NEC PD750008 User Manual
Page 83
6 3
CHAPTER 4 INTERNAL CPU FUNCTIONS
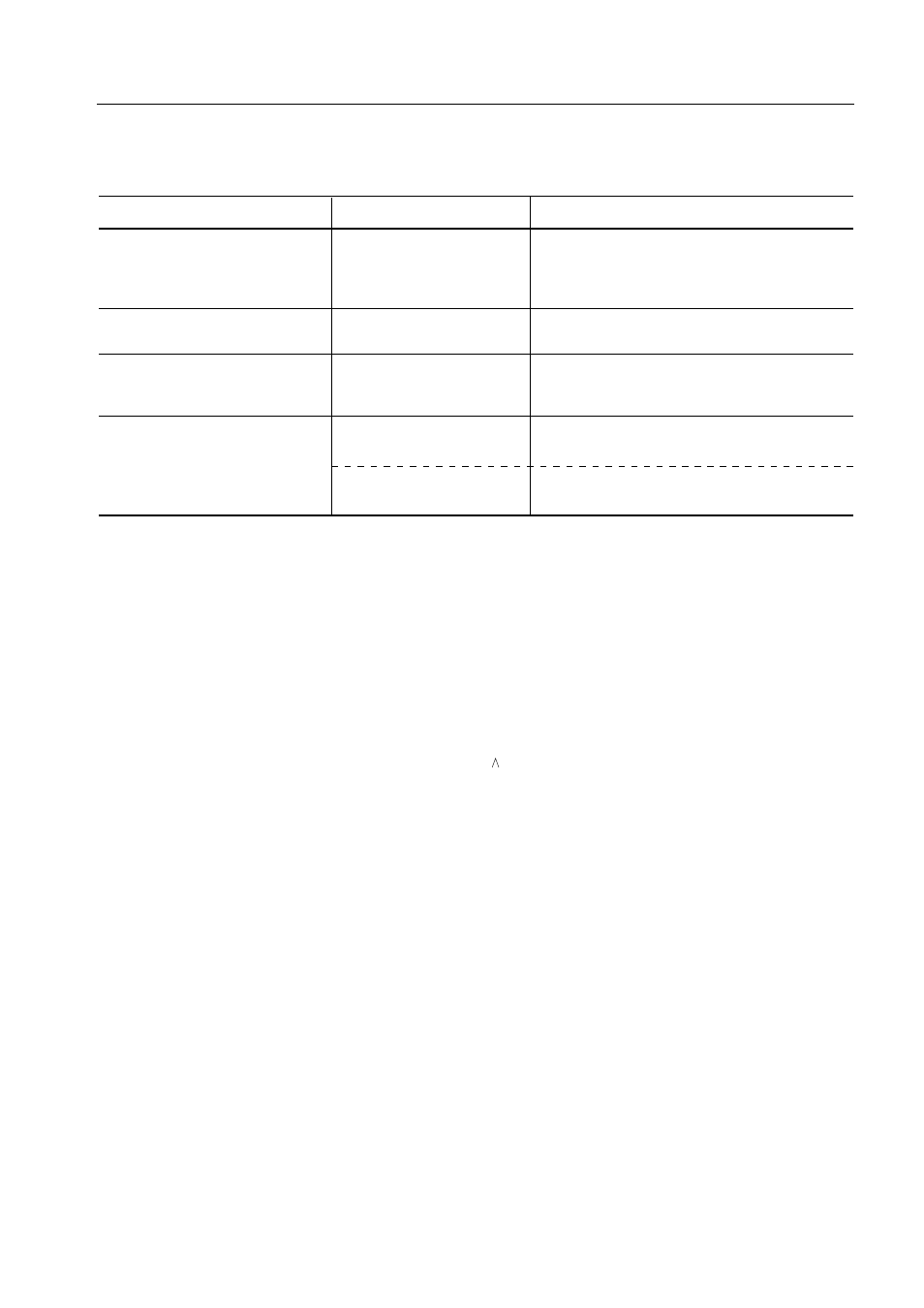
Table 4-4. Carry Flag Manipulation Instructions
Instruction (mnemonic)
Carry flag operation/processing
Instruction dedicated to carry
SET1
CY
Sets CY to 1.
flag manipulation
CLR1
CY
Clears CY to 0.
NOT1
CY
Inverts the state of CY.
SKT
CY
Skips if CY is 1.
Bit transfer instruction
MOV1
mem*.bit, CY
Transfers the state of CY to a specified bit.
MOV1
CY, mem*.bit
Transfers the state of a specified bit to CY.
Bit Boolean instruction
AND1
CY, mem*.bit
ANDs, ORs, or XORs CY with a specified bit,
OR1
CY, mem*.bit
then sets the result in CY.
XOR1
CY, mem*.bit
Interrupt handling
Interrupt execution
Saves CY and all other PSW bits to
stack memory in parallel.
RETI
Restores CY together with the other PSW bits
from stack memory in parallel.
Remark mem*.bit represents the following bit addressing:
• fmem.bit
• pmem.@L
• @H+mem.bit
Example Bit 3 at address 3FH is ANDed with P33, then the result is set in P50.
MOV
H,#3H
; Set the high-order 4 bits of the address in H register
MOV1
CY,@H+0FH.3
; CY <– bit 3 at 3FH
AND1
CY,PORT3.3
; CY <– CY P33
MOV1
PORT5.0,CY
; P50 <– CY
(2) Skip flags (SK2, SK1, SK0)
The skip flags are used to store skip status, and are automatically set or reset when the CPU executes
an instruction.
The user cannot directly manipulate these flags by specifying an operand.
(3) Interrupt status flag (IST1, IST0)
The interrupt status flag is a 2-bit flag used to store the status of processing being performed.
See Table 6-3 for details.
