Using 1ćslot addressing – Rockwell Automation 1785-LTx,D17856.2.1 Classic PLC-5 Programmable Controllers Users Manual User Manual
Page 48
Assigning Addressing Modes,
Racks, and Groups
Chapter 4
4-6
Using 1ĆSlot Addressing
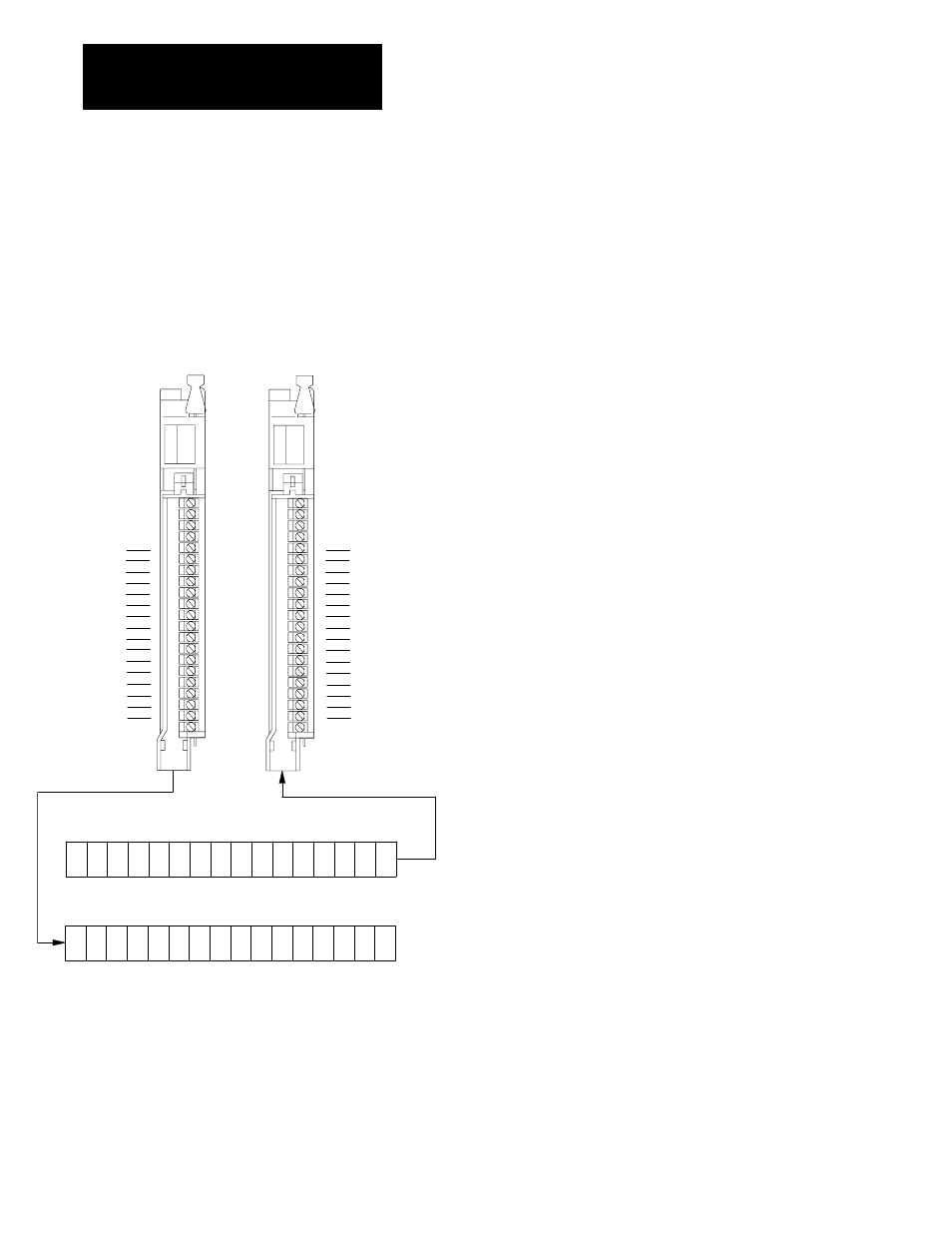
When you select 1-slot addressing, the processor addresses one I/O
module slot as one I/O group. Each physical slot in the chassis
corresponds to an input and output image-table word. The type
(unidirectional or bidirectional) and density of module that you install
determines the number of bits used in these words.
8-Point I/O Modules
You can place any mix of 8- or 16-point I/O modules
(including bidirectional modules such as
block-transfer modules) in any order with 1-slot
addressing. The 8- or 16-point modules do not
interfere with the I/O image of the other 8- or
16-point modules.
16-Point I/O Modules
A single 16-point module uses an entire word of the
processor image table.
Block-Transfer Module Addressing
To address a single-slot block transfer module in a
1-slot I/O group, use the assigned I/O rack and group
numbers of the slot (in which the module resides) and
0 for the module number. To address a double-slot
block-transfer module, use the assigned I/O rack
number, the lower assigned I/O group number, and 0
for the module number.
0
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
17 16 15 14
12
10 07 06 05
03 02 01 00
04
11
13
17 16 15 14
12
10 07 06 05
03 02 01 00
04
11
13
o r
11869
1ĆSlot I/O Group with One 16Ćpt Digital Discrete
I/O Module
A single 16Ćpt module uses an entire word of image table.
1-Slot
I/O Group
Output ImageĆTable Word Corresponding to the I/O Group.
Input ImageĆTable Word Corresponding to the I/O Group.
1-Slot
I/O Group
Input
Terminals
Output
Terminals
