Reference modes, Types of calibration – Ronan X96S MASS FLOW GAUGE User Manual
Page 52
48
Reference Modes
One of your first tasks will be to calibrate the system. The first step in the calibration procedure is to
"reference" the gauge on some known value. The steps involved in the referencing procedure will vary
slightly depending upon the mode selected in the “Ref Constants”.
One of these four REFERENCE MODES will be active on your system:
• Referencing EMPTY (SpG = 0)
• Referencing with WATER (SpG = 1)
• Referencing with PROCESS OF KNOWN DENSITY
• Referencing with ABSORBER
Most applications use the "Reference with Water" or the "Reference with Process" Mode.
Types of Calibration
Two types of Calibration are available for Ronan's Density Monitor.
Dual-Point Calibration requires an accurate laboratory analysis of truly representative samples of
two process densities. Dual-Point Calibration is preferred when the process can be varied to obtain
two process densities (one at each end of the measurement range).
Single-Point Calibration requires an accurate laboratory analysis of a truly representative sample of
one process density. Single-Point Calibration is used as an alternative method when it is not
physically or economically practical to vary the process density. In these cases, a second point is
estimated based on the mathematical formula for radiation transmission/absorption.
Calibration Constant
The two values, the reference density (d
o
) and the calibration constant (1/ut), are used by the X96S
algorithm to calculate process density (d).
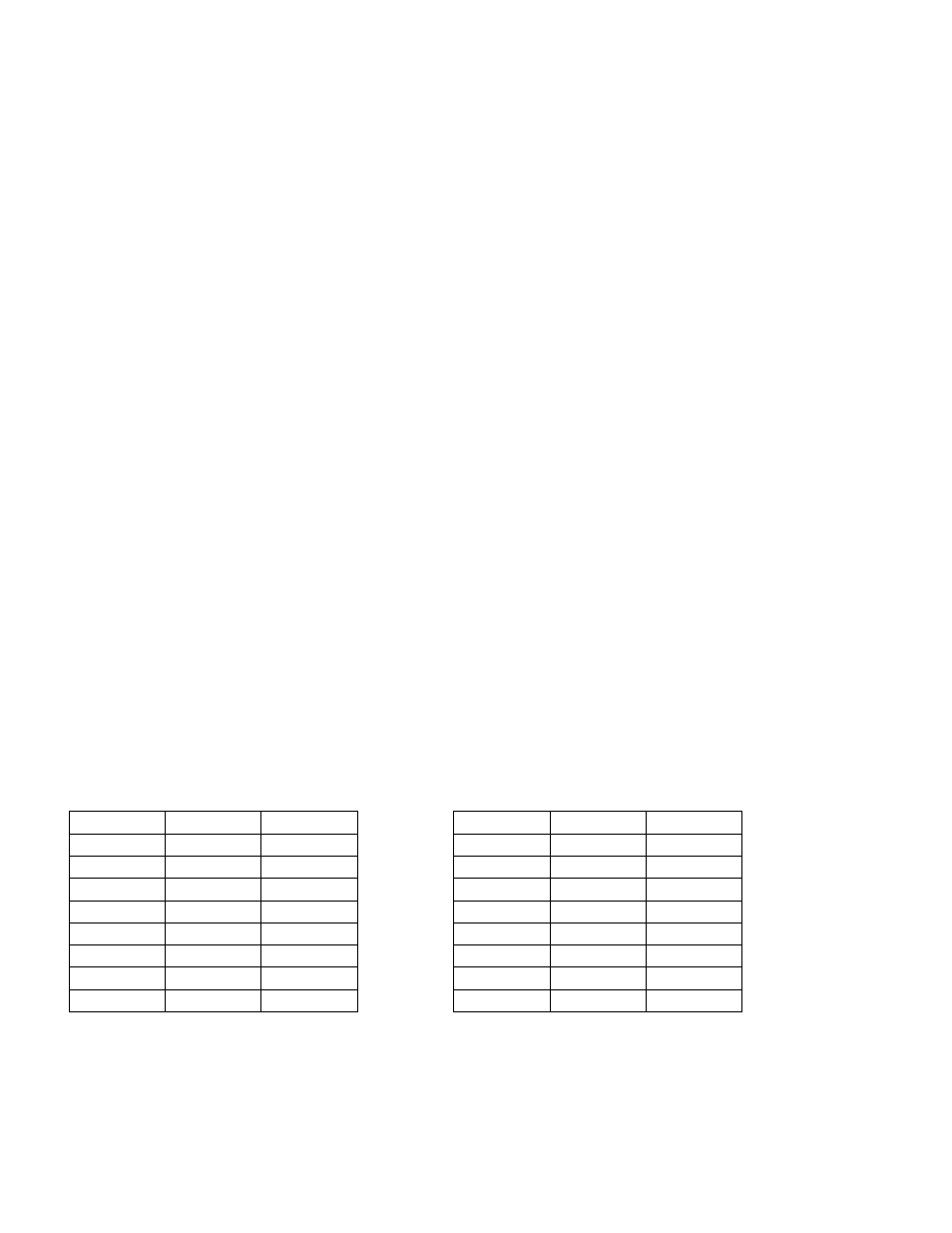
IF USING SA1:
IF USING RLL:
t
ut
1/ut
t
ut
1/ut
0.312
2”
0.4
2.5
2”
.32
2.083
3”
0.6
1.6
3”
.48
1.562
4”
0.8
1.25
4”
.64
1.25
5”
1.0
1.0
5”
.80
1.042
6”
1.2
0.825
6”
.96
0.781
8”
1.6
0.625
8”
1.28
0.625
10”
2.0
0.5
10”
1.6
t = mat'l thickness (pipe I.D.)
t = mat’l thickness (pipe I.D.)
u = absorption coefficient
u = absorption coefficient
= 0.2 for Cs137
= .16 for Cs137
1/ut = calibration constant
1/ut = calibration constant
Transmission/Absorption Table
