Types of data subject to backup (sql server), Sql server data and requirements – HP XP P9000 Command View Advanced Edition Software User Manual
Page 371
SQL Server data and requirements
The following are the types of SQL Server data subject to backup using Replication Manager. Backed-up
databases differ depending on the option specified in the Create Replica Wizard.
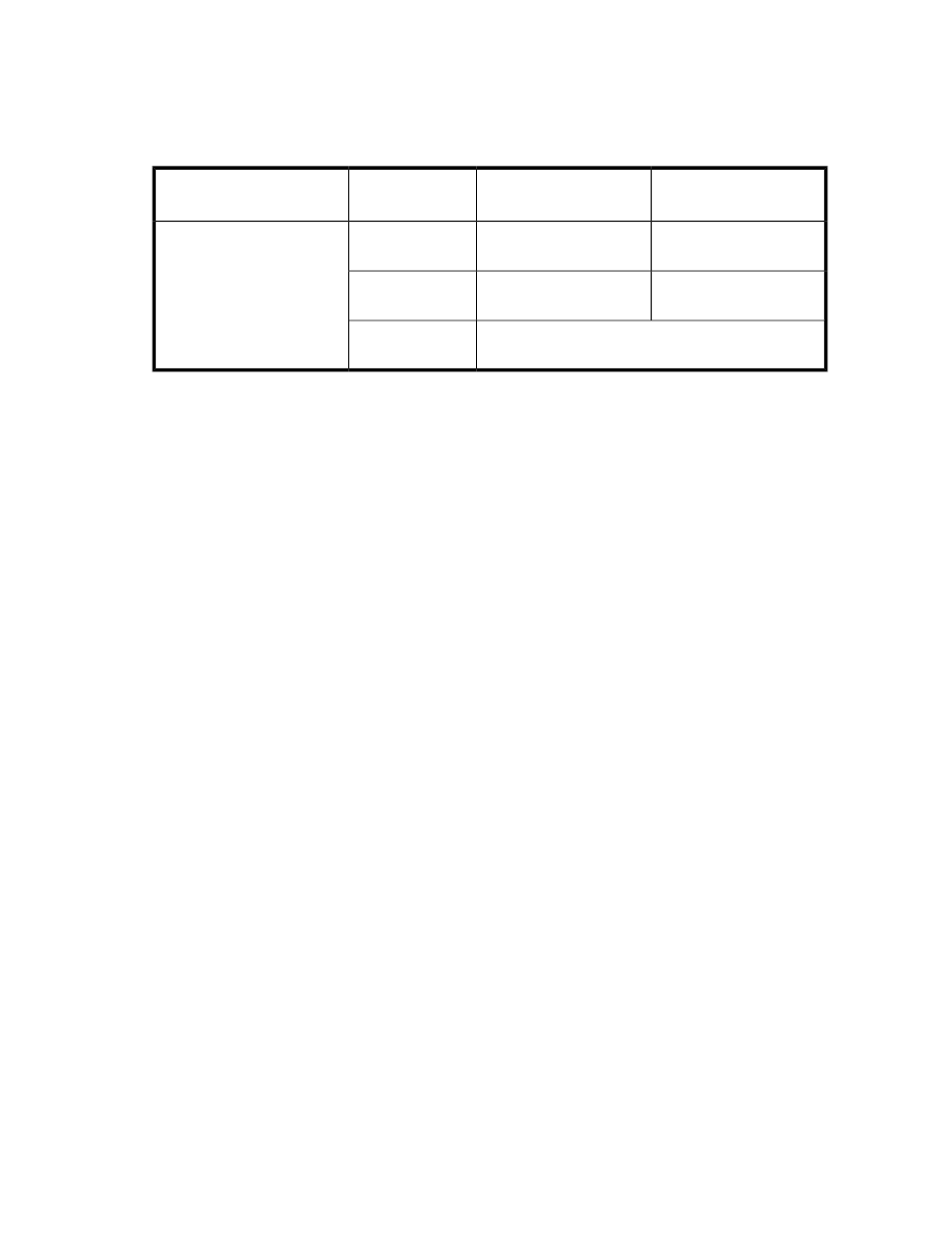
Table 18 Types of data subject to backup (SQL Server)
Storage destination for
backup files
Backup file name
Files subject to
backup
Database subject to backup
Secondary volume
Same as the backup
source file name
Data file
master
model
msdb
User database
Distribution database
Secondary volume
Same as the backup
source file name
Transaction log file
Varies depending on the VDI metafile storage directory
specified.*
Metafile
Legend:
*: When a VDI metafile storage directory is registered in the SQL Options tab of the Setup Application
Agent dialog box, the metafile is stored in the registered directory. The file name is
backup-ID_database-ID.dmp
. When default is selected for the VDI metafile storage directory,
the metafile is stored in the directory that contains the file whose management number (
file_id
) for
SQL Server in the database file is a minimum value. The file name is
META_xxx.dmp
.
Databases are backed up and restored in units of volumes, so the object configuration of an SQL
Server database requires the following:
•
Configure each instance so that its data files are on one volume. In addition, do not place data
files of multiple instances on a single volume.
•
The following should not be placed in the same directory as the database configuration files
(
*.mdf
,
*.ndf
, and
*.ldf
):
• Metafile directory (only when specified)
• Transaction log backup files
Roll-forward recovery processing can only be performed if the above directory and file are placed
on separate volumes. (In the event of a restoration, this prevents the metadata and transaction log
files from reverting to a previous state.) If this requirement is not satisfied, the backup terminates
with an error.
•
You can use the following characters when naming a database:
• ASCII characters
• Multi-byte characters (one character must be expressed using 1- or 2-byte characters)
However, do not use the following characters:\ / : , ; * ? < > | “
•
Do not use names in the following form for database data files:
META_database-ID.dmp
Where
database-ID
is a 10-digit number.
•
In a cluster environment, specify a user on each node for the owner of a database subject to
backup. Local users with the same user name and password on different nodes are not considered
to be the same user. Therefore, use a domain user account that is common to all nodes. If a failover
is performed to a node where the database-owner user does not exist, backup fails because the
database owner is unknown.
•
If the system databases (master, model, and msdb) are to be backed up, specify, as the output
destination for SQL Server error log files, a volume different than the one that contains the system
User Guide
371
