Proportional, integral, and derivative, Pulse, width, modulation), Control – YSI 5500D-1 User Manual
Page 72
YSI 5X00
143
YSI 5X00
142
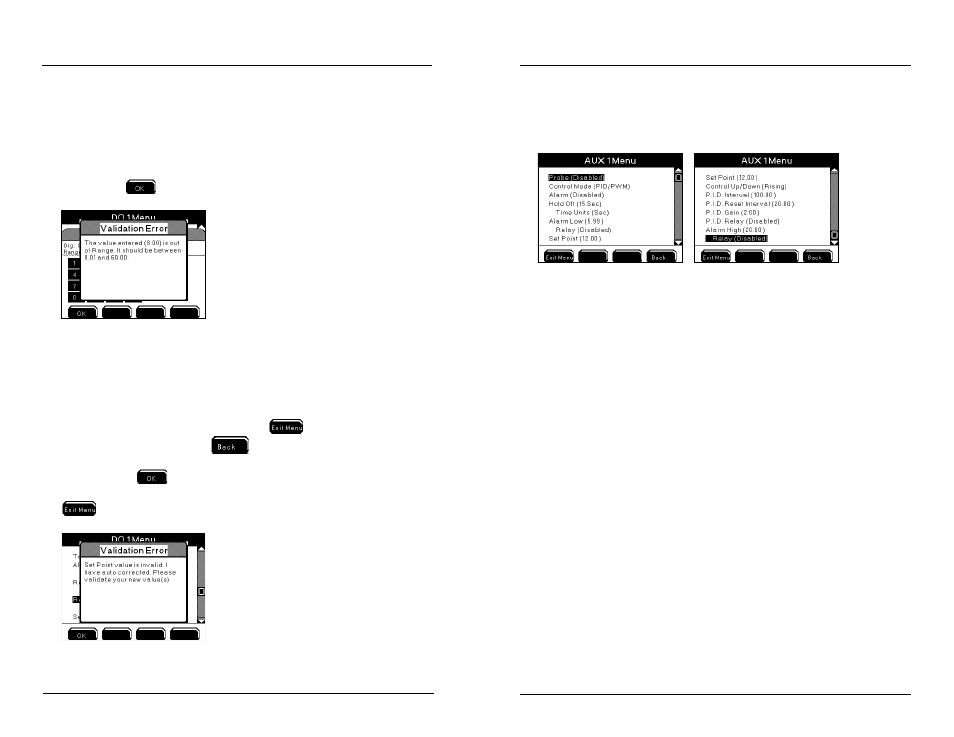
Example - entering “63” for DO set point results in validation error because the
valid range for the DO sensor system is 0.00 to 60.0 mg/l. User must configure
value within valid range. In addition, the value cannot breach respective control
and alarm system values.
Example - configuring set point value of 8.00 mg/L with range low value of 8.00
mg/l results in validation error. Valid set point range is displayed at validation error
display. Press
to return to numeric keypad to enter valid value.
Autofix occurs when a high or low control value is entered that breaches the set point
value. Autofix changes the high or low control value by one least significant digit
away from the set point value. The set point value is never adjusted.
Example - Entering 8.00 mg/L as the range low value when the set point value is
8.00 mg/L results in an auto fix of the control value. The invalid control value is
displayed at the sensor setup menu. Pressing
is not an option after saving
a value at numeric keypad. Press
from the sensor setup menu to continue
with the autofix. A validation error window is displayed to show that the autofix has
occurred. Press
to return to sensor setup menu. Verify that the autofixed
values are configured for user’s specific application and reconfigure as needed. Press
to save configuration and return to Run Screen.
PID
(Proportional, Integral, and Derivative
)
/
PWM
(Pulse, Width, Modulation)
Control
PID/PWM control menu options are shown below for an aux analog system.
PID/PWM Control uses a complex algothrium in determining the best way to sustain
water system value(s) around a set point. PID/PWM control is a feed back control
system. Three factors determine how PID/PWM control seeks to maintain water
system value(s) around a set point. The three factors are:
-the error (distance) from present measurement of input to set point (present time);:
-the duration of the error (accumulation of past errors)
-the speed at which the value is approaching the set point (predicts future errors) ;
The PID/PWM control system is considered active whenever error exists away from
the configured set point. (See PID/PWM up/down control configuration -page 144)
The PID/PWM control system is flexible and can be tuned to keep water systems
around their set points even though the environment is exposed to disturbances
that drive the input value away from set point. An example of a PID/PWM control
system that most readers will be familiar with is a cruise control system in a car. Ac-
celeration and deacceleration adjustments are continually being made to maintain
the car at a constant speed or set point.
Configure PID/PDW control systems at Sensor Setup menus.
PID/PWM control also allows configuration of high and low alarm systems to
activate peripheral devices and/or to provide alarm notification messages when
alarm condition(s) exist.
Notes:
- Changing control method between PID/PWM and Set Point may result in
invalid setp point, control and alarm value configurations. Always reconfirm
sensor setup system menu configuration when control mode is changed.
- PID/PWM control is not available for aux digital systems.
- DO system(s) PID/PWM set point can be configured using either mg/L or
%Sat set point.
Configuring the 5X00
Configuring the 5X00
