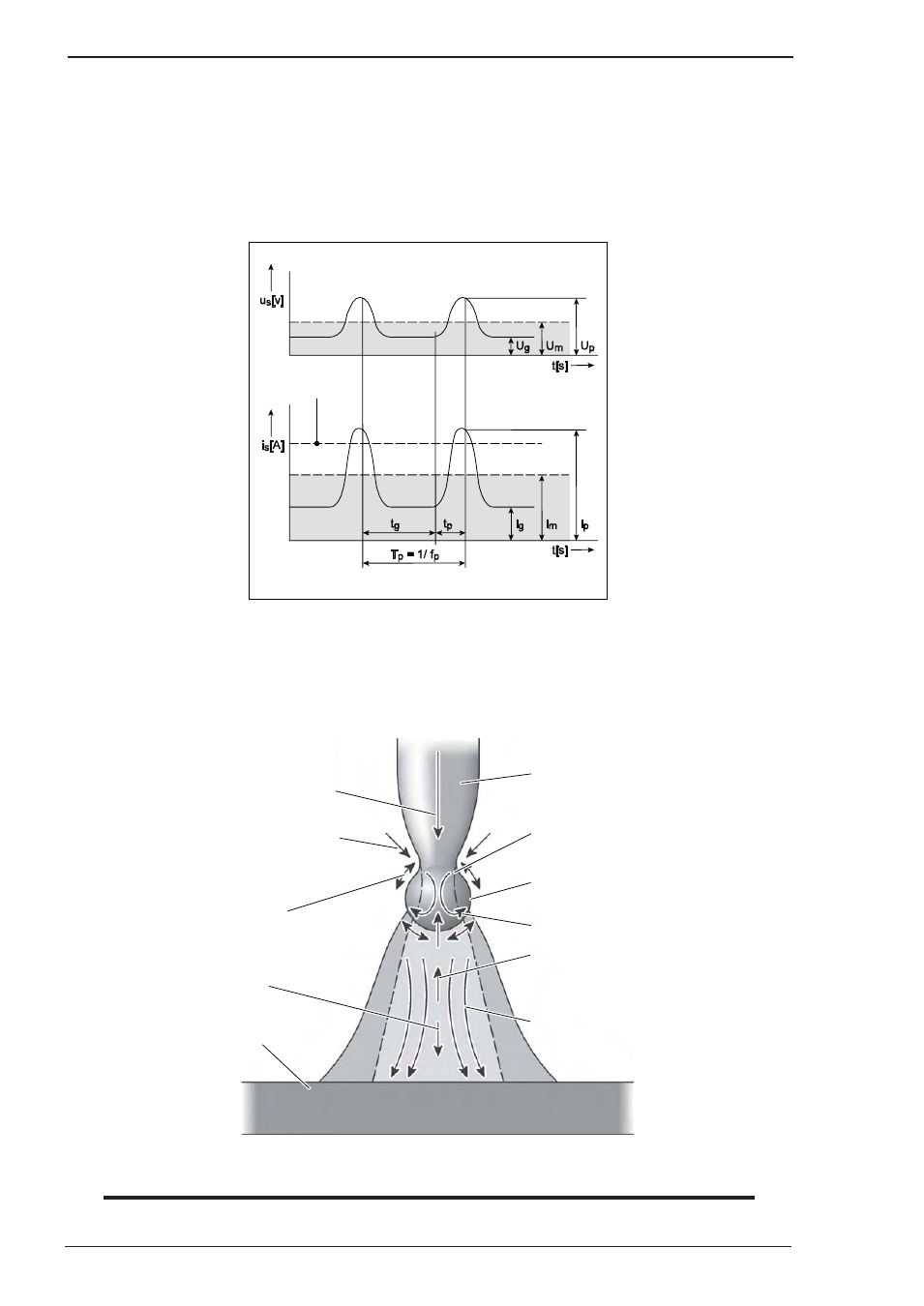
A. Current and voltage pulses
Material transfer is achieved by current and voltage pulses controlled at the same rate as the pulse frequency.
The arc power is changed by the ratio between background and pulses current, the pulse duty cycle and the
pulse frequency.
Art # A-06383
Spray Transfer
Current Range
B. Forces acting during material transfer
A number of forces come into play which influences the resulting molten metal drop formation and separation.
Electrostatic
Forces
Workpiece
Surface
tension S
Acceleration due
Electromagnetic force
F
L
(pinch effect)
Eddying forces
caused by
Forces of
repulsion (F
R
) of
evaporating
Force of inertia
Constrict drops
Viscosity
Wire electrode
to gravity
material
plasma flow
Electrostatic
Forces
Workpiece
Surface
tension S
Acceleration due
Electromagnetic force
F
L
(pinch effect)
Eddying forces
caused by
Forces of
repulsion (F
R
) of
evaporating
Force of inertia
Constrict drops
Viscosity
Wire electrode
to gravity
material
plasma flow
Art # A-06385
NOTE
The main force components for separating the drops are electromagnetic force (pinch effect).
