I/o scanning – Rockwell Automation 1785-LTx,D17856.2.1 Classic PLC-5 Programmable Controllers Users Manual User Manual
Page 120
Calculating Program Timing
Chapter 9
9-3
Effects of Different Input States on Logic Scan Time
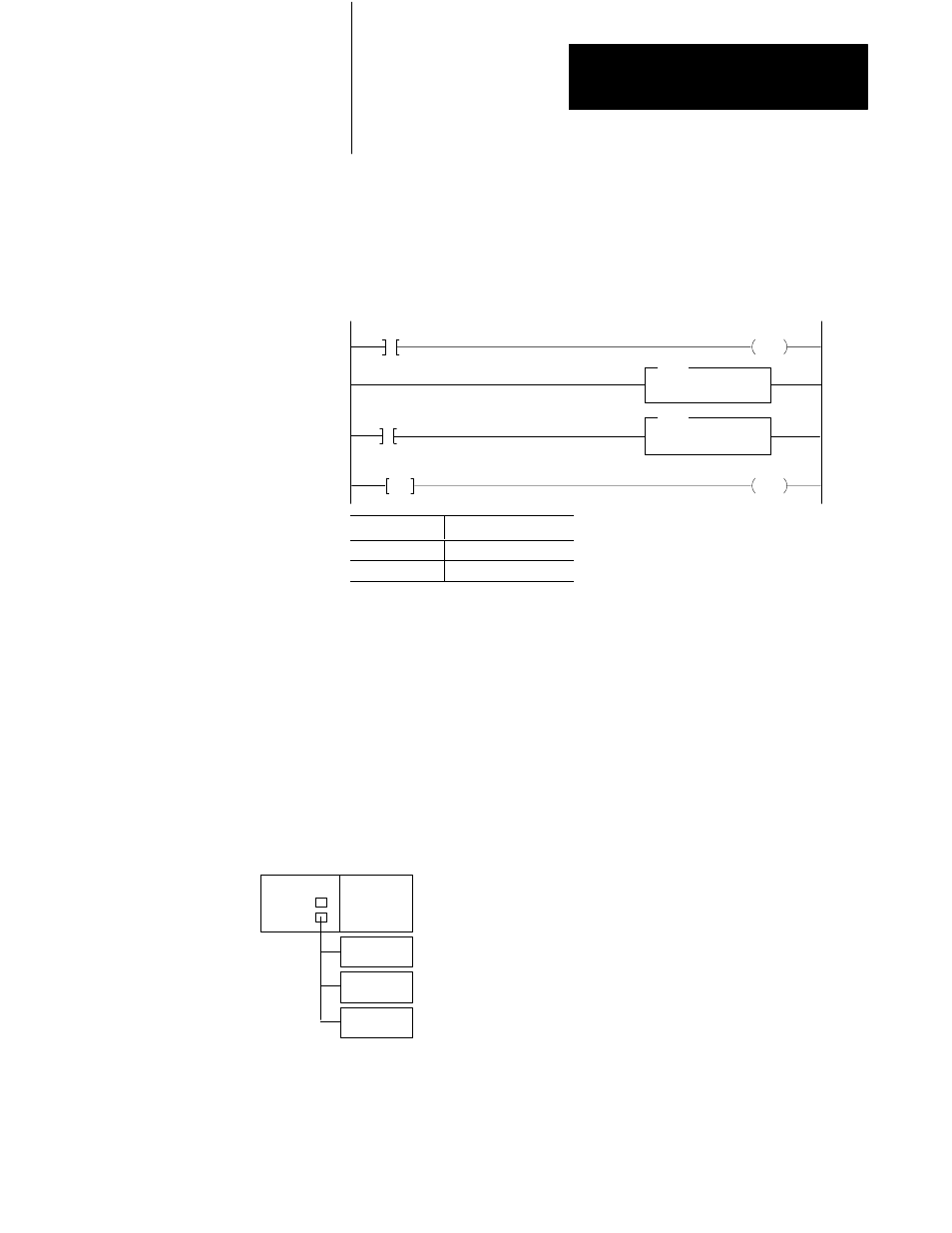
You can write your logic so that it executes different rungs at different
times, based on input conditions. The different amounts of logic executed
in the logic scans causes differences in program scan times. For example,
the simple differences in rung execution in the following example cause
the logic scan times to vary.
00
JMP
rung 1
B3:0
20
I:000
02
MVM
MVM
JMP
O:013
20
LBL
02
rung 2
rung 3
rung 4
If I:000/02 is:
Rungs 2 and 3 are:
On
Skipped
Off
Executed
If you use subroutines, program scan times can vary by the scan time of
entire logic files.
I/O Scanning
The remote I/O scan cycle is the time that it takes for the processor
(configured as a scanner) to communicate with all of the entries in its rack
scan-list once. The remote I/O scan is independent of and asynchronous to
the program scan.
The scanner processor keeps a list of all of the devices connected to each
remote I/O link. An example system would look like this:
PLCĆ5/25
Rack 1
Rack 2
Rack 3
DH+
Rem I/O
I/O Status
Rack
Address
Rack
Size
1
2
3
Full
1/2
Full
In this example, the remote I/O channel continually scans the three racks in its scan list
and places the data in the remote I/O buffer in the processor. The processor updates
its own buffer and the I/O image table. During housekeeping, the two buffers are
updated by exchanging the input and output data with each other.
I/O Range
IO 010/00 to 017/17
IO 020/00 to 023/17
IO 030/00 to 037/17
