Dakota Ultrasonics DFX-8 plus MANUAL1 User Manual
Page 109
DFX-8 Series Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors
105
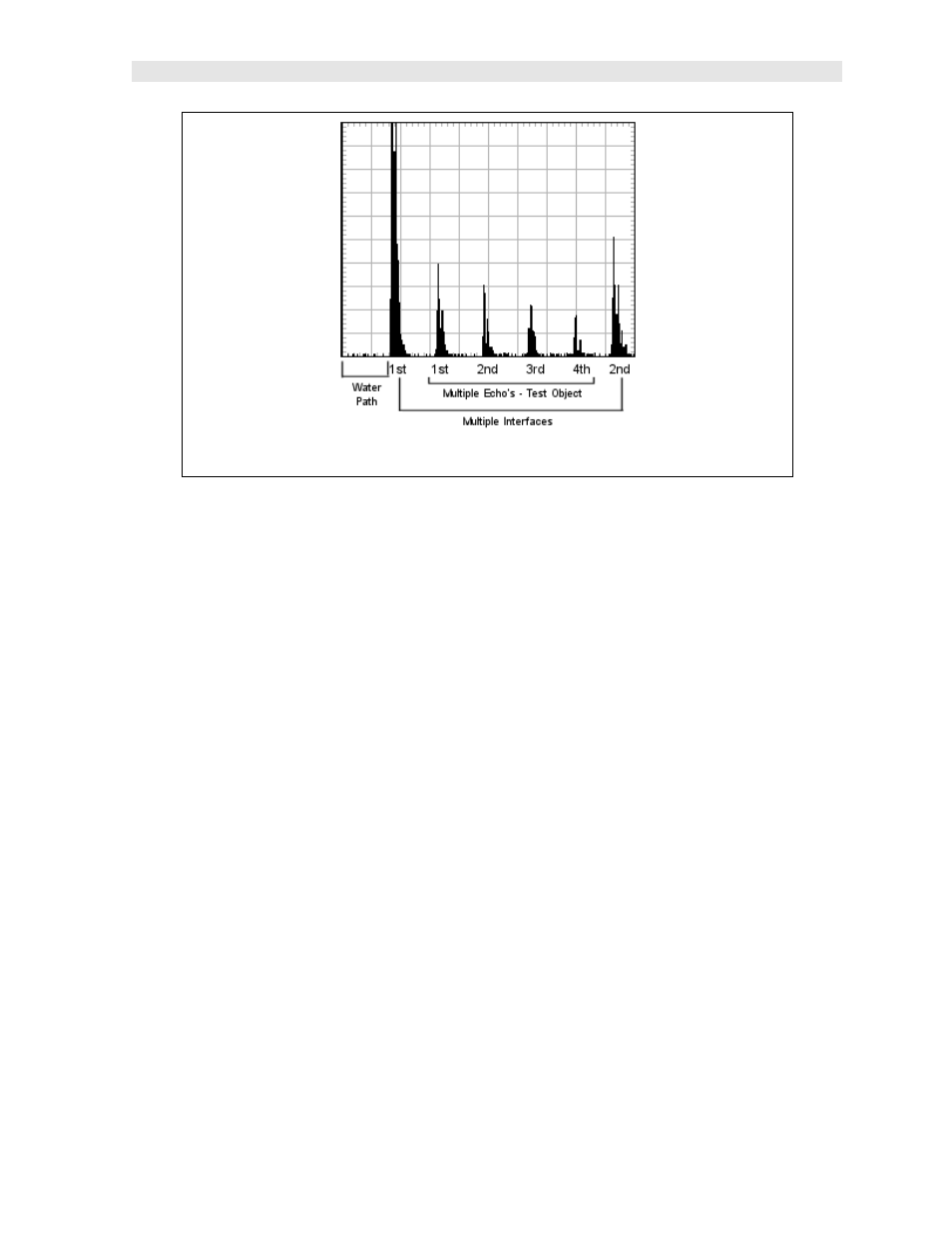
Immersion Testing
Considerations:
There is a significant difference between sound traveling in water versus steel,
for example. The longitudinal velocity of sound traveling through water is
approximately 0.058 in/µs, while 0.2320 in/µs in steel. Since the DFX-8+ has
been setup and calibrated for a steel test object, this would find the water path
interface at approximately 4”, considering an actual 1” water path, or 4 times
the depth/distance on the calibrated display.
It is recommended that the water path be greater than 25% of the thickness of
the test object, and that the water path is long enough to keep the flaw
evaluation process beyond the “near zone” and entirely in the “far zone” where
sound has achieved the most uniform wave front (near zone will be contained
in the water path).
Additionally, any movements of the transducer or test object that change the
water path distance are then compounded by a factor of 4x. Therefore, a
mechanical fixture or carriage is typically used on the top side of the tank in
order to maintain the positioning of the transducer to the test object.
Changes in the targets angle and water path distance will reduce the
amplitude/output, and should be considered during the evaluation of a flaw.
Obviously, the optimal evaluation would be a perfectly fixed transducer
position with a perfectly parallel reflector and water path distance.
