4 slave transmitter buffered mode, Figure 14, Pca9665 – NXP Semiconductors PCA9665 User Manual
Page 45: Nxp semiconductors
PCA9665_2
© NXP B.V. 2006. All rights reserved.
Product data sheet
Rev. 02 — 7 December 2006
45 of 91
NXP Semiconductors
PCA9665
Fm+ parallel bus to I
2
C-bus controller
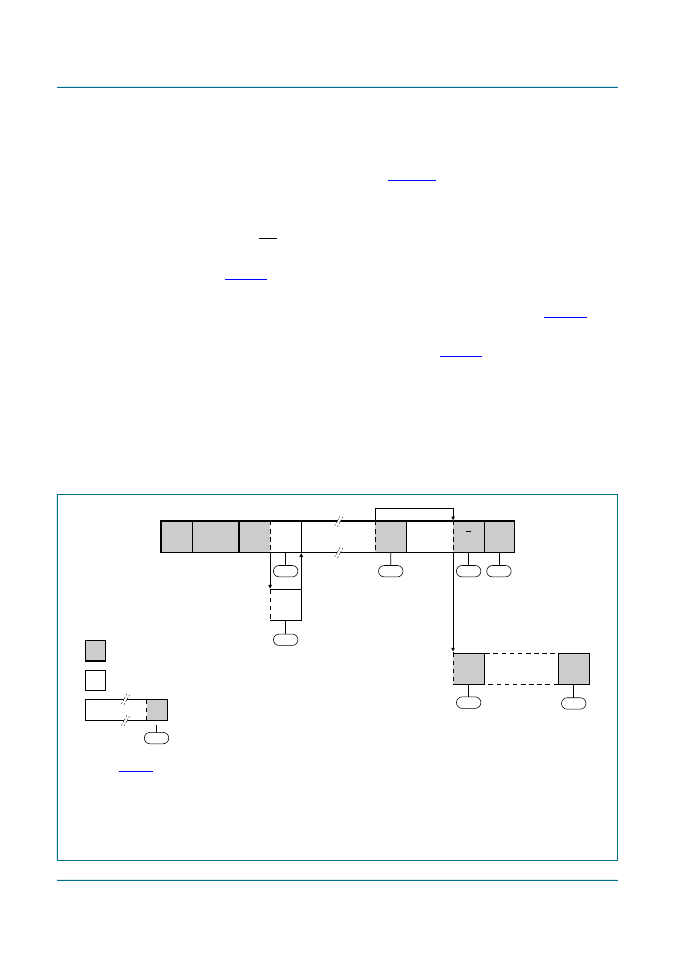
8.4.4 Slave Transmitter Buffered mode
In the Slave Transmitter Buffered mode, a number of data bytes are transmitted to a
master receiver several bytes at a time (see
). Data transfer is initialized as in the
Slave Receiver Buffered mode. When I2CADR and I2CCON have been initialized, the
PCA9665 waits until it is addressed by its own slave address followed by the data direction
bit which must be ‘1’ (R) for the PCA9665 to operate in the Slave Transmitter mode. After
its own slave address and the R bit have been received, the Serial Interrupt flag (SI) is set,
the Interrupt line (INT) goes LOW and I2CSTA is loaded with A8h. This status code is
used to vector to an interrupt service routine, and the appropriate action to be taken is
detailed in
.
The Slave Transmitter Buffered mode may also be entered if arbitration is lost while the
PCA9665 is in the master mode. See state B0h and appropriate actions in
The byte count register (I2CCOUNT) is programmed with the number of bytes that need
to be sent in a single sequence (BC[6:0]) as shown in
. LB bit is only used for the
Receiver Buffered modes and can be programmed to either logic 0 or logic 1.
If the AA bit is reset during a transfer, the PCA9665 will transmit all the bytes of the
transfer (values defined by BC[6:0]) and enter state C8h. The PCA9665 is switched to the
not addressed slave mode and will ignore the master receiver if it continues the transfer.
Thus the master receiver receives all ‘1’s as serial data. While AA is reset, the PCA9665
does not respond to its own slave address. However, the I
2
C-bus is still monitored, and
address recognition may be resumed at any time by setting AA. This means that the AA
bit may be used to temporarily isolate the PCA9665 from the I
2
C-bus.
(1) See
(2) Defined state when the number of bytes sent is equal to the value in I2CCOUNT register.
(3) Defined state when a NACK is received. The number of bytes transmitted is lower than or equal to the value in the
I2CCOUNT register.
(4) Defined state after the last byte has been transmitted and the PCA9665 goes to the non-addressed mode (AA = 0) and an
ACK is received. The number of bytes that are transmitted is equal to the value in I2CCOUNT register.
Fig 14. Format and states in the Slave Transmitter Buffered mode (MODE = 1)
S
SLA
R
A
DATA
A
P or S
B8h
F8h
002aab662
reception of own
slave address and
transmission of one
or more data bytes
arbitration lost as MST and
addressed as slave
n
This number (contained in I2CSTA) corresponds
to a defined state of the I
2
C-bus.
(1)
DATA
A
any number of data bytes and
their associated Acknowledge bits
from master to slave
from slave to master
DATA
A
C0h
P or S
F8h
A
C8h
on STOP
on STOP
A
B0h
last data byte transmitted;
switched to Not Addressed slave
(AA bit in I2CCON = 0)
ALL '1's
(2)
(3)
(4)
A8h
